Effective relationship management requires distinguishing between planning, which sets strategic goals, and forecasting, which predicts future outcomes based on data. Explore the detailed comparison of planning versus forecasting and their impacts on relationship success in this article.
Table of Comparison
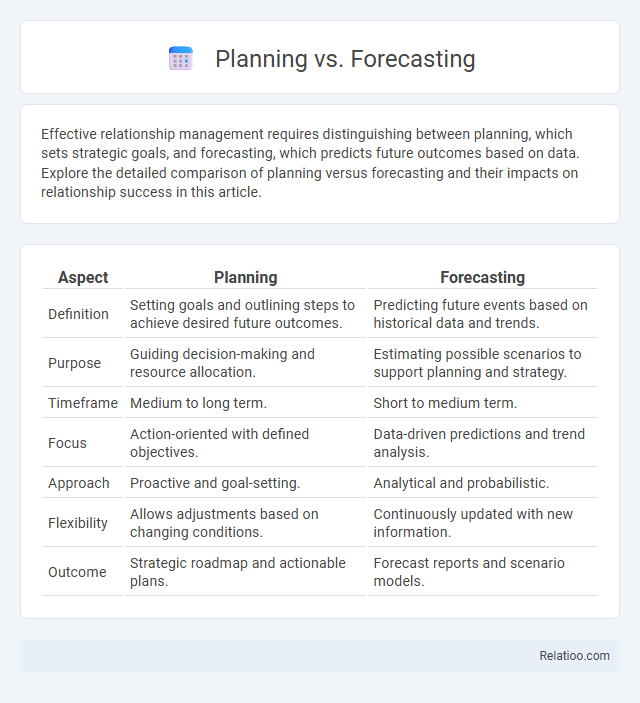
| Aspect | Planning | Forecasting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Setting goals and outlining steps to achieve desired future outcomes. | Predicting future events based on historical data and trends. |
| Purpose | Guiding decision-making and resource allocation. | Estimating possible scenarios to support planning and strategy. |
| Timeframe | Medium to long term. | Short to medium term. |
| Focus | Action-oriented with defined objectives. | Data-driven predictions and trend analysis. |
| Approach | Proactive and goal-setting. | Analytical and probabilistic. |
| Flexibility | Allows adjustments based on changing conditions. | Continuously updated with new information. |
| Outcome | Strategic roadmap and actionable plans. | Forecast reports and scenario models. |
Introduction to Planning and Forecasting
Planning involves setting clear objectives and outlining specific actions to achieve desired outcomes, while forecasting predicts future conditions based on historical data and trends. Your ability to effectively combine planning with accurate forecasting reduces risks associated with future uncertainty and enhances decision-making. Understanding the distinction between proactive planning and predictive forecasting empowers you to adapt strategies in dynamic environments.
Defining Planning: Purpose and Scope
Planning involves setting clear objectives and determining the necessary actions to achieve specific goals within a defined timeframe and resources. It serves to create a structured approach that guides decision-making and resource allocation, reducing uncertainty and aligning efforts with organizational priorities. Your ability to plan effectively enhances strategic direction by anticipating potential obstacles and organizing tasks to meet desired outcomes.
What is Forecasting? Key Concepts
Forecasting is the process of estimating future values based on historical data, statistical models, and trend analysis to support decision-making. Key concepts in forecasting include time series analysis, regression models, and moving averages, which help predict demand, sales, or market trends with varying degrees of accuracy. Forecasting addresses future uncertainty by providing probabilistic insights rather than definitive outcomes, enabling organizations to plan resources and strategies effectively.
Differences Between Planning and Forecasting
Planning involves setting specific goals and outlining detailed steps to achieve them, focusing on control and decision-making based on current information. Forecasting predicts future outcomes using historical data and statistical models but does not dictate actions, serving as an input to the planning process. Your strategic success depends on understanding that planning is proactive and prescriptive, while forecasting is predictive and descriptive, helping you navigate future uncertainty effectively.
The Relationship Between Planning and Forecasting
Planning and forecasting are interdependent processes where forecasting provides data-driven insights about potential future scenarios, enabling informed decision-making in planning. Effective planning integrates forecasting outputs to allocate resources and set strategic goals, reducing future uncertainty. Your ability to adapt plans based on accurate forecasts strengthens organizational resilience and improves predictive accuracy over time.
Importance of Accurate Forecasting in Planning
Accurate forecasting is crucial in planning as it provides reliable data to make informed decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and set realistic goals for Your business or project. While planning involves outlining the steps and strategies to achieve objectives, forecasting predicts future trends and potential outcomes based on historical data and market analysis. Understanding future uncertainty requires integrating forecasting into planning to minimize risks and adapt proactively to changing conditions.
Techniques for Effective Planning
Techniques for effective planning include scenario analysis, which helps visualize different future outcomes based on varying assumptions, and sensitivity analysis, identifying key variables that impact results. Incorporating rolling forecasts enables continual adjustment to plans by integrating the latest data and trends, enhancing flexibility amid future uncertainty. Risk assessment tools such as Monte Carlo simulations quantify uncertainty and guide decision-making under complex conditions.
Forecasting Methods and Tools
Forecasting methods utilize quantitative techniques such as time series analysis, regression models, and machine learning algorithms to predict future trends based on historical data. Tools like ARIMA, exponential smoothing, and neural networks enable precise demand forecasting, financial projections, and risk assessment in uncertain environments. Integrating these methodologies with scenario analysis enhances decision-making by addressing future uncertainty and improving planning accuracy.
Common Challenges in Planning and Forecasting
Common challenges in planning and forecasting stem from the inherent uncertainty of future events, making accurate predictions difficult due to incomplete or rapidly changing data. You often face difficulties integrating diverse data sources and aligning forecasts with strategic goals while adapting to unforeseen market shifts. Overcoming these obstacles requires sophisticated models and continuous updates to maintain relevance and reliability in decision-making processes.
Best Practices for Integrating Planning and Forecasting
Effective integration of planning and forecasting requires aligning your strategic goals with dynamic data-driven projections to enhance decision-making accuracy. Leveraging scenario analysis and continuous real-time updates mitigates future uncertainty by providing flexible responses to market fluctuations and operational risks. Employing advanced analytics platforms ensures your organization can seamlessly reconcile short-term forecasts with long-term plans for optimized resource allocation and performance outcomes.
Infographic: Planning vs Forecasting
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com