Firstborn children often develop strong leadership skills and a heightened sense of responsibility, while youngest siblings tend to be more social and adaptable due to their family role. Discover more insights on how birth order shapes personality and relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
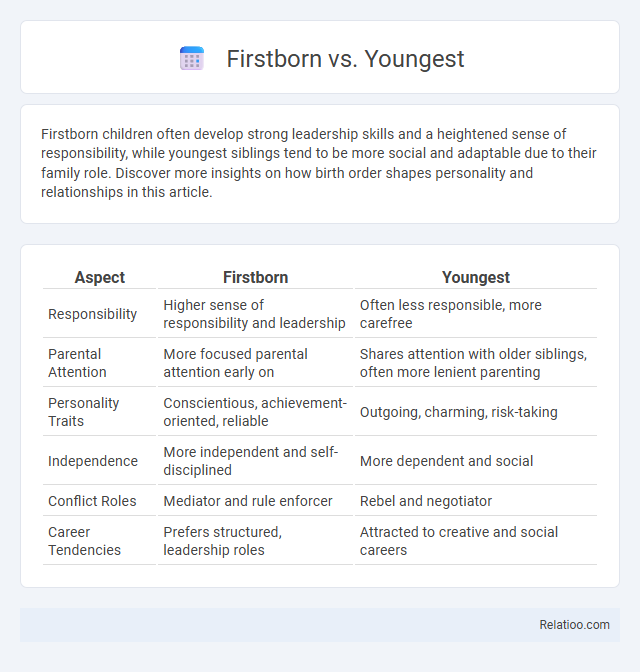
| Aspect | Firstborn | Youngest |
|---|---|---|
| Responsibility | Higher sense of responsibility and leadership | Often less responsible, more carefree |
| Parental Attention | More focused parental attention early on | Shares attention with older siblings, often more lenient parenting |
| Personality Traits | Conscientious, achievement-oriented, reliable | Outgoing, charming, risk-taking |
| Independence | More independent and self-disciplined | More dependent and social |
| Conflict Roles | Mediator and rule enforcer | Rebel and negotiator |
| Career Tendencies | Prefers structured, leadership roles | Attracted to creative and social careers |
Birth Order Psychology: Firstborn vs Youngest
Birth order psychology reveals distinct personality traits between firstborns and youngest siblings, with firstborns often exhibiting leadership, responsibility, and perfectionism due to early parental attention and expectations. Youngest children typically display traits like sociability, charm, and risk-taking, benefiting from more relaxed parenting and learned negotiation skills within family dynamics. Hierarchies within sibling groups influence cognitive development and social behaviors, shaping individuality based on birth order roles and family structure.
Personality Traits of Firstborn Children
Firstborn children often exhibit leadership qualities, high conscientiousness, and a strong sense of responsibility due to their role in the family hierarchy. They tend to be achievement-oriented and perfectionistic, influenced by parental expectations and the need to set an example for younger siblings. In contrast, youngest children may display more sociability and risk-taking behaviors, while middle children often develop negotiation and independence skills.
Defining Characteristics of Youngest Siblings
Youngest siblings often develop traits like adaptability, social skills, and charm due to their position in the family hierarchy, where they receive more attention and leniency compared to firstborns and middle children. Your youngest sibling may also display creativity and risk-taking tendencies, benefiting from observing older siblings' experiences and mistakes. This unique role influences their personality development, shaping distinct strengths within family dynamics.
Leadership and Responsibility in Firstborns
Firstborn children often exhibit strong leadership qualities and a heightened sense of responsibility, shaped by their role as family pioneers and caretakers of younger siblings. Their position in the sibling hierarchy frequently instills confidence, decision-making skills, and accountability, setting them apart from youngest siblings who might receive more leniency. This dynamic influences their development into natural leaders both within family settings and broader social or professional environments.
Creativity and Risk-Taking in Youngest Children
Youngest children often exhibit higher creativity and greater willingness to take risks compared to firstborns and middle siblings, attributed to their unique family position and less pressure to conform to established expectations. Research indicates that youngest siblings develop innovative problem-solving skills and embrace unconventional approaches, fostering distinctive creative capacities. Hierarchical birth order dynamics shape personality traits, with the youngest child's openness and adaptability crucial factors enhancing risk-taking behavior.
Parental Expectations and Treatment Differences
Firstborn children often face higher parental expectations for leadership, responsibility, and academic achievement compared to their younger siblings, leading to more strict treatment and pressure from parents. Youngest siblings typically receive more leniency and attention but might be underestimated in terms of independence and accountability. Hierarchical family dynamics influence differential parenting styles, where birth order significantly shapes emotional support, discipline, and expectations within the household.
Social Skills: Comparing Firstborns and Youngest
Firstborns often develop strong leadership and social skills due to early responsibility and parental expectations, which shape their confidence and communication abilities. Youngest siblings tend to be more sociable and charming, leveraging their role as the baby of the family to build relationships and gain attention. Understanding these differences can help you recognize how birth order influences social dynamics and interpersonal skills within family hierarchies.
Achievement and Academic Success: Who Leads?
Firstborn children often lead in achievement and academic success due to higher parental expectations and more focused attention during early development. Youngest siblings may excel in creativity and social skills but tend to have lower academic performance compared to firstborns. Your family hierarchy influences educational outcomes by shaping resource allocation, motivation, and competitive dynamics among siblings.
Sibling Rivalry and Relationship Dynamics
Firstborns often assume leadership roles within the sibling hierarchy, leading to protective yet authoritative dynamics that can trigger rivalry with younger siblings competing for parental attention. Youngest children may leverage their position to gain favor and challenge established roles, intensifying sibling rivalry and shaping complex relationship patterns. These hierarchical positions significantly influence sibling interaction styles, with rivalry frequently stemming from competition for status, affection, and identity within the family system.
Real-Life Success Stories: Firstborn vs Youngest
Firstborn children often excel in leadership roles and academic achievement due to early responsibilities, as exemplified by leaders like Bill Gates, the oldest sibling in his family. Youngest siblings, such as Elon Musk, frequently exhibit creativity and risk-taking abilities that contribute to groundbreaking innovation and success. Your understanding of sibling hierarchy can reveal how birth order influences personality traits and career paths, shaping diverse real-life success stories.
Infographic: Firstborn vs Youngest
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com