Jealousy often stems from insecurity and fear of loss, while admiration is rooted in respect and inspiration. Discover how these emotions impact relationships and ways to transform jealousy into healthy admiration in this article.
Table of Comparison
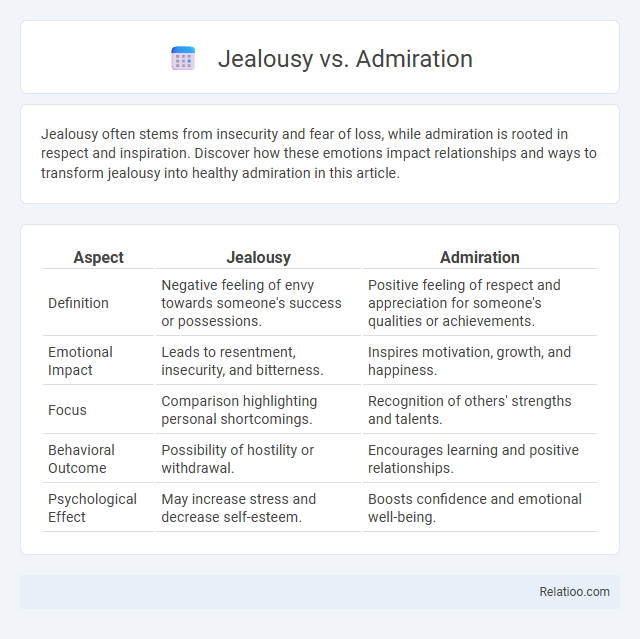
| Aspect | Jealousy | Admiration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Negative feeling of envy towards someone's success or possessions. | Positive feeling of respect and appreciation for someone's qualities or achievements. |
| Emotional Impact | Leads to resentment, insecurity, and bitterness. | Inspires motivation, growth, and happiness. |
| Focus | Comparison highlighting personal shortcomings. | Recognition of others' strengths and talents. |
| Behavioral Outcome | Possibility of hostility or withdrawal. | Encourages learning and positive relationships. |
| Psychological Effect | May increase stress and decrease self-esteem. | Boosts confidence and emotional well-being. |
Understanding Jealousy: Definition and Roots
Jealousy is an emotional response that arises from the fear of losing something valuable to you, often rooted in insecurity, low self-esteem, or past experiences. Unlike admiration, which involves recognizing and appreciating someone's qualities or achievements, jealousy centers on a perceived threat to your own status or relationships. Understanding jealousy requires identifying its deep psychological roots and distinguishing it from healthy feelings of admiration or harmless comparison.
What is Admiration? A Positive Perspective
Admiration is an emotional response characterized by respect and appreciation for someone's qualities, achievements, or virtues, fostering motivation and personal growth. Unlike jealousy, which often involves envy and negativity, admiration encourages recognition of others' strengths without diminishing self-worth. Embracing admiration promotes a positive mindset that values inspiration and healthy benchmarks for self-improvement.
The Psychology Behind Jealousy and Admiration
Jealousy stems from a fear of losing something valuable to you, often triggering feelings of insecurity and resentment, while admiration arises from recognizing and valuing positive qualities in others without self-threat. Psychological studies reveal that jealousy activates brain regions linked to social pain and threat detection, whereas admiration engages reward and motivation circuits, encouraging personal growth. Understanding these neural and emotional distinctions helps you transform jealousy into admiration, fostering healthier relationships and self-improvement.
Key Differences Between Jealousy and Admiration
Jealousy involves fear of losing something valuable to others, often triggering negative emotions like envy and resentment, while admiration reflects positive regard and appreciation for someone's qualities or achievements. Jealousy typically stems from insecurity and a scarcity mindset, whereas admiration inspires motivation and personal growth through recognizing others' strengths. The key difference lies in jealousy generating harmful feelings that divide, whereas admiration fosters connection and constructive reflection.
Emotional Triggers: Why We Feel Jealous or Admiring
Jealousy arises from emotional triggers linked to fear of loss, insecurity, and low self-worth, often spurred by perceived threats to personal relationships or social status. Admiration, however, is triggered by recognition of others' achievements or qualities that inspire motivation and positive feelings, reflecting a desire for self-improvement rather than competition. Comparison activates both jealousy and admiration based on how individuals interpret others' successes relative to their own, influencing emotional responses through personal values and self-perception.
Effects on Relationships: Jealousy vs Admiration
Jealousy can erode trust and create tension in relationships, leading to insecurity and resentment. Admiration, on the other hand, fosters positive feelings, encouraging growth and deeper connections between individuals. By embracing admiration instead of jealousy, you strengthen bonds and promote mutual respect in your relationships.
Social and Cultural Influences on Both Emotions
Social and cultural influences shape how jealousy, admiration, and comparison manifest within individuals by reinforcing specific values and norms that dictate acceptable emotional responses. Your experience of jealousy often stems from competitive social environments that emphasize scarcity and status, while admiration flourishes in cultures promoting achievement and inspiration. Comparison operates as a cognitive tool influenced by social media and communal standards, amplifying emotions based on collective ideals and identity frameworks.
Transforming Jealousy into Admiration
Transforming jealousy into admiration shifts your mindset from envy to appreciation, allowing you to recognize others' strengths without feeling threatened. By focusing on what inspires you in others' achievements, you can channel that energy into personal growth and motivation. This positive reframing helps build confidence and fosters healthier relationships, replacing destructive comparison with constructive inspiration.
Healthy Ways to Cope with Jealousy
Jealousy can be transformed into personal growth by recognizing it as a signal to identify unmet needs or goals, promoting self-awareness and motivation. Practicing gratitude and focusing on individual strengths helps shift attention from others' achievements, reducing negative emotions and fostering admiration instead of envy. Embracing comparison as a tool for inspiration rather than competition encourages healthy self-reflection and constructive goal-setting.
Fostering Admiration for Personal Growth
Fostering admiration instead of jealousy encourages personal growth by inspiring individuals to recognize and learn from others' achievements without negative self-judgment. Admiration motivates constructive behavior and goal-setting, whereas jealousy often leads to resentment and stagnation. Cultivating a mindset that values others' success as a source of inspiration fosters resilience, creativity, and continuous self-improvement.
Infographic: Jealousy vs Admiration
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com