Sibling caregiving often involves emotional support and shared history, while child caregiving focuses more on developmental guidance and long-term dependency. Explore the unique dynamics and challenges of both caregiving roles in this article.
Table of Comparison
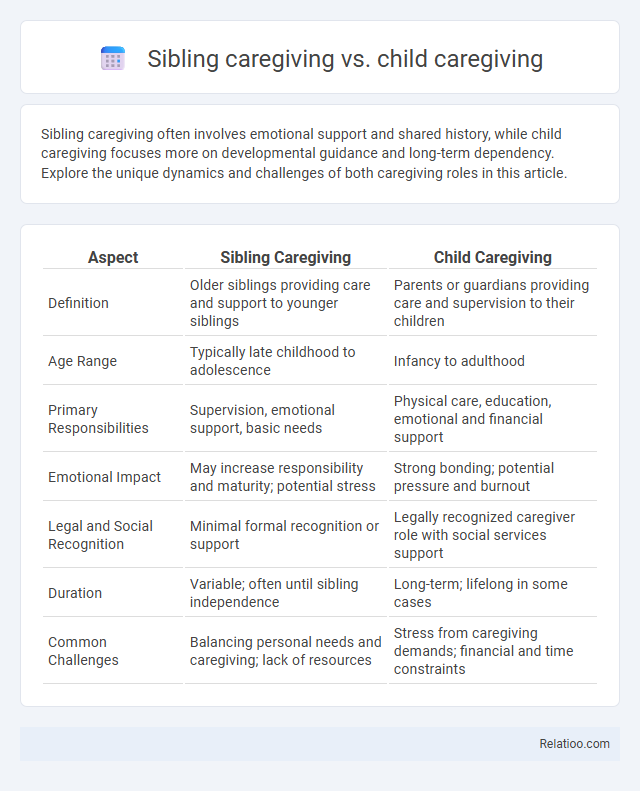
| Aspect | Sibling Caregiving | Child Caregiving |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Older siblings providing care and support to younger siblings | Parents or guardians providing care and supervision to their children |
| Age Range | Typically late childhood to adolescence | Infancy to adulthood |
| Primary Responsibilities | Supervision, emotional support, basic needs | Physical care, education, emotional and financial support |
| Emotional Impact | May increase responsibility and maturity; potential stress | Strong bonding; potential pressure and burnout |
| Legal and Social Recognition | Minimal formal recognition or support | Legally recognized caregiver role with social services support |
| Duration | Variable; often until sibling independence | Long-term; lifelong in some cases |
| Common Challenges | Balancing personal needs and caregiving; lack of resources | Stress from caregiving demands; financial and time constraints |
Understanding Sibling Caregiving: Definition and Scope
Sibling caregiving involves providing support and assistance to aging or disabled brothers or sisters, distinct from child caregiving which centers on nurturing and raising one's own children. This type of caregiving often requires balancing personal responsibilities while addressing the emotional and physical needs unique to sibling relationships. Understanding sibling caregiving helps you recognize its scope, including coordinating medical care, managing household tasks, and offering companionship, highlighting its vital role in family caregiving dynamics.
What Is Child Caregiving? Exploring the Basics
Child caregiving involves providing physical, emotional, and developmental support to minors who require assistance due to age, illness, or disability. This form of caregiving demands a focus on education, safety, and nurturing to promote healthy growth and well-being. Understanding the distinctions between child, sibling, and general caregiving helps you tailor care approaches effectively to meet the unique needs of each role.
Key Differences between Sibling and Child Caregiving
Sibling caregiving involves supporting a brother or sister who may have health or developmental challenges, whereas child caregiving focuses on the care and development of one's own children, often involving education, discipline, and emotional nurturing. Key differences include the nature of the relationship, where sibling caregiving is typically peer-based and reciprocal, while child caregiving is more hierarchical and responsibility-driven. Your experience as a caregiver will vary significantly based on these relational dynamics, emotional roles, and caregiving expectations.
Emotional Impact on Sibling Caregivers
Sibling caregiving often involves a unique emotional impact compared to child caregiving, as sibling caregivers frequently balance shared childhood memories with current caregiving responsibilities, which can lead to complex feelings of guilt, frustration, and loyalty. You may experience heightened emotional stress and anxiety because sibling caregivers typically have closer emotional bonds and less social recognition than adult children providing care. Research indicates that sibling caregivers face increased risk of depression and caregiver burnout, emphasizing the need for tailored emotional support and coping strategies.
Psychological Effects on Child Caregivers
Child caregivers often experience significant psychological effects, including increased anxiety, depression, and stress due to the dual responsibility of managing their own development while supporting a family member. Sibling caregiving can create a unique dynamic where emotional bonds intensify, sometimes leading to feelings of guilt or role confusion. Your mental health may be particularly vulnerable if caregiving duties interfere with social interactions and educational opportunities, highlighting the need for targeted psychological support.
Social Responsibilities and Family Dynamics
Sibling caregiving often involves managing complex family dynamics where social responsibilities include balancing individual needs with collective family support, differing from child caregiving which centers on nurturing and developmental obligations. Caregiving within families extends beyond physical care to encompass emotional labor and social role adaptation, highlighting the varied responsibilities that siblings, children, or other caregivers undertake. Family dynamics shift as social responsibilities redistribute, affecting communication patterns, decision-making processes, and intergenerational relationships.
Benefits and Challenges of Sibling Caregiving
Sibling caregiving offers unique benefits such as strengthened family bonds and shared responsibility, contrasting with child caregiving that often focuses on parental roles. Challenges of sibling caregiving include managing diverse personalities and potential conflicts among siblings, which can impact Your ability to provide consistent support. Unlike general caregiving roles, sibling caregivers must balance their personal lives with complex family dynamics, requiring effective communication and collaboration.
Risks and Drawbacks of Child Caregiving
Child caregiving often involves higher emotional and physical stress compared to sibling caregiving, due to the intense responsibility of managing daily needs and medical care for minors. The risks include burnout, financial strain, and psychological challenges such as anxiety or depression, which can adversely affect the caregiver's well-being and the quality of care provided. Unlike sibling caregiving, child caregiving typically requires extensive time commitment and may limit opportunities for education and career advancement.
Support Strategies for Sibling and Child Caregivers
Sibling and child caregiving require distinct support strategies tailored to their unique emotional and practical challenges, recognizing the sibling's dual role as family member and caregiver and the child's developmental needs. You can enhance caregiving effectiveness by implementing age-appropriate resources, emotional support, and respite options specifically designed for each group's circumstances. Access to counseling, educational materials, and community support networks are essential to alleviate stress and improve the caregiving experience for both siblings and child caregivers.
Future Implications for Caregiving Roles in Families
Sibling caregiving, child caregiving, and general caregiving roles each present unique future implications for family dynamics and resource allocation. As lifespans increase and family structures diversify, your responsibility may shift toward shared caregiving among siblings, potentially easing individual burdens but requiring enhanced coordination and communication. Technology integration and policy support will become crucial in adapting caregiving strategies to meet evolving family needs and health care challenges.
Infographic: Sibling caregiving vs child caregiving
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com