Emotional bandwidth refers to the capacity to process and manage feelings within a relationship, while mental bandwidth involves cognitive focus and problem-solving abilities. Explore how balancing these bandwidths enhances relationship quality in this article.
Table of Comparison
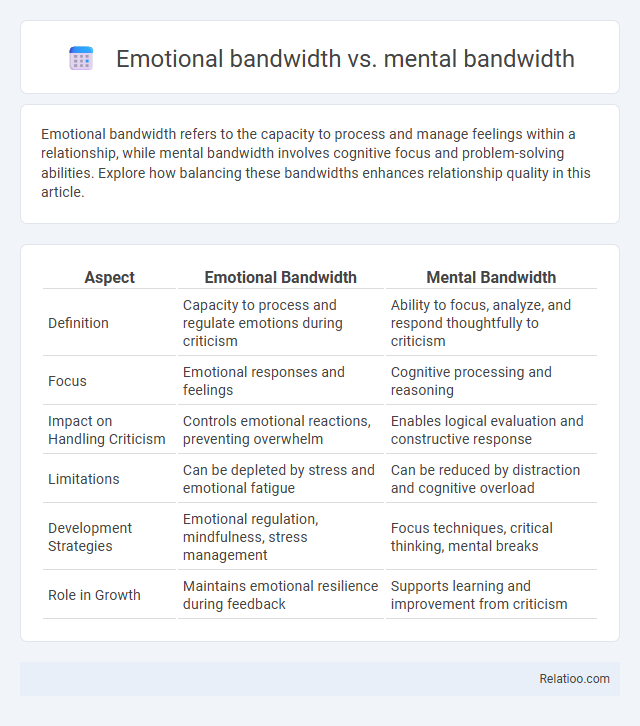
| Aspect | Emotional Bandwidth | Mental Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Capacity to process and regulate emotions during criticism | Ability to focus, analyze, and respond thoughtfully to criticism |
| Focus | Emotional responses and feelings | Cognitive processing and reasoning |
| Impact on Handling Criticism | Controls emotional reactions, preventing overwhelm | Enables logical evaluation and constructive response |
| Limitations | Can be depleted by stress and emotional fatigue | Can be reduced by distraction and cognitive overload |
| Development Strategies | Emotional regulation, mindfulness, stress management | Focus techniques, critical thinking, mental breaks |
| Role in Growth | Maintains emotional resilience during feedback | Supports learning and improvement from criticism |
Understanding Emotional Bandwidth
Emotional bandwidth refers to your capacity to process and manage emotions effectively, influencing how you respond to stress and interpersonal dynamics. Mental bandwidth encompasses cognitive resources for problem-solving, decision-making, and information processing, while emotional bandwidth specifically targets emotional regulation and resilience. Understanding emotional bandwidth enhances your ability to maintain emotional balance, improving overall mental well-being and interpersonal relationships.
Defining Mental Bandwidth
Mental bandwidth refers to the cognitive capacity your brain uses to process information, solve problems, and make decisions, while emotional bandwidth involves managing and regulating your feelings and emotional responses. Emotional bandwidth specifically highlights the energy available for handling stress, empathy, and emotional interactions, which can directly affect your mental bandwidth by either draining or freeing cognitive resources. Understanding and balancing your mental bandwidth is crucial for maintaining focus, productivity, and emotional well-being in demanding situations.
Key Differences Between Emotional and Mental Bandwidth
Emotional bandwidth refers to your capacity to process and manage feelings, while mental bandwidth involves cognitive functions like attention, memory, and problem-solving. Key differences lie in emotional bandwidth impacting stress tolerance and emotional regulation, whereas mental bandwidth governs logical thinking and decision-making. Understanding these distinctions helps you optimize your overall performance by balancing emotional resilience and cognitive load effectively.
Signs of Limited Emotional Bandwidth
Limited emotional bandwidth often manifests as irritability, difficulty managing stress, and emotional numbness, signaling your inability to process complex feelings effectively. Unlike mental bandwidth, which relates to cognitive processing capacity and problem-solving skills, emotional bandwidth specifically governs how well you handle emotional information and interpersonal dynamics. Recognizing these signs can help you address emotional overload and improve overall mental well-being.
Indicators of Mental Bandwidth Overload
Indicators of mental bandwidth overload include difficulty concentrating, frequent forgetfulness, and decreased decision-making ability. Emotional bandwidth overload manifests through heightened irritability, anxiety, and emotional exhaustion. Tracking cognitive fatigue and emotional stress signals can help differentiate between mental and emotional bandwidth challenges effectively.
Causes of Bandwidth Depletion
Emotional bandwidth depletion occurs due to prolonged stress, unresolved emotional conflicts, and intense interpersonal interactions that drain one's capacity to process feelings effectively. Mental bandwidth reduction stems from cognitive overload, multitasking, and constant information influx that impair focus, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities. Both forms of bandwidth depletion are exacerbated by inadequate rest, poor self-care, and environmental distractions, leading to decreased performance and emotional resilience.
Emotional Bandwidth and Stress Management
Emotional bandwidth refers to the capacity to process and respond to emotional experiences, which directly impacts your stress management abilities by determining how well you can handle emotional strain. Mental bandwidth involves cognitive resources needed for tasks such as problem-solving and decision-making, while emotional bandwidth specifically addresses managing feelings and emotional resilience. Enhancing your emotional bandwidth improves stress tolerance, enabling more effective coping strategies during high-pressure situations.
Mental Bandwidth in Decision Making
Mental bandwidth refers to the cognitive capacity available for processing information and making decisions, which can become limited under stress or multitasking. Emotional bandwidth captures the ability to manage and respond to emotional stimuli, influencing your overall mental clarity and focus. Prioritizing mental bandwidth in decision making enhances your ability to analyze options logically and reduces cognitive overload, leading to more effective and rational choices.
Strategies to Balance Emotional and Mental Bandwidth
Effective strategies to balance emotional and mental bandwidth include practicing mindfulness to increase self-awareness and regulate emotional responses, allowing for clearer cognitive processing. Prioritizing tasks and setting boundaries helps conserve mental bandwidth, reducing cognitive overload and stress. Incorporating regular breaks and stress management techniques supports sustained focus and emotional resilience, enhancing overall productivity and well-being.
Enhancing Overall Personal Bandwidth for Well-being
Emotional bandwidth refers to your capacity to process and manage feelings, while mental bandwidth involves cognitive resources for attention and problem-solving. Enhancing overall personal bandwidth requires balancing both emotional and mental capacities to reduce stress and improve decision-making and resilience. Prioritizing self-care and mindfulness practices boosts your ability to navigate challenges effectively, promoting well-being and sustained productivity.
Infographic: Emotional bandwidth vs mental bandwidth
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com