Attending involves actively focusing on a partner's verbal and nonverbal cues, while interpreting requires assigning meaning to those signals to understand their emotions and intentions accurately. Explore this article to deepen your understanding of how attending and interpreting shape effective relationship communication.
Table of Comparison
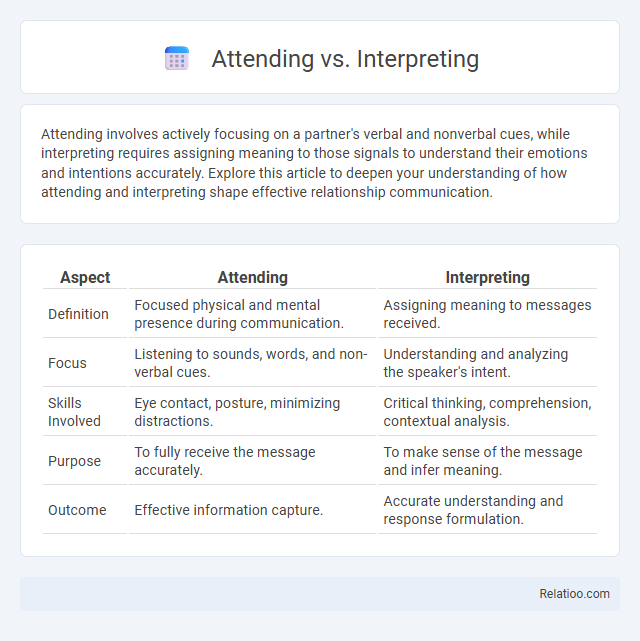
| Aspect | Attending | Interpreting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focused physical and mental presence during communication. | Assigning meaning to messages received. |
| Focus | Listening to sounds, words, and non-verbal cues. | Understanding and analyzing the speaker's intent. |
| Skills Involved | Eye contact, posture, minimizing distractions. | Critical thinking, comprehension, contextual analysis. |
| Purpose | To fully receive the message accurately. | To make sense of the message and infer meaning. |
| Outcome | Effective information capture. | Accurate understanding and response formulation. |
Understanding the Roles: Attending vs Interpreting
Attending involves fully focusing on and processing the speaker's message to ensure clear communication, while interpreting requires converting spoken or signed language from one form to another in real-time. You must distinguish that attending is about active listening and comprehension, whereas interpreting demands language proficiency and cultural understanding to relay accurate meaning. Mastering these roles enhances communication effectiveness in multilingual or professional settings.
Core Responsibilities of Attending Professionals
Attending professionals hold primary responsibility for patient care decisions, including diagnosis, treatment planning, and oversight of medical teams. They ensure accuracy in clinical evaluation, maintain comprehensive documentation, and guide the coordination of multidisciplinary care to optimize patient outcomes. Your role as an attending demands leadership in clinical judgment and accountability for the overall healthcare delivery process.
Key Duties of Interpreters in Various Settings
Interpreters facilitate clear and accurate communication by converting spoken language in real-time across diverse settings such as medical, legal, and conference environments. Key duties include ensuring cultural and contextual appropriateness, maintaining confidentiality, and managing terminology specific to the field to prevent misunderstandings. Effective interpreters also adapt to diverse dialects and jargon, enabling seamless interaction between speakers with different linguistic backgrounds.
Skillsets Required: Attending vs Interpreting
Attending requires active listening, focused attention, and nonverbal communication skills to fully understand verbal and emotional cues during interactions. Interpreting demands advanced language proficiency, quick cognitive processing, cultural competence, and accuracy in converting spoken or signed messages between languages in real-time. Both skill sets emphasize concentration, but interpreting involves complex linguistic expertise and rapid decision-making beyond the attentive presence needed in attending.
Ethical Considerations in Attending and Interpreting
Ethical considerations in attending and interpreting prioritize confidentiality, impartiality, and cultural sensitivity to ensure accurate communication and respect for all parties involved. Attending requires active listening and presence without judgment, maintaining professional boundaries and ensuring the speaker's message is conveyed authentically. Interpreters must adhere to codes of ethics set by organizations like the National Association of Judiciary Interpreters and Translators, avoiding conflicts of interest, maintaining neutrality, and ensuring completeness and accuracy in every interpretation.
Communication Strategies: Direct vs Mediated Approaches
Direct communication strategies emphasize unfiltered interaction where you convey messages personally, ensuring clarity and immediate feedback. Mediated approaches rely on interpreters or technological tools to bridge language barriers, facilitating understanding across diverse linguistic contexts. Choosing between attending and interpreting hinges on the balance between authenticity and accessibility in your communication goals.
Educational Pathways: Training for Attending and Interpreting
Training for attending roles in healthcare often involves intensive residency programs following medical school, emphasizing clinical skills, patient management, and decision-making. Interpreting educational pathways require specialized language and cultural proficiency programs, typically including certification courses in medical or legal interpretation to ensure accurate and ethical communication. Your choice between these paths depends on your commitment to clinical practice versus linguistic expertise, as both require dedicated training but lead to distinct professional roles.
Challenges Faced by Attenders and Interpreters
Attenders often face challenges such as maintaining continuous focus, managing sensory overload, and processing complex information in real-time, which can lead to cognitive fatigue. Interpreters encounter difficulties including accurately conveying nuanced meanings across languages, handling cultural differences, and maintaining quick mental agility under time constraints. Both roles demand exceptional concentration and adaptability, yet interpreters face added pressure of linguistic precision alongside the necessity to manage emotional tone and context effectively.
Impact on Client Outcomes: Comparing Both Roles
Attending and interpreting play distinct roles that influence client outcomes in communication settings; attending involves actively listening and providing emotional support, which fosters trust and rapport, while interpreting ensures accurate and clear translation of messages, crucial for informed decision-making. Your client's experience and satisfaction improve significantly when both skilled attending and precise interpreting are integrated, as misunderstandings and emotional disconnects are minimized. Effective collaboration between attending and interpreting enhances overall clarity, empathy, and client engagement, directly impacting positive results in counseling, medical, or legal contexts.
Choosing Between Attending and Interpreting as a Career
Choosing between attending and interpreting as a career depends heavily on your communication skills and interest in language nuances. Interpreting demands quick thinking, fluency in multiple languages, and the ability to convey meaning accurately in real time, while attending roles often focus on overseeing operations, coordination, and direct interaction within specific environments. Your decision should align with your strengths in linguistic agility or organizational expertise to ensure long-term job satisfaction and success.
Infographic: Attending vs Interpreting
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com