Jealousy often stems from insecurity and fear of loss, whereas obsession involves an uncontrollable fixation that can harm relationships. Explore the detailed differences and impacts of jealousy and obsession in this article.
Table of Comparison
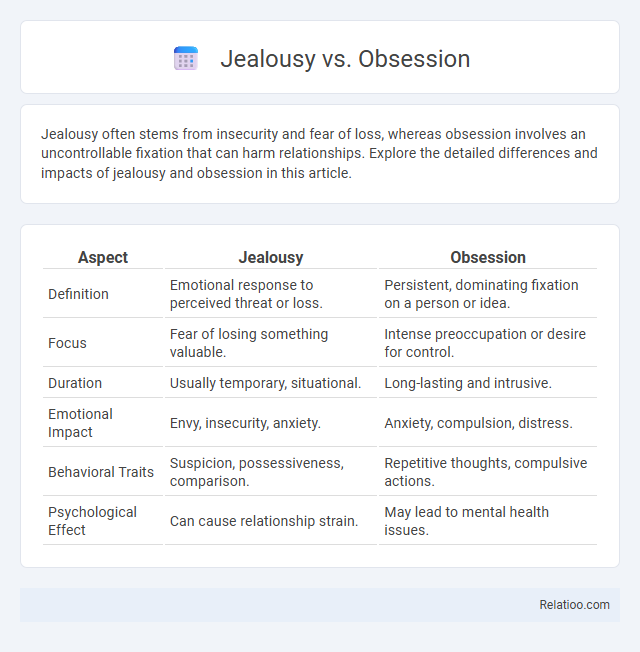
| Aspect | Jealousy | Obsession |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional response to perceived threat or loss. | Persistent, dominating fixation on a person or idea. |
| Focus | Fear of losing something valuable. | Intense preoccupation or desire for control. |
| Duration | Usually temporary, situational. | Long-lasting and intrusive. |
| Emotional Impact | Envy, insecurity, anxiety. | Anxiety, compulsion, distress. |
| Behavioral Traits | Suspicion, possessiveness, comparison. | Repetitive thoughts, compulsive actions. |
| Psychological Effect | Can cause relationship strain. | May lead to mental health issues. |
Understanding Jealousy: Definition and Roots
Jealousy arises from fear of losing something valuable, often triggered by perceived threats to your relationships or possessions. Rooted in insecurity and attachment, it differs from obsession, which involves compulsive, repetitive thoughts or behaviors centered on a person or object. Understanding jealousy's emotional basis helps you manage its impact and differentiate it from unhealthy obsessions.
What Is Obsession? Signs and Symptoms
Obsession is an intense, persistent preoccupation with a person, idea, or activity that dominates your thoughts and behaviors. Common signs and symptoms include repetitive thoughts, anxiety when separated from the object of obsession, and compulsive actions aimed at relieving the distress caused by these fixations. Understanding the difference between jealousy, obsession, and obsession-related behaviors helps identify when thoughts escalate from normal concern to unhealthy fixation.
Key Differences Between Jealousy and Obsession
Jealousy involves fear of losing something valuable, often triggered by perceived threats to relationships or possessions, leading to protective or anxious behavior. Obsession is characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts focused intensely on a particular person, object, or idea, often resulting in compulsive actions. Key differences lie in jealousy's reactive nature to external threats, while obsession centers on uncontrollable internal fixation regardless of external factors.
Psychological Effects of Jealousy
Jealousy triggers intense emotional responses such as anxiety, insecurity, and fear of loss, which can significantly impact mental health and interpersonal relationships. Unlike obsession, which involves compulsive thoughts and behaviors centered on a specific object or person, jealousy is typically a reaction to perceived threats to a valued relationship. Understanding the psychological effects of jealousy is crucial for managing emotional distress and preventing destructive behaviors in social dynamics.
How Obsession Impacts Relationships
Obsession in relationships often leads to intense preoccupation with a partner, causing emotional distress and impairing trust. Unlike jealousy, which arises from fear of losing someone, obsession drives controlling behaviors and invades personal boundaries. This relentless fixation can erode intimacy, triggering conflict, and potentially resulting in relationship breakdown.
Triggers for Jealousy vs Obsession
Triggers for jealousy often stem from perceived threats to a valued relationship, such as attention given to a rival or fear of losing a partner. Obsession triggers focus more on intrusive thoughts and fixation on a person or idea, frequently fueled by insecurity or unmet emotional needs. Understanding these triggers helps you differentiate between feelings rooted in protective instincts and those driven by unhealthy preoccupation.
Healthy vs Unhealthy Emotions in Love
Jealousy, obsession, and infatuation differ significantly in their impact on your emotional well-being and relationships. Healthy jealousy involves recognizing the value of your partner and maintaining trust, while obsession represents an unhealthy fixation that can lead to controlling behaviors and emotional distress. Understanding these distinctions helps you foster love grounded in respect and balance, avoiding harmful patterns that damage intimacy.
Coping Strategies for Jealousy
Jealousy arises from fear of loss or insecurity, while obsession involves intrusive, persistent thoughts often linked to anxiety or fixation. Coping strategies for jealousy include practicing open communication, building self-esteem, and focusing on personal growth to reduce insecurity. Mindfulness and cognitive-behavioral techniques can help manage emotional responses and prevent jealousy from escalating into obsessive behavior.
Managing and Overcoming Obsession
Effective management of obsession involves recognizing obsessive thoughts early and implementing cognitive-behavioral strategies to reframe negative patterns. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, journaling, and seeking professional therapy can help reduce compulsive behaviors and promote emotional regulation. Building a support system and setting healthy boundaries are essential steps in overcoming obsession and fostering long-term mental well-being.
When to Seek Professional Help
Jealousy becomes harmful when it evolves into obsession, characterized by intrusive thoughts and uncontrollable behaviors that negatively impact Your relationships and well-being. Obsession often requires professional help when it triggers anxiety, disrupts daily functioning, or leads to compulsive actions that You cannot manage alone. Seeking therapy or counseling can provide strategies to address underlying issues, helping You regain control and establish healthier emotional boundaries.
Infographic: Jealousy vs Obsession
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com