Respite care provides temporary relief for primary caregivers, while long-term foster care involves permanent placement and ongoing support for children in need. Discover the key differences and benefits of both options in this article.
Table of Comparison
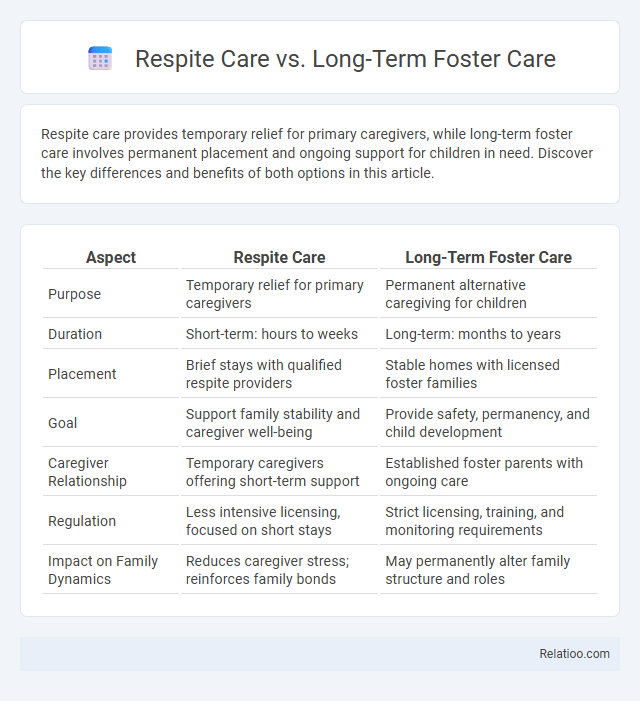
| Aspect | Respite Care | Long-Term Foster Care |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Temporary relief for primary caregivers | Permanent alternative caregiving for children |
| Duration | Short-term: hours to weeks | Long-term: months to years |
| Placement | Brief stays with qualified respite providers | Stable homes with licensed foster families |
| Goal | Support family stability and caregiver well-being | Provide safety, permanency, and child development |
| Caregiver Relationship | Temporary caregivers offering short-term support | Established foster parents with ongoing care |
| Regulation | Less intensive licensing, focused on short stays | Strict licensing, training, and monitoring requirements |
| Impact on Family Dynamics | Reduces caregiver stress; reinforces family bonds | May permanently alter family structure and roles |
Understanding Respite Care: A Brief Overview
Respite care provides temporary relief for foster families by offering short-term, scheduled breaks from caregiving duties, ensuring children still receive consistent support during transitions. Long-term foster care involves placing a child in a stable, ongoing home environment when reunification with birth parents is not possible, aiming for permanent stability. Fostering broadly encompasses both respite and long-term care, emphasizing the commitment to nurturing children in need through varying durations and levels of support.
What Is Long-Term Foster Care?
Long-term foster care provides stable, ongoing family placements for children who cannot return to their biological families, offering a permanent substitute living arrangement. It differs from respite care, which is short-term and designed to give temporary relief to primary caregivers, and general fostering, which may include both short and long-term placements depending on the child's needs. The goal of long-term foster care is to support the child's developmental and emotional needs while maintaining continuity and stability over years.
Key Differences Between Respite and Long-Term Foster Care
Respite care provides short-term relief for primary caregivers, offering temporary placement for children during brief periods, whereas long-term foster care involves extended or permanent child placement with foster families. Respite care is designed for emergency or occasional breaks, typically lasting hours to weeks, while long-term foster care supports ongoing care until reunification or adoption. Key differences include duration, purpose, and the level of commitment required from foster families.
Who Benefits from Respite Care?
Respite care provides temporary relief for primary caregivers of children or adults with special needs, chronic illnesses, or disabilities, enabling them to rest and recharge. Families facing high-stress caregiving situations, such as parents of children with autism or elderly individuals with dementia, benefit most from respite care by preventing burnout and maintaining overall well-being. Unlike long-term foster care or traditional fostering, which involve permanent or extended placements, respite care is short-term, supporting both caregivers and care recipients during challenging periods.
The Role of Long-Term Foster Parents
Long-term foster parents provide stability and consistent nurturing for children unable to live with their birth families, playing a critical role in emotional and developmental growth. Unlike respite care, which offers temporary relief for primary caregivers, long-term foster care involves ongoing commitment to meet a child's evolving needs. Their role encompasses supporting educational progress, healthcare management, and fostering a sense of belonging and security.
Eligibility Requirements for Each Care Type
Respite care eligibility typically requires that the child has special needs or the primary caregiver needs temporary relief from caregiving duties. Long-term foster care eligibility involves children who cannot safely return to their biological family and require a stable home environment for an extended period. Fostering eligibility varies by jurisdiction but generally includes background checks, training, and the ability to provide a safe, nurturing environment for children of different ages and needs.
Pros and Cons of Respite Care
Respite care offers temporary relief for primary caregivers, providing short-term support that helps prevent burnout and maintains family stability, but it may lack the continuity and deeper bonding found in long-term foster care. Unlike long-term foster care, which involves prolonged placement and comprehensive developmental support for children, respite care prioritizes immediate, short-duration assistance and flexibility. While fostering overall ensures a safe and nurturing environment for children unable to live with their biological families, respite care specifically benefits caregivers by offering scheduled breaks without the long-term commitment or emotional challenges associated with extended foster care placements.
Pros and Cons of Long-Term Foster Care
Long-term foster care provides stability and a nurturing environment for children unable to live with their biological families, offering consistent support and opportunities for emotional growth. However, it may limit family reunification prospects and can be emotionally challenging for both the child and foster parents due to the indefinite duration. You should weigh these benefits and drawbacks against alternatives like respite care, which offers temporary relief, and general fostering, which may be short-term or emergency-based.
How to Decide Which Care Option Is Right
Choosing between respite care, long-term foster care, and traditional fostering depends on your family's specific needs and capacity to provide support. Respite care offers short-term relief for primary caregivers, ideal if you require temporary assistance without permanent placement. Long-term foster care suits situations where a child needs stable, extended support, while traditional fostering ranges in commitment and duration; understanding these distinctions helps you decide the best care option tailored to your child's well-being.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Foster Care Solution
Selecting the best foster care solution depends on your family's needs and the child's circumstances, with respite care offering short-term relief, long-term foster care providing stability, and general fostering balancing both. Carefully assessing the child's emotional, developmental, and safety requirements helps determine the appropriate placement. Your decision should prioritize the child's well-being and long-term growth while offering your family manageable support.
Infographic: Respite Care vs Long-Term Foster Care
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com