Stable attribution assigns consistent causes to behavior, while unstable attribution attributes actions to temporary factors. Explore this article to understand how these perspectives impact relationship dynamics.
Table of Comparison
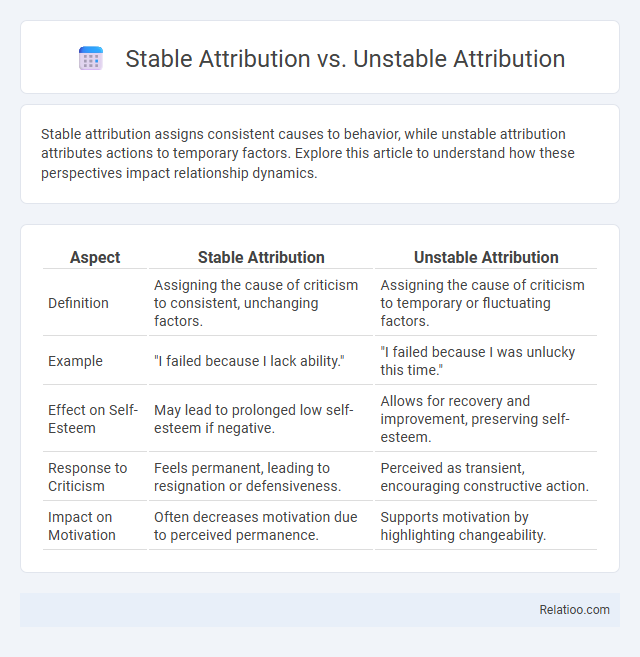
| Aspect | Stable Attribution | Unstable Attribution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assigning the cause of criticism to consistent, unchanging factors. | Assigning the cause of criticism to temporary or fluctuating factors. |
| Example | "I failed because I lack ability." | "I failed because I was unlucky this time." |
| Effect on Self-Esteem | May lead to prolonged low self-esteem if negative. | Allows for recovery and improvement, preserving self-esteem. |
| Response to Criticism | Feels permanent, leading to resignation or defensiveness. | Perceived as transient, encouraging constructive action. |
| Impact on Motivation | Often decreases motivation due to perceived permanence. | Supports motivation by highlighting changeability. |
Introduction to Attribution Theory
Attribution theory explores how individuals interpret causes of behavior and events, distinguishing between stable, unstable, and general attribution types. Stable attribution involves causes perceived as consistent over time, such as innate ability, while unstable attribution refers to temporary factors like effort or luck. Understanding your attribution style influences motivation and how you respond to successes and failures in various contexts.
Defining Stable Attribution
Stable Attribution refers to consistently assigning credit for outcomes to enduring factors such as skills, personality traits, or intentions, ensuring reliable explanations across different contexts. Unstable Attribution attributes outcomes to temporary, fluctuating causes like mood or luck, leading to less predictable interpretations of behavior. Attribution is the broader process of determining the causes behind actions or events, encompassing both stable and unstable elements to explain motivation and responsibility.
Understanding Unstable Attribution
Unstable attribution refers to explanations of behavior that assign causes to temporary, changeable factors such as moods, luck, or situational circumstances, contrasting with stable attribution which attributes causes to enduring, consistent traits or abilities. Understanding unstable attribution is crucial in psychology and social cognition because it highlights how individuals perceive and react to events differently based on whether they believe outcomes are beyond permanent personal control. This distinction impacts motivation, decision-making, and emotional responses, as unstable attributions often lead to variability in expectations and efforts over time.
Key Differences Between Stable and Unstable Attribution
Stable attribution refers to explanations for outcomes or behaviors that are consistent over time and across situations, attributing causes to enduring traits or factors. Unstable attribution assigns causes that vary across circumstances, emphasizing temporary or fluctuating elements such as mood or effort. The key difference lies in the temporal consistency and perceived control, where stable attributions imply long-term influence and predictability, while unstable attributions indicate short-term, changeable conditions.
Examples of Stable Attribution in Everyday Life
Stable attribution attributes the cause of behaviors or events to consistent, unchanging factors such as personality traits or abilities, for example, believing you succeed in tasks because of your intelligence or work ethic. Unstable attribution, by contrast, assigns causes to temporary or fluctuating factors like effort, mood, or luck, such as attributing a good exam grade to luck on that day. Understanding these distinctions helps you accurately interpret causes behind actions and outcomes, improving your decision-making and interpersonal relationships.
Examples of Unstable Attribution in Real-World Scenarios
Unstable attribution occurs when people explain behaviors or events as caused by temporary, changeable factors, such as mood, luck, or specific circumstances, rather than consistent traits or external rules. For example, a student attributing a poor exam grade to having a bad day rather than lack of preparation demonstrates unstable attribution. Similarly, a driver blaming a sudden accident on slippery roads due to unexpected weather conditions instead of reckless driving represents unstable attribution in real-world settings.
Psychological Impact of Attribution Styles
Stable attribution attributes outcomes to consistent, enduring factors, fostering a sense of predictability and control that enhances resilience and motivation. Unstable attribution links results to temporary, fluctuating causes, which can induce uncertainty and impede long-term confidence in personal capabilities. Your understanding of these attribution styles influences emotional responses and coping strategies, shaping overall psychological well-being and motivation levels.
Role of Attribution in Motivation and Performance
Attribution plays a crucial role in motivation and performance by influencing how you interpret the causes of your successes or failures. Stable attributions, such as ability or task difficulty, lead to consistent expectations about future outcomes, while unstable attributions, like effort or luck, cause fluctuations in motivation and confidence. Understanding these differences helps optimize your motivational strategies and improve performance through targeted interventions.
Improving Self-Awareness Through Attribution Analysis
Stable attribution involves recognizing consistent causes behind behaviors, such as inherent personality traits, which helps individuals develop a more accurate and enduring self-awareness. Unstable attribution attributes behavior to temporary or situational factors, encouraging flexibility in self-perception and adaptation to changing circumstances. Analyzing both stable and unstable attributions enhances self-awareness by allowing individuals to discern which aspects of their behavior are enduring and which are context-dependent, promoting personal growth and effective self-regulation.
Conclusion: Importance of Recognizing Attribution Patterns
Recognizing attribution patterns is crucial for understanding how individuals explain behavior and events, impacting personal growth and social interactions significantly. Stable attributions attribute causes to consistent, enduring factors, while unstable attributions link outcomes to temporary circumstances, influencing your response to success or failure. Accurate attribution awareness enhances emotional regulation and decision-making by clarifying whether your experiences are due to controllable or uncontrollable factors.
Infographic: Stable Attribution vs Unstable Attribution
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com