Negativity bias causes individuals to focus more on negative experiences or information, whereas positivity bias leads them to emphasize positive aspects and memories. Explore this article to understand how these biases influence relationship dynamics and emotional well-being.
Table of Comparison
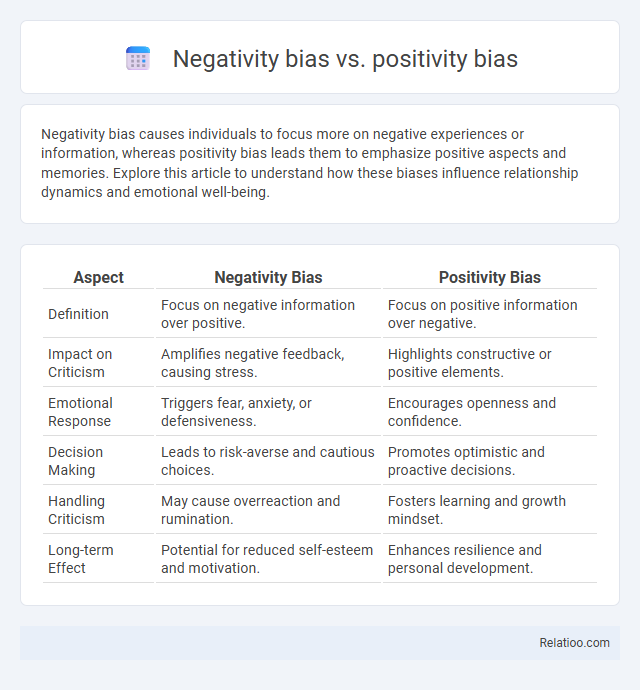
| Aspect | Negativity Bias | Positivity Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on negative information over positive. | Focus on positive information over negative. |
| Impact on Criticism | Amplifies negative feedback, causing stress. | Highlights constructive or positive elements. |
| Emotional Response | Triggers fear, anxiety, or defensiveness. | Encourages openness and confidence. |
| Decision Making | Leads to risk-averse and cautious choices. | Promotes optimistic and proactive decisions. |
| Handling Criticism | May cause overreaction and rumination. | Fosters learning and growth mindset. |
| Long-term Effect | Potential for reduced self-esteem and motivation. | Enhances resilience and personal development. |
Understanding Negativity Bias: Definition and Origins
Negativity bias refers to the psychological phenomenon where negative events, emotions, or information have a greater impact on an individual's thoughts, feelings, and behavior than neutral or positive stimuli. This bias originates from evolutionary mechanisms, as attentiveness to threats enhanced survival by prompting faster reactions to danger. Understanding negativity bias helps explain why people often remember negative experiences more vividly and respond more strongly to adverse feedback compared to positive inputs.
Exploring Positivity Bias: What It Means
Positivity bias refers to the psychological tendency to focus on positive information more than negative, influencing your perception and decision-making processes. This bias helps enhance well-being, boost motivation, and foster stronger social connections by encouraging optimistic thinking and emotional resilience. Understanding positivity bias reveals how your brain prioritizes uplifting experiences, shaping a more hopeful and constructive outlook on life.
The Psychological Foundations of Negativity and Positivity Bias
Negativity bias and positivity bias are rooted in the brain's psychological foundations, where negativity bias refers to the tendency to prioritize and remember negative experiences more intensely due to evolutionary survival mechanisms. Positivity bias, on the other hand, reflects a cognitive inclination to focus on positive information, supporting emotional well-being and resilience. Understanding these contrasting biases enables you to recognize how your mind processes emotional stimuli, shaping your perceptions and reactions.
How Negativity Bias Affects Decision Making
Negativity bias causes Your brain to prioritize negative information over positive or neutral inputs, leading to a skew in decision-making processes that emphasize potential threats or losses. This cognitive bias can result in risk-averse choices, as negative outcomes often weigh heavier in Your evaluation compared to equal-sized positive outcomes. Understanding the impact of negativity bias on decision-making helps mitigate its influence by encouraging more balanced assessments that account for both risks and benefits equally.
The Impact of Positivity Bias on Perception and Behavior
Positivity bias influences your perception by enhancing the recall of positive experiences and diminishing attention to negative information, which can lead to increased optimism and improved mental well-being. This bias affects behavior by encouraging risk-taking and social bonding, as individuals focus more on potential rewards than threats. However, an excessive positivity bias may skew realistic assessment, impacting decision-making and long-term planning.
Real-life Examples of Negativity vs Positivity Bias
Negativity bias causes people to remember negative events, such as criticism at work or social rejection, more vividly than positive experiences like praise or compliments. In contrast, positivity bias is observed in situations like the "Pollyanna principle," where individuals recall positive feedback more readily, often seen in customer satisfaction surveys or personal relationships. Real-life examples include news media emphasizing tragedies (negativity bias) versus interpersonal moments where people focus on compliments to boost self-esteem (positivity bias).
Negativity Bias in Media and News Consumption
Negativity bias in media and news consumption causes audiences to focus more on negative events, leading to heightened fear and anxiety, as negative headlines often attract greater attention and engagement. Positivity bias, in contrast, emphasizes optimistic stories but is less prevalent in mainstream news, which frequently prioritizes sensational or alarming content to increase viewership. Understanding negativity bias helps explain why news outlets disproportionately highlight conflicts, disasters, and scandals, shaping public perception and influencing social behavior.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Bias
Negativity bias enhances survival by prioritizing threat detection and risk avoidance, but it can lead to excessive pessimism and anxiety, impairing decision-making and social interactions. Positivity bias promotes optimism and resilience, supporting mental health and motivation, yet it may cause underestimation of risks and poor judgment in challenging situations. Understanding the balance between negativity and positivity biases enables better emotional regulation, improving overall well-being and adaptive responses to life's complexities.
Strategies to Balance Negativity and Positivity Bias
To balance negativity bias and positivity bias, you can practice mindfulness to increase awareness of your thought patterns and consciously shift focus toward positive experiences without ignoring valid concerns. Cognitive-behavioral techniques, such as reframing negative thoughts and gratitude journaling, help counteract the automatic tendency to prioritize negative information. Your balanced approach enhances emotional resilience and decision-making by integrating realistic optimism with critical evaluation.
Cultivating Awareness for Healthier Mindsets
Negativity bias causes Your mind to prioritize negative information, impacting emotions and decisions, while positivity bias highlights positive experiences, promoting optimism and resilience. Cultivating awareness of these biases enables balanced perspective, essential for healthier mindset and emotional regulation. Mindfulness practices and reflective journaling help identify and manage bias effects, fostering mental well-being.
Infographic: Negativity bias vs Positivity bias
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com