Preschool programs typically emphasize structured group activities and social development, whereas Montessori education focuses on individualized learning and hands-on exploration to foster independence. Explore this article to understand the key differences and benefits of Preschool versus Montessori approaches.
Table of Comparison
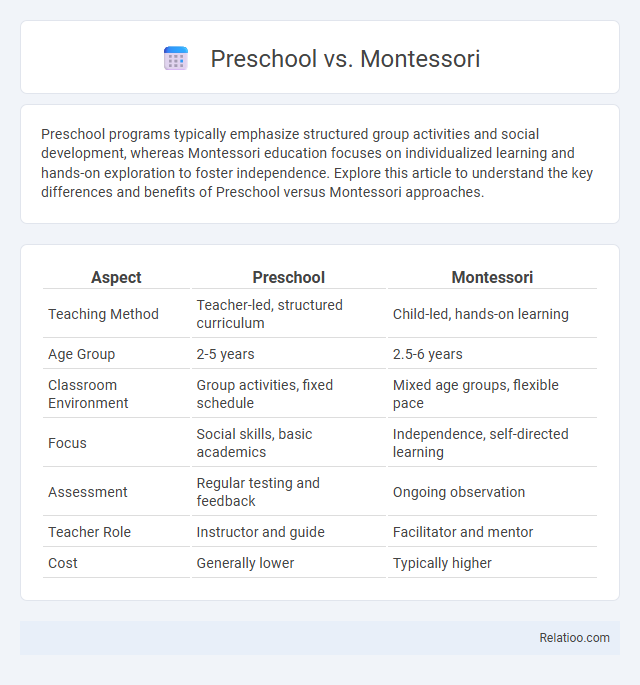
| Aspect | Preschool | Montessori |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Method | Teacher-led, structured curriculum | Child-led, hands-on learning |
| Age Group | 2-5 years | 2.5-6 years |
| Classroom Environment | Group activities, fixed schedule | Mixed age groups, flexible pace |
| Focus | Social skills, basic academics | Independence, self-directed learning |
| Assessment | Regular testing and feedback | Ongoing observation |
| Teacher Role | Instructor and guide | Facilitator and mentor |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
Understanding Preschool and Montessori: Key Differences
Preschool programs typically follow a structured curriculum designed to prepare children aged 3 to 5 for kindergarten, emphasizing social skills and early academic development. Montessori education centers on child-led learning within a prepared environment, fostering independence through hands-on activities tailored to individual developmental stages. Childcare services primarily focus on supervision and basic care for infants and toddlers, often incorporating early learning but lacking the formalized educational approaches found in preschool and Montessori settings.
Educational Philosophies: Traditional vs Montessori
Traditional preschools emphasize structured curricula with teacher-led instruction, focusing on cognitive skill development and socialization within a group setting. Montessori education prioritizes self-directed learning through hands-on activities, fostering independence, creativity, and individualized pacing aligned with Maria Montessori's method. Childcare centers typically blend basic care and developmental activities but lack the intentional educational philosophy that defines preschools and Montessori programs.
Classroom Environment: Structure and Flexibility
Preschool classrooms typically balance structured activities with free play, promoting early academic skills alongside social development. Montessori environments emphasize prepared, child-centered spaces with flexible, self-directed learning materials that foster independence and concentration. Childcare settings often prioritize a flexible, nurturing atmosphere tailored to meet diverse developmental needs while providing basic educational and social interaction opportunities.
Teacher Roles and Student Interaction
In preschool settings, teachers primarily lead structured activities aimed at developing foundational skills, maintaining a balance between guided instruction and free play to foster socialization. Montessori educators act as facilitators, observing and customizing individualized learning experiences that encourage autonomy and self-directed exploration. Childcare providers focus on ensuring safety and meeting basic needs while promoting social interaction through routine activities, often supporting early learning in a more flexible, caregiving context.
Curriculum and Learning Activities
Preschool programs typically follow a structured curriculum emphasizing social, cognitive, and motor skill development through group activities and teacher-led lessons. Montessori education uses a child-centered approach with hands-on learning materials and self-directed activities designed to foster independence and intrinsic motivation. Childcare centers prioritize care and supervision but often incorporate basic early learning activities and play to support developmental milestones in a safe environment.
Social and Emotional Development Approaches
Preschool programs typically emphasize group activities and structured play to foster socialization and emotional regulation among children. Montessori education utilizes child-led learning with a focus on independence, practical life skills, and peer collaboration to support emotional self-awareness and empathy. Childcare centers often provide a nurturing environment with consistent routines and caregiver interactions aimed at promoting secure attachments and basic social skills development.
Assessments and Progress Tracking
Preschool programs typically use standardized assessments to monitor children's cognitive, language, and social development at regular intervals, providing structured progress reports to parents. Montessori education emphasizes continuous observational assessments, allowing teachers to tailor activities based on each child's individual progress and intrinsic motivation, fostering personalized growth pathways. Your choice between preschool, Montessori, or childcare settings will influence how developmental milestones are tracked and communicated, impacting your child's learning experience and parental engagement.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
Preschool programs typically offer structured early education at moderate costs and are widely accessible through public and private options. Montessori schools emphasize individualized learning with specialized materials, often resulting in higher tuition fees and limited availability depending on location. Your choice should consider the balance between budget constraints and the accessibility of quality early childhood education that fits your family's needs.
Parent Involvement and Communication
Parent involvement in preschool typically centers around scheduled meetings and occasional classroom activities, fostering direct interaction with teachers. Montessori education emphasizes a collaborative partnership between parents and educators, encouraging ongoing communication and active participation in the child's learning journey. Childcare centers often prioritize regular updates through daily reports or digital apps, ensuring parents stay informed about their child's routines and well-being.
Choosing the Right Fit: Factors for Your Child
Choosing the right early education setting depends on your child's learning style, social needs, and family schedule. Preschools offer structured curricula focusing on school readiness, while Montessori emphasizes self-directed learning with hands-on materials promoting independence. Childcare centers provide flexible hours and social interaction, making them ideal for working parents seeking a safe environment with age-appropriate activities.
Infographic: Preschool vs Montessori
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com