Single-parent families often face unique challenges such as financial strain and limited support systems compared to two-parent families, which typically benefit from shared responsibilities and resources. Explore the detailed comparison of single-parent and two-parent family dynamics and their impact on child development in this article.
Table of Comparison
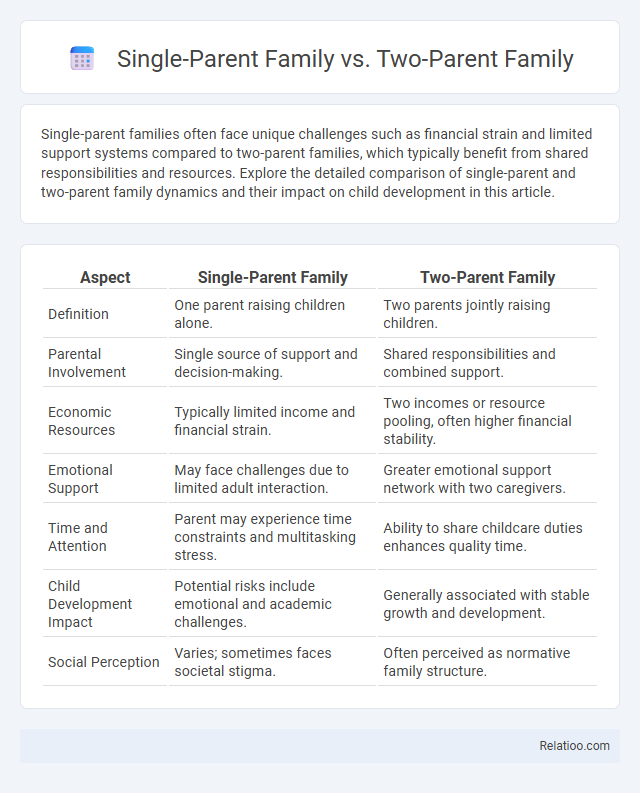
| Aspect | Single-Parent Family | Two-Parent Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One parent raising children alone. | Two parents jointly raising children. |
| Parental Involvement | Single source of support and decision-making. | Shared responsibilities and combined support. |
| Economic Resources | Typically limited income and financial strain. | Two incomes or resource pooling, often higher financial stability. |
| Emotional Support | May face challenges due to limited adult interaction. | Greater emotional support network with two caregivers. |
| Time and Attention | Parent may experience time constraints and multitasking stress. | Ability to share childcare duties enhances quality time. |
| Child Development Impact | Potential risks include emotional and academic challenges. | Generally associated with stable growth and development. |
| Social Perception | Varies; sometimes faces societal stigma. | Often perceived as normative family structure. |
Introduction to Family Structures
Single-parent families consist of one adult raising children, often resulting in unique financial and emotional challenges compared to two-parent families, where responsibilities and resources are shared. Two-parent families generally benefit from combined incomes and support systems, fostering stability in child development and household management. Understanding your family's structure helps tailor support and resources to meet specific needs effectively.
Defining Single-Parent and Two-Parent Families
A single-parent family consists of one adult raising one or more children, managing all parenting responsibilities and household duties alone, often facing unique social and economic challenges. In contrast, a two-parent family features two adults who share caregiving and financial roles, providing a collaborative environment for child development. Understanding these definitions helps you recognize the diverse dynamics and support systems influencing family well-being.
Financial Stability and Economic Impact
Single-parent families often face greater financial challenges due to a single income source, which can limit economic stability compared to two-parent families that typically benefit from dual earnings and shared expenses. Your economic resilience is influenced by factors such as employment opportunities, access to social support programs, and childcare costs, which tend to be more burdensome for single-parent households. Two-parent families generally exhibit higher savings rates and better access to resources, contributing to stronger long-term financial stability and reduced economic vulnerability.
Emotional Support and Parenting Roles
Single-parent families often face unique challenges in providing consistent emotional support due to limited parental availability and increased stress levels. Two-parent families typically benefit from shared parenting roles, allowing for balanced emotional nurturing and diverse disciplinary approaches. In contrast, single-parent families must integrate multiple roles and responsibilities, which can impact the depth and frequency of emotional engagement with children.
Child Development and Educational Outcomes
Children in two-parent families often experience higher educational achievement and better emotional stability due to increased parental resources and support. Single-parent families may face challenges such as limited income and time, affecting child development and academic performance, though strong social support can mitigate these effects. Research indicates that consistent parental involvement and quality time are crucial factors influencing positive educational outcomes regardless of family structure.
Socialization and Community Involvement
Children in two-parent families often benefit from more diverse social interactions and community involvement due to combined parental networks and resources. Single-parent families may face challenges in socialization opportunities but frequently foster strong resilience and close-knit bonds that encourage active community participation. Your support in community programs can enhance social skills and networks for children from all family structures.
Stress Factors and Coping Mechanisms
Single-parent families often face higher stress levels due to financial strain, limited social support, and increased caregiving responsibilities compared to two-parent families, which typically benefit from shared parental duties and emotional support. Coping mechanisms common in single-parent households include building strong community networks, seeking professional counseling, and practicing time management to balance work and family demands. Your ability to manage stress improves with proactive communication, accessing social services, and developing resilience strategies tailored to your family's unique dynamics.
Societal Perceptions and Stigmas
Societal perceptions of single-parent families often involve stigmas related to economic instability and perceived lack of parental support compared to two-parent families, which are traditionally viewed as more stable and ideal for child development. Single-parent families face challenges such as biased assumptions about parenting competence and social marginalization, impacting access to community resources and social networks. Increasing awareness and advocacy efforts aim to dismantle these stigmas by highlighting the diversity and strengths within all family structures.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Family Type
Single-parent families offer increased independence and closer parent-child bonding but often face financial strain and time management challenges. Two-parent families typically benefit from shared responsibilities and financial stability while sometimes encountering conflicts arising from differing parenting styles. Your choice of family structure influences emotional support systems, resource availability, and overall household dynamics.
Conclusion: Embracing Family Diversity
Embracing family diversity involves recognizing the unique strengths and challenges of single-parent families and two-parent families, each contributing valuable perspectives to child development. Research highlights that supportive environments, emotional stability, and economic resources significantly impact children's well-being, regardless of family structure. Promoting inclusivity and tailored support systems fosters resilience and growth across all family types.
Infographic: Single-Parent Family vs Two-Parent Family
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com