Self-pity often leads to negative relationship patterns by fostering helplessness and resentment, while self-compassion strengthens emotional resilience and promotes healthier connections. Discover how cultivating self-compassion can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
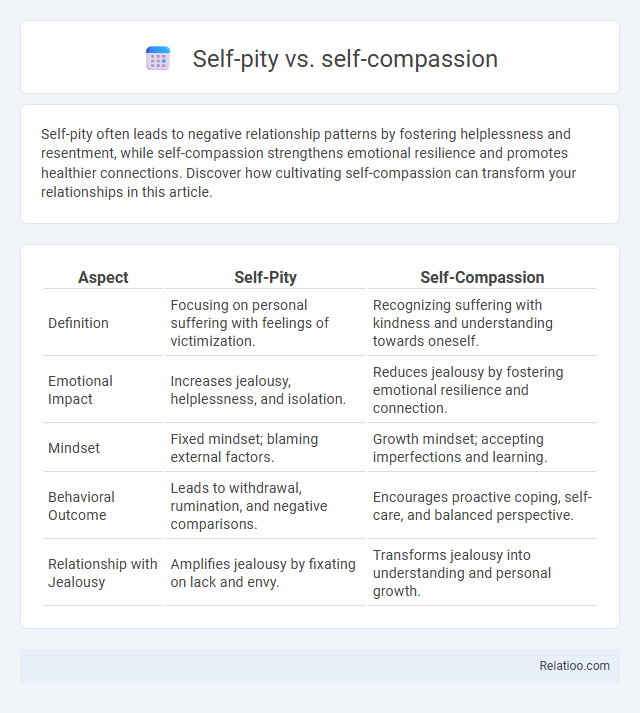
| Aspect | Self-Pity | Self-Compassion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focusing on personal suffering with feelings of victimization. | Recognizing suffering with kindness and understanding towards oneself. |
| Emotional Impact | Increases jealousy, helplessness, and isolation. | Reduces jealousy by fostering emotional resilience and connection. |
| Mindset | Fixed mindset; blaming external factors. | Growth mindset; accepting imperfections and learning. |
| Behavioral Outcome | Leads to withdrawal, rumination, and negative comparisons. | Encourages proactive coping, self-care, and balanced perspective. |
| Relationship with Jealousy | Amplifies jealousy by fixating on lack and envy. | Transforms jealousy into understanding and personal growth. |
Understanding Self-Pity: Definition and Signs
Self-pity involves excessive focus on one's own pain and misfortune, often leading to feelings of helplessness and victimhood. Signs of self-pity include persistent negative self-talk, blaming others for personal difficulties, and withdrawing from social interactions. Understanding these behaviors helps differentiate self-pity from self-compassion, which emphasizes kindness and acceptance toward oneself during struggles.
What Is Self-Compassion? A Clear Overview
Self-compassion involves treating yourself with kindness and understanding during times of failure or suffering, rather than engaging in harsh self-criticism or self-pity. Unlike self-pity, which focuses on feeling sorry for your problems, self-compassion encourages recognition of shared human experiences and promotes emotional resilience. Your practice of self-compassion can improve mental health by fostering acceptance and reducing negative emotions.
The Psychological Impact of Self-Pity
Self-pity often leads to negative psychological effects such as increased feelings of helplessness, anxiety, and depression, which can hinder your emotional growth and resilience. In contrast, self-compassion promotes emotional healing by encouraging kindness towards yourself during difficult times, fostering a healthier mindset and greater psychological well-being. Understanding the psychological impact of self-pity helps you recognize when shifting towards self-compassion is essential for improving mental health and maintaining a balanced emotional state.
Benefits of Practicing Self-Compassion
Practicing self-compassion enhances emotional resilience by promoting kindness and understanding toward oneself during difficult times, which reduces negative self-judgment and feelings of isolation often associated with self-pity. It fosters mental well-being by encouraging acceptance and growth, improving overall psychological health and reducing stress levels. Research shows that individuals who practice self-compassion experience increased motivation and emotional regulation compared to those trapped in cycles of self-pity.
Self-Pity vs Self-Compassion: Key Differences
Self-pity involves dwelling on personal suffering with a sense of helplessness, often leading to negative emotions and stagnation, whereas self-compassion encourages embracing your pain with kindness, understanding, and a desire for growth. You can transform your emotional response by practicing self-compassion, which fosters resilience and emotional well-being instead of reinforcing feelings of victimization common in self-pity. The key difference lies in self-pity's focus on despair and self-compassion's emphasis on acceptance and positive transformation.
How Self-Pity Sabotages Personal Growth
Self-pity creates a cycle of negative emotions that hinder personal growth by focusing attention on failures and externalizing blame rather than fostering resilience. This mindset lowers motivation and reinforces feelings of helplessness, preventing individuals from learning from setbacks or pursuing positive change. In contrast, self-compassion encourages acceptance and constructive self-reflection, enabling growth and emotional healing.
Self-Compassion as a Tool for Emotional Resilience
Self-compassion serves as a powerful tool for emotional resilience by fostering kindness toward oneself during difficult times, unlike self-pity which often leads to feelings of helplessness and isolation. Embracing self-compassion activates brain regions associated with emotional regulation and stress reduction, enhancing overall mental well-being. This practice encourages a balanced perspective on personal struggles, promoting adaptive coping mechanisms and sustained psychological strength.
Recognizing the Triggers of Self-Pity
Recognizing the triggers of self-pity involves identifying specific situations such as failure, rejection, or perceived injustice that often lead to feelings of helplessness and victimization. Unlike self-compassion, which promotes understanding and kindness toward oneself during difficult times, self-pity fosters a cycle of negativity and stagnation. Developing awareness of these emotional triggers enables a shift from self-pity to self-compassion, encouraging resilience and healthier coping mechanisms.
Practical Strategies to Cultivate Self-Compassion
Self-pity traps you in a cycle of negative emotions, while self-compassion encourages kindness toward yourself during difficult times. Practical strategies to cultivate self-compassion include mindful awareness of your feelings, reframing negative self-talk with supportive language, and practicing self-care activities that nurture your well-being. Developing these habits helps you build emotional resilience and fosters a healthier relationship with yourself.
Transforming Self-Pity into Self-Compassion: A Step-by-Step Guide
Transforming self-pity into self-compassion requires recognizing negative self-talk and replacing it with kind, understanding inner dialogue. You can practice mindfulness to observe your emotions without judgment and actively challenge the narratives that fuel self-pity. Developing self-compassion involves consistent self-care, reframing setbacks as learning experiences, and embracing your humanity with empathy and patience.
Infographic: Self-pity vs Self-compassion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com