Intergenerational trauma explores how unresolved emotional pain passes through generations, impacting family members' mental health and relationships. Family Systems Theory examines family interactions and roles influencing behavior and emotional well-being. Discover deeper insights into their connection and effects in this article.
Table of Comparison
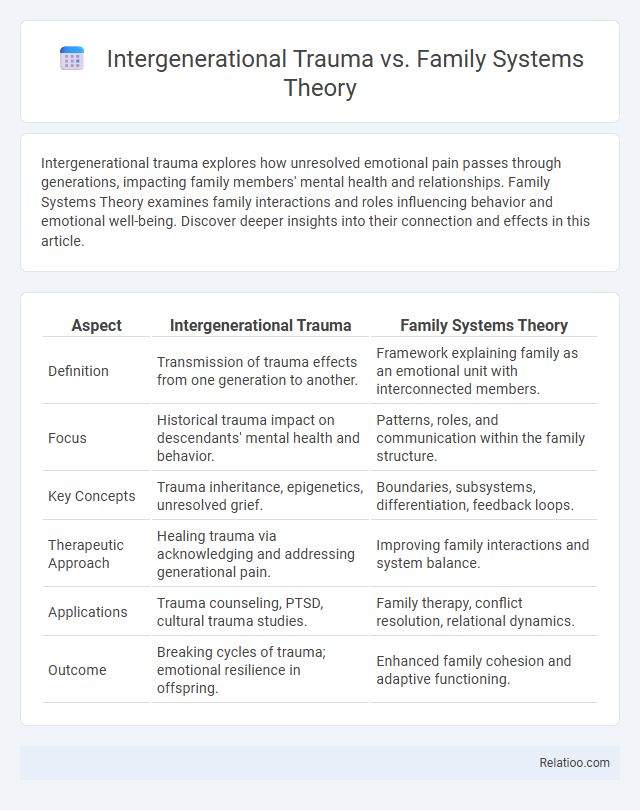
| Aspect | Intergenerational Trauma | Family Systems Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transmission of trauma effects from one generation to another. | Framework explaining family as an emotional unit with interconnected members. |
| Focus | Historical trauma impact on descendants' mental health and behavior. | Patterns, roles, and communication within the family structure. |
| Key Concepts | Trauma inheritance, epigenetics, unresolved grief. | Boundaries, subsystems, differentiation, feedback loops. |
| Therapeutic Approach | Healing trauma via acknowledging and addressing generational pain. | Improving family interactions and system balance. |
| Applications | Trauma counseling, PTSD, cultural trauma studies. | Family therapy, conflict resolution, relational dynamics. |
| Outcome | Breaking cycles of trauma; emotional resilience in offspring. | Enhanced family cohesion and adaptive functioning. |
Understanding Intergenerational Trauma
Understanding intergenerational trauma involves recognizing how traumatic experiences affect multiple generations within a family, often manifesting as emotional, psychological, and behavioral patterns passed down unconsciously. Family Systems Theory provides a framework to analyze these patterns by viewing the family as an interconnected system where each member's behaviors influence the whole. Your awareness of how trauma is transmitted through family dynamics can guide healing processes and break cycles of inherited pain.
Key Principles of Family Systems Theory
Family Systems Theory emphasizes the interconnectedness of family members and views the family as an emotional unit where patterns of behavior and communication affect each individual's psychological health. Key principles include homeostasis, where families strive for balance; differentiation of self, enabling members to maintain individuality while remaining connected; and the importance of multigenerational transmission processes that influence relational dynamics and emotional functioning. Understanding these principles helps to analyze how patterns of intergenerational trauma are maintained or altered within the family system.
Historical Roots of Intergenerational Trauma
Intergenerational trauma traces its historical roots to collective experiences of oppression, colonization, and violence endured by marginalized communities, deeply impacting successive generations. Family Systems Theory examines how these traumas manifest within family dynamics, emphasizing patterns of behavior, communication, and emotional responses passed down through familial interactions. Understanding the historical context of intergenerational trauma is crucial for revealing the underlying systemic and familial processes that perpetuate psychological and emotional distress across generations.
Core Concepts in Family Systems Theory
Core concepts in Family Systems Theory emphasize the interconnectedness and interdependence of family members, highlighting patterns of communication, roles, and boundaries that influence behavior. Intergenerational trauma involves the transmission of traumatic experiences and adaptive responses across generations, often perpetuating maladaptive family dynamics. Understanding these core principles helps you identify how unresolved trauma within the family system affects individual mental health and relational patterns.
Mechanisms of Trauma Transmission Across Generations
Mechanisms of trauma transmission across generations involve complex interactions between psychological, biological, and social factors. Intergenerational trauma explains the transfer of trauma symptoms through families via behavioral patterns, attachment disruptions, and epigenetic changes, while Family Systems Theory highlights the role of relational dynamics, communication patterns, and systemic boundaries in perpetuating trauma responses. Both frameworks emphasize how unresolved trauma can alter family roles and emotional regulation, leading to cyclical patterns of distress transmitted from parents to children.
Comparing Intergenerational Trauma and Family Systems Theory
Intergenerational trauma refers to the transmission of traumatic experiences and their psychological effects across generations, impacting family members' mental health and behavior. Family Systems Theory emphasizes the interconnectedness of family members, viewing the family as an emotional unit where individual behaviors are influenced by the family system's dynamics. Comparing the two, intergenerational trauma focuses on the content of traumatic experiences passed down, while Family Systems Theory highlights the systemic relationships and patterns within the family that shape individual functioning.
Impacts on Family Dynamics and Relationships
Intergenerational trauma manifests through patterns of unresolved emotional pain passed down across generations, profoundly influencing family dynamics by fostering maladaptive behaviors and strained relationships. Family Systems Theory emphasizes the interconnectedness of family members, highlighting how trauma disrupts equilibrium, leading to roles such as scapegoating or enmeshment that perpetuate dysfunction. Both frameworks underscore the cyclical nature of trauma's impact on relational patterns, affecting communication, attachment styles, and emotional regulation within the family unit.
Therapeutic Approaches to Addressing Trauma and Family Systems
Therapeutic approaches addressing intergenerational trauma often integrate family systems theory to explore how trauma patterns transmit across generations within family dynamics. Techniques such as systemic family therapy and trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT) aim to disrupt maladaptive relational patterns while fostering resilience. Evidence highlights the efficacy of combining narrative therapy and genogram mapping to contextualize trauma and promote healing within family systems.
Cultural Contexts in Trauma and Family Systems
Understanding intergenerational trauma requires examining how cultural contexts influence family systems, shaping the transmission of trauma across generations. Family Systems Theory highlights the interconnected roles and communication patterns within families that perpetuate trauma responses, especially in culturally distinct environments. Your healing journey benefits from recognizing how cultural values and family dynamics jointly affect trauma recovery and resilience.
Integrating Both Perspectives for Holistic Healing
Integrating Intergenerational Trauma and Family Systems Theory offers a comprehensive approach to understanding and healing deep-rooted familial wounds. You benefit by addressing individual trauma within the context of family dynamics, recognizing how emotional patterns and behaviors are transmitted across generations. This holistic healing method fosters resilience by combining psychological insight with systemic interventions to break cycles of trauma and promote healthier family relationships.
Infographic: Intergenerational Trauma vs Family Systems Theory
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com