Hierarchical relationships prioritize clear authority and structured roles, while egalitarian relationships emphasize equal power and mutual respect among participants. Discover the key differences and impacts of these dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
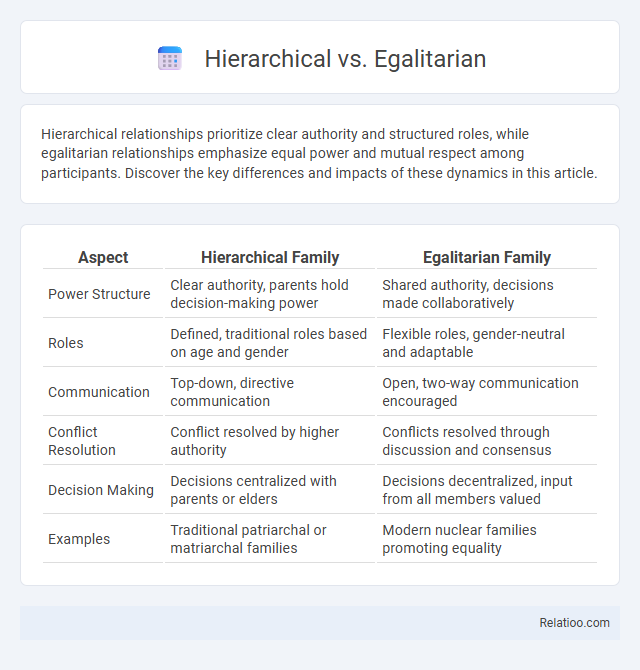
| Aspect | Hierarchical Family | Egalitarian Family |
|---|---|---|
| Power Structure | Clear authority, parents hold decision-making power | Shared authority, decisions made collaboratively |
| Roles | Defined, traditional roles based on age and gender | Flexible roles, gender-neutral and adaptable |
| Communication | Top-down, directive communication | Open, two-way communication encouraged |
| Conflict Resolution | Conflict resolved by higher authority | Conflicts resolved through discussion and consensus |
| Decision Making | Decisions centralized with parents or elders | Decisions decentralized, input from all members valued |
| Examples | Traditional patriarchal or matriarchal families | Modern nuclear families promoting equality |
Understanding Hierarchical and Egalitarian Structures
Hierarchical structures organize authority in a top-down manner, where decision-making flows from upper management to lower levels, emphasizing clear roles and responsibilities. Egalitarian structures promote equal participation and collaboration among members, reducing power distances to foster inclusivity and shared accountability. Understanding these two frameworks helps you identify how control and communication function within organizations, enabling more effective management and teamwork strategies.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical and Egalitarian Models
Hierarchical models emphasize structured levels of authority, where decision-making flows from top management to subordinates, promoting clear roles and responsibilities. Egalitarian models prioritize equal participation and collaboration, enabling shared decision-making and reducing power distance among members. Key differences include the degree of centralization, communication style, and flexibility, with hierarchical systems favoring control and order, while egalitarian systems encourage openness and innovation.
Historical Contexts of Hierarchical Systems
Hierarchical systems have shaped civilizations for millennia, exemplified by ancient Egypt's pharaohs and medieval Europe's feudal lords who maintained rigid social orders through centralized authority and clearly defined roles. These historical contexts reveal how power distribution in hierarchical structures often solidified social stratification and controlled resources. Understanding your position within these frameworks can illuminate the legacy and influence of hierarchical governance on contemporary organizational models.
The Rise of Egalitarian Approaches
Egalitarian approaches emphasize equal participation and shared decision-making, challenging traditional hierarchical systems where power is concentrated at the top. The rise of egalitarian models has transformed organizational cultures by promoting transparency, collaboration, and inclusive leadership, resulting in increased employee engagement and innovation. You can leverage egalitarian principles to foster a more democratic environment that values diverse perspectives and collective problem-solving.
Advantages of Hierarchical Workplaces
Hierarchical workplaces offer clear chains of command that enhance decision-making efficiency and accountability, reducing role ambiguity among employees. Structured levels of authority facilitate effective communication flow from top management to operational staff, ensuring alignment with organizational goals. This system supports professional development by providing defined career paths and opportunities for leadership growth within the hierarchy.
Benefits of Egalitarian Organizations
Egalitarian organizations foster collaboration and innovation by promoting equal participation and reducing power imbalances, which enhances employee motivation and job satisfaction. These structures facilitate transparent communication and quicker decision-making processes, leading to increased adaptability in dynamic markets. Research indicates that companies with egalitarian cultures often experience higher productivity and lower turnover rates due to a supportive and inclusive work environment.
Challenges in Hierarchical Environments
Hierarchical environments often face challenges such as limited communication flow, slower decision-making processes, and reduced employee autonomy, which can hinder innovation and adaptability. The rigid structure may create power imbalances and discourage collaboration, leading to decreased job satisfaction and higher turnover rates. Addressing these issues requires organizations to foster transparency, encourage feedback, and implement flexible leadership practices.
Drawbacks of Egalitarian Structures
Egalitarian structures often face challenges such as slower decision-making processes and a lack of clear authority, which can lead to confusion and inefficiency in organizational operations. Your team may experience difficulty in accountability and conflict resolution due to the equal distribution of power, making it hard to enforce discipline or strategic direction. These drawbacks can hinder timely responses and effective leadership compared to more hierarchical or system-based models.
Choosing Between Hierarchical and Egalitarian Cultures
Choosing between hierarchical and egalitarian cultures depends on your organization's goals, communication style, and decision-making processes. Hierarchical cultures emphasize structured roles, clear authority levels, and top-down control, which can enhance efficiency and clarity in large or complex organizations. Egalitarian cultures promote collaboration, equal input, and shared responsibility, fostering innovation and employee engagement in dynamic or creative environments.
Future Trends in Organizational Structures
Future trends in organizational structures emphasize hybrid models blending hierarchical, egalitarian, and system approaches to enhance agility and innovation. Hierarchical frameworks are increasingly integrated with egalitarian principles, promoting decentralized decision-making and collaborative cultures supported by advanced digital platforms. System-based structures leverage technology and data analytics to create adaptive, interconnected networks that respond dynamically to market changes and foster continuous learning.
Infographic: Hierarchical vs Egalitarian
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com