Self-justification in relationships often leads individuals to deflect blame, hindering growth and mutual understanding. Embracing personal accountability fosters trust and deeper connection; discover effective strategies to balance these dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
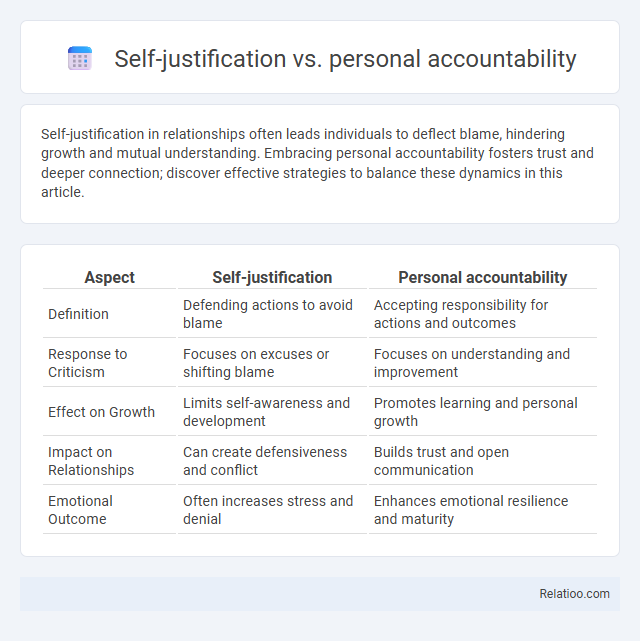
| Aspect | Self-justification | Personal accountability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Defending actions to avoid blame | Accepting responsibility for actions and outcomes |
| Response to Criticism | Focuses on excuses or shifting blame | Focuses on understanding and improvement |
| Effect on Growth | Limits self-awareness and development | Promotes learning and personal growth |
| Impact on Relationships | Can create defensiveness and conflict | Builds trust and open communication |
| Emotional Outcome | Often increases stress and denial | Enhances emotional resilience and maturity |
Understanding Self-Justification
Understanding self-justification involves recognizing the psychological mechanism where individuals defend their actions or decisions to preserve self-esteem and reduce cognitive dissonance. Unlike personal accountability, which requires owning one's mistakes and accepting responsibility, self-justification often leads to biased reasoning and avoidance of blame. This cognitive strategy can hinder personal growth by obstructing honest self-reflection and learning from errors.
Defining Personal Accountability
Personal accountability is the commitment to take responsibility for your actions, decisions, and their outcomes without shifting blame or making excuses. Unlike self-justification, which involves rationalizing mistakes to protect self-image, personal accountability fosters growth by acknowledging errors and learning from them. Embracing personal accountability leads to improved trust, stronger relationships, and enhanced professional and personal development.
Psychological Roots of Self-Justification
Self-justification often stems from cognitive dissonance, where Your mind seeks to reduce psychological discomfort caused by conflicting beliefs or behaviors. This defense mechanism contrasts with personal accountability, which involves recognizing mistakes and accepting responsibility without distortion. Understanding the psychological roots of self-justification highlights its role in protecting self-esteem but potentially hindering growth and honest self-assessment.
The Impact of Self-Justification on Growth
Self-justification hinders personal growth by encouraging denial of mistakes and resistance to feedback, limiting self-awareness and developmental opportunities. Personal accountability fosters growth by promoting responsibility, learning from errors, and adapting behavior based on constructive criticism. The impact of self-justification is a persistent barrier to progress, whereas embracing accountability drives continuous improvement and emotional maturity.
Benefits of Embracing Personal Accountability
Embracing personal accountability cultivates trust and integrity by encouraging individuals to own their actions and decisions without deflecting blame through self-justification. This mindset enhances personal growth and professional development as you learn from mistakes and demonstrate commitment to continuous improvement. Prioritizing accountability over self-justification leads to stronger relationships and greater respect within teams and communities.
Common Traps: Excuses vs. Responsibility
Self-justification often leads to common traps where individuals create excuses to avoid responsibility, hindering personal growth and accountability. Personal accountability requires recognizing mistakes without blaming external factors, empowering you to learn and improve. Avoiding excuses helps foster a mindset focused on solution-oriented actions and genuine responsibility.
How Self-Justification Hinders Relationships
Self-justification often obstructs open communication by causing individuals to deflect responsibility and resist acknowledging mistakes, which erodes trust and mutual understanding in relationships. Personal accountability, in contrast, fosters stronger connections by encouraging honest self-reflection and a willingness to address one's shortcomings constructively. When self-justification dominates, it creates emotional distance and conflict, undermining the foundation of healthy, supportive relationships.
Strategies to Cultivate Personal Accountability
Self-justification often leads to avoiding responsibility by rationalizing mistakes, whereas personal accountability requires acknowledging errors and learning from them to foster growth. Strategies to cultivate personal accountability include setting clear goals, practicing honest self-reflection, and seeking constructive feedback to improve decision-making. Embracing these approaches helps you develop resilience and integrity, transforming challenges into opportunities for personal and professional development.
The Role of Feedback in Overcoming Self-Justification
Feedback plays a critical role in overcoming self-justification by providing objective insights that challenge biased explanations and encourage personal accountability. Constructive feedback facilitates reflection on actions and decisions, enabling individuals to recognize their mistakes without defensiveness and promoting behavioral change. Incorporating timely, specific, and actionable feedback mechanisms enhances the development of personal accountability by reducing the tendency to rationalize failures or avoid responsibility.
Building a Culture of Accountability in Daily Life
Building a culture of accountability in daily life requires shifting from self-justification to personal accountability, where you take ownership of your actions instead of deflecting blame. Personal accountability fosters trust and transparency, empowering individuals to learn and grow from their experiences. Emphasizing responsibility over excuses strengthens relationships and promotes a more honest and productive environment.
Infographic: Self-justification vs Personal accountability
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com