Preventive care in relationships involves regular communication and proactive efforts to address potential issues, fostering long-term trust and emotional intimacy. Reactive care typically responds only after conflicts arise, which can weaken bonds and increase misunderstandings; explore effective strategies for both approaches in this article.
Table of Comparison
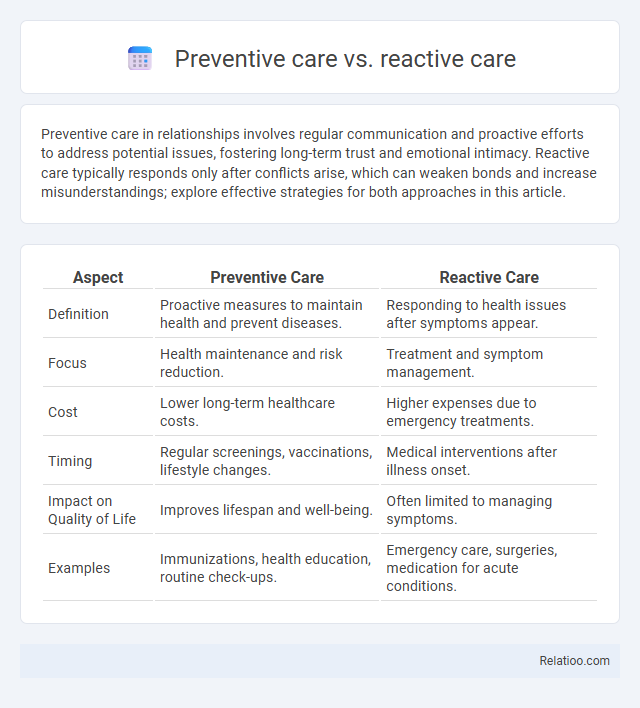
| Aspect | Preventive Care | Reactive Care |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive measures to maintain health and prevent diseases. | Responding to health issues after symptoms appear. |
| Focus | Health maintenance and risk reduction. | Treatment and symptom management. |
| Cost | Lower long-term healthcare costs. | Higher expenses due to emergency treatments. |
| Timing | Regular screenings, vaccinations, lifestyle changes. | Medical interventions after illness onset. |
| Impact on Quality of Life | Improves lifespan and well-being. | Often limited to managing symptoms. |
| Examples | Immunizations, health education, routine check-ups. | Emergency care, surgeries, medication for acute conditions. |
Understanding Preventive Care
Preventive care involves proactive measures such as vaccinations, routine screenings, and lifestyle counseling to identify and mitigate health risks before they develop into serious conditions. It contrasts with reactive care, which addresses illnesses or injuries only after symptoms arise, often leading to more complex and costly treatments. Understanding preventive care emphasizes its role in reducing the incidence of health crises by maintaining wellness and detecting diseases early.
Defining Reactive Care
Reactive care refers to medical treatment delivered after the onset of symptoms or the diagnosis of illness, focusing on addressing existing health problems rather than preventing them. It often involves emergency interventions, acute care, and hospitalization when health issues have already escalated into a crisis. Unlike preventive care, which emphasizes early detection and risk reduction, reactive care prioritizes symptom management and immediate treatment of health crises.
Key Differences Between Preventive and Reactive Care
Preventive care involves proactive measures such as vaccinations, screenings, and lifestyle counseling to maintain health and avoid disease onset, whereas reactive care addresses symptoms and illnesses only after they occur. Key differences between preventive and reactive care include the timing of intervention, cost-effectiveness, and overall impact on patient outcomes; preventive care reduces the risk of chronic diseases and healthcare costs by early detection and management, while reactive care often results in higher expenses and more complex treatments. Health crises typically emerge when reactive care fails or is delayed, emphasizing the importance of preventive strategies to minimize emergency situations and improve long-term public health.
Benefits of Preventive Healthcare
Preventive healthcare significantly reduces the risk of developing chronic diseases by identifying and addressing health issues early through regular screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle counseling. This proactive approach decreases healthcare costs and improves quality of life by avoiding complex treatments associated with reactive care during health crises. Emphasizing prevention leads to better population health outcomes, lowered hospital admissions, and enhanced productivity.
Drawbacks of Relying on Reactive Care
Relying on reactive care often results in delayed diagnoses, leading to more severe health complications and higher treatment costs. Your body may experience prolonged damage because symptoms are addressed only after they manifest, making recovery more difficult and less effective. Preventive care focuses on early detection and lifestyle adjustments, which reduces the risk of reaching a health crisis that demands urgent intervention.
Common Preventive Care Strategies
Common preventive care strategies include routine screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle counseling aimed at detecting and mitigating health risks before symptoms appear. Regular check-ups enable early identification of conditions, reducing the need for reactive care that addresses health issues after they arise. By prioritizing preventive measures, your overall well-being improves, minimizing the likelihood of costly and severe health crises.
Cost Comparisons: Preventive vs Reactive Approaches
Preventive care significantly reduces healthcare costs by identifying and managing health risks early, often minimizing the need for expensive treatments associated with health crises. Reactive care, which addresses illnesses only after symptoms appear, tends to result in higher medical expenses due to emergency interventions and prolonged hospital stays. Investing in your health through preventive measures ultimately lowers overall healthcare spending compared to the costly management of advanced health crises.
Impact on Patient Outcomes
Preventive care significantly improves patient outcomes by reducing the incidence of chronic diseases and enabling early detection of health issues, leading to timely intervention and lower healthcare costs. Reactive care often results in delayed treatment, increased complications, and higher hospitalization rates, negatively affecting long-term patient health and quality of life. Health crises typically demand urgent, intensive interventions that carry higher risks, longer recovery times, and increased mortality rates, underscoring the critical importance of prioritizing preventive strategies in healthcare systems.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Prevention
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in preventive care by conducting regular screenings, vaccinations, and health education to reduce the risk of illness before symptoms arise. Reactive care primarily addresses symptoms after a health issue occurs, often leading to more complex and costly treatments. Your engagement with preventive care guided by healthcare professionals can minimize the likelihood of a health crisis, improving long-term outcomes and reducing strain on medical resources.
Building a Preventive Care Plan for Long-Term Health
Building a preventive care plan involves regular health screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle modifications to identify and mitigate risks before they escalate into serious health issues. Reactive care addresses symptoms and illnesses after they occur, often leading to higher medical costs and prolonged recovery times. Prioritizing preventive care empowers you to maintain long-term health, reduce the likelihood of health crises, and improve overall quality of life.
Infographic: Preventive care vs Reactive care
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com