Hyper-vigilance is an intense state of alertness to potential threats in relationships, while paranoia involves irrational distrust and suspicion without evidence. Explore this article to understand how these behaviors impact relational dynamics and strategies for managing them.
Table of Comparison
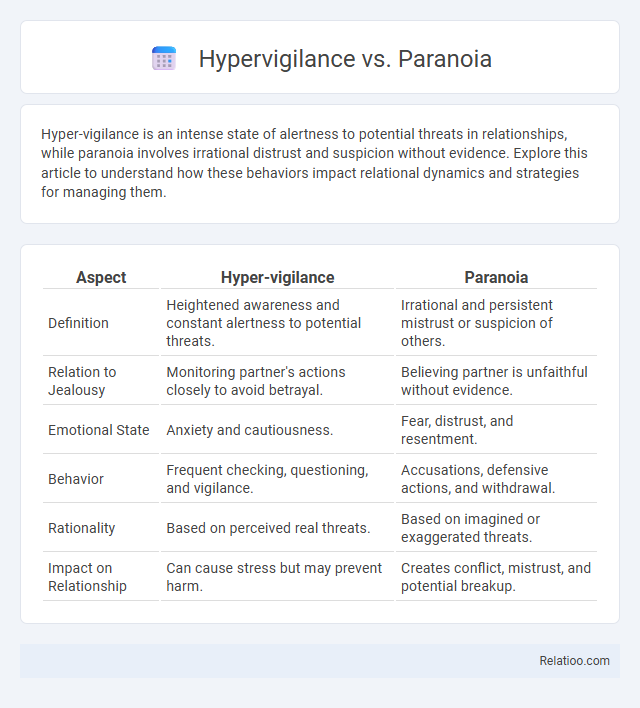
| Aspect | Hyper-vigilance | Paranoia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heightened awareness and constant alertness to potential threats. | Irrational and persistent mistrust or suspicion of others. |
| Relation to Jealousy | Monitoring partner's actions closely to avoid betrayal. | Believing partner is unfaithful without evidence. |
| Emotional State | Anxiety and cautiousness. | Fear, distrust, and resentment. |
| Behavior | Frequent checking, questioning, and vigilance. | Accusations, defensive actions, and withdrawal. |
| Rationality | Based on perceived real threats. | Based on imagined or exaggerated threats. |
| Impact on Relationship | Can cause stress but may prevent harm. | Creates conflict, mistrust, and potential breakup. |
Understanding Hyper-vigilance: Definition and Key Features
Hyper-vigilance is a heightened state of sensory sensitivity accompanied by an intense focus on potential threats, often caused by trauma or anxiety disorders. Unlike paranoia, which involves irrational mistrust or suspicion of others, hyper-vigilance centers on an enhanced alertness to environmental stimuli. Understanding hyper-vigilance helps you recognize its key features, such as persistent scanning of surroundings and exaggerated startle responses, distinguishing it from similar conditions.
What Is Paranoia? Core Symptoms Explained
Paranoia is characterized by intense, irrational mistrust and suspicion of others, often involving beliefs that people are plotting harm against you without concrete evidence. Core symptoms include persistent feelings of being threatened, unjustified doubts about the loyalty or intentions of others, and hyper-awareness of potential dangers. While hyper-vigilance involves heightened sensory sensitivity and alertness, paranoia extends to pathological thoughts that distort reality and can severely impact your daily functioning.
Hyper-vigilance vs Paranoia: Main Differences
Hyper-vigilance is an intense state of heightened sensory sensitivity and constant scanning for threats, often linked to anxiety and trauma, whereas paranoia involves irrational and persistent distrust or suspicion of others without clear evidence. Your hyper-vigilance makes you acutely aware of your surroundings to stay safe, while paranoia distorts reality by convincing you others have harmful intentions. Understanding these differences helps distinguish adaptive alertness from maladaptive mistrust.
Psychological Causes of Hyper-vigilance
Hyper-vigilance stems from psychological causes such as trauma, anxiety disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), which heighten Your brain's alertness to potential threats. Unlike paranoia, which involves irrational distrust and suspicion of others, hyper-vigilance is characterized by an excessive focus on environmental stimuli and danger cues. Understanding these psychological roots is crucial for addressing hyper-vigilance through appropriate therapeutic interventions.
Common Triggers and Origins of Paranoia
Hyper-vigilance often stems from experiences of trauma or chronic stress, leading to heightened sensory sensitivity and an exaggerated awareness of surroundings, while paranoia originates from deep-seated fears and mistrust, frequently triggered by past betrayals or psychological conditions such as schizophrenia or borderline personality disorder. Common triggers of paranoia include perceived threats to personal safety, social rejection, or ambiguous social cues that Your mind may interpret as hostile. Understanding these origins helps differentiate paranoid thoughts from hyper-vigilant responses, enabling targeted coping strategies for managing anxiety and mistrust.
Effects on Daily Life: Hyper-vigilance vs Paranoia
Hyper-vigilance causes constant scanning of the environment for potential threats, resulting in heightened anxiety, difficulty concentrating, and disrupted sleep patterns. Paranoia involves irrational mistrust or suspicion of others, often leading to social withdrawal, strained relationships, and impaired judgment. Both conditions significantly impact daily functioning, but hyper-vigilance primarily induces physical and emotional exhaustion, while paranoia more profoundly affects interpersonal dynamics and decision-making.
How to Recognize Signs of Each Condition
Recognizing hyper-vigilance involves observing constant scanning of the environment for threats, heightened startle responses, and difficulty relaxing, often linked to trauma or anxiety disorders. Paranoia is identified by persistent suspiciousness, unfounded beliefs of being targeted or persecuted, and social withdrawal, commonly associated with psychotic disorders or severe stress. Differentiating hyper-vigilance from hyper-awareness requires noting that hyper-awareness includes increased sensory perception without the fear or anxiety that characterizes hyper-vigilance, often seen in conditions like autism or heightened focus scenarios.
Impact on Relationships and Social Interactions
Hyper-vigilance often leads to heightened alertness to social cues, causing strain in Your relationships due to constant suspicion and difficulty relaxing around others. Paranoia involves persistent, irrational distrust that damages trust and communication, frequently resulting in social isolation. While hyper-vigilance is generally a response to trauma or anxiety affecting social engagement, paranoia creates deeper relational barriers by fostering fear and misunderstanding.
Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches
Evidence-based treatment approaches for hyper-vigilance often involve cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) targeting anxiety and trauma-related triggers, with components like exposure therapy and relaxation techniques to reduce excessive alertness. Paranoia treatments prioritize antipsychotic medications combined with CBT focusing on reality testing and social skills training to address distorted beliefs. Effective management of hyper-vigilance and paranoia requires personalized interventions guided by clinical assessment to improve functional outcomes and reduce distress.
Healthy Coping Strategies and Support Resources
Hyper-vigilance involves an enhanced state of sensory sensitivity often triggered by trauma, while paranoia is characterized by irrational distrust and suspicion. Healthy coping strategies include mindfulness exercises, grounding techniques, and cognitive-behavioral therapy to manage symptoms effectively. Support resources such as mental health professionals, peer support groups, and trauma-informed care programs provide essential assistance for individuals navigating these conditions.
Infographic: Hyper-vigilance vs Paranoia
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com