Single-parent families often face unique challenges in financial stability and emotional support compared to blended families, which benefit from shared resources and diverse parental influences. Explore this article to understand the dynamics and advantages of both family structures.
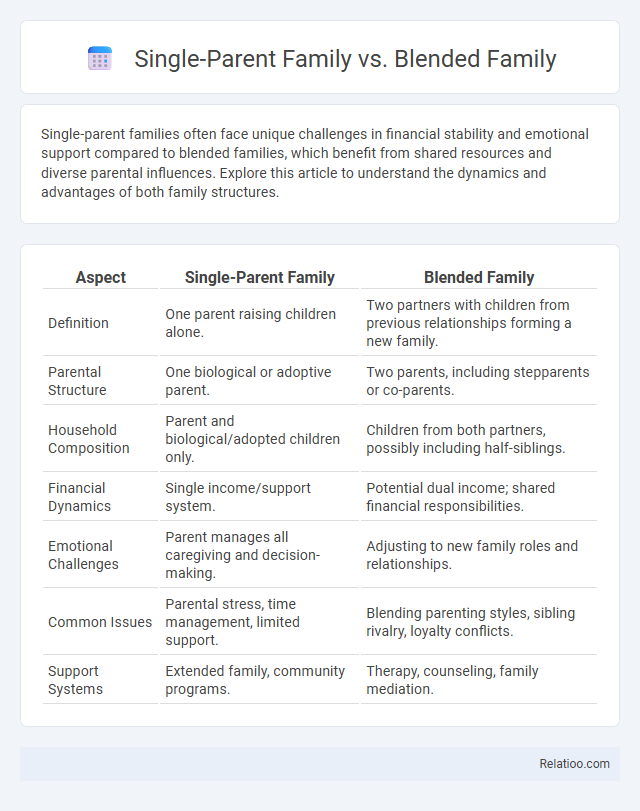
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Single-Parent Family | Blended Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One parent raising children alone. | Two partners with children from previous relationships forming a new family. |
| Parental Structure | One biological or adoptive parent. | Two parents, including stepparents or co-parents. |
| Household Composition | Parent and biological/adopted children only. | Children from both partners, possibly including half-siblings. |
| Financial Dynamics | Single income/support system. | Potential dual income; shared financial responsibilities. |
| Emotional Challenges | Parent manages all caregiving and decision-making. | Adjusting to new family roles and relationships. |
| Common Issues | Parental stress, time management, limited support. | Blending parenting styles, sibling rivalry, loyalty conflicts. |
| Support Systems | Extended family, community programs. | Therapy, counseling, family mediation. |
Introduction to Family Structures
Family structures vary widely, with single-parent families consisting of one caregiver raising children independently, while blended families combine members from previous relationships, creating a unique dynamic. Your understanding of these family types helps recognize the distinct challenges and strengths each structure embodies. Exploring these differences provides insight into how family roles and relationships adapt in modern society.
Defining Single-Parent Families
Single-parent families are characterized by one adult raising one or more children without the presence of a second parent in the household, distinguishing them from blended families which consist of partners and their children from previous relationships. Your experience in a single-parent family often involves managing both caregiving and financial responsibilities independently. Understanding this family structure highlights the unique challenges and strengths that single-parent households possess compared to blended or two-parent families.
What is a Blended Family?
A blended family, also known as a stepfamily, consists of partners who bring children from previous relationships into a new, unified household. This family structure involves navigating complex dynamics as step-siblings and parents adjust to new roles and relationships. Understanding how a blended family differs from a single-parent family helps you manage expectations and foster strong, supportive bonds.
Emotional Dynamics in Single-Parent Households
Emotional dynamics in single-parent households often involve heightened stress levels due to the sole responsibility of caregiving and financial support, impacting both parent and child well-being. Unlike blended families where emotional adjustment includes integrating step-siblings and navigating new parental roles, single-parent families may experience stronger parent-child bonds but greater vulnerability to emotional strain. Research highlights that single parents benefit from social support networks to mitigate stress and foster resilience, promoting healthier emotional environments for children.
Relationship Challenges in Blended Families
Blended families face unique relationship challenges, including managing loyalty conflicts between step-siblings and biological parents, navigating differing parenting styles, and establishing trust with new partners and children. You must address communication barriers and emotional adjustments to foster healthy bonds and create a cohesive family unit. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for overcoming the complexities that differ significantly from those encountered in single-parent families.
Financial Considerations: Comparing Both Families
Financial considerations vary significantly between single-parent and blended families, affecting budgeting, expenses, and resource allocation. Single-parent families often face tighter budgets due to relying on a single income, while blended families may benefit from combined incomes but encounter higher costs related to larger households and blending financial obligations. Understanding your family's specific financial dynamics is crucial for effective money management and long-term stability.
Parenting Styles and Discipline Approaches
Single-parent families often adopt authoritative or permissive parenting styles due to managing household responsibilities alone, focusing on clear rules but flexible discipline to maintain stability. Blended families tend to use collaborative parenting approaches that emphasize negotiation and consistency between biological and stepparents to address complex family dynamics. In comparison, single-parent families sometimes face challenges balancing discipline with emotional support, often relying on routines and open communication to foster resilience and trust.
Impact on Children’s Development
Single-parent families often face challenges such as limited financial resources and reduced parental attention, impacting children's emotional stability and academic performance. Blended families introduce complexities like adjusting to new family dynamics and step-relationships, which can influence children's social development and identity formation. Your understanding of these differences helps tailor support strategies that promote resilience and positive developmental outcomes for children in diverse family structures.
Support Systems and Community Resources
Support systems for single-parent families often include government assistance programs, local food banks, and parenting support groups tailored to address financial and emotional challenges. Blended families benefit from counseling services and community workshops designed to navigate complex family dynamics and foster healthy relationships among step-relatives. Both family types can access educational resources, childcare services, and community centers that promote social integration and provide essential stability for children's development.
Choosing What’s Best: Key Takeaways
Choosing the best family structure involves considering emotional stability, financial resources, and support systems. Single-parent families often emphasize close parent-child bonds, while blended families provide a broader network but require navigating complex relationships. Prioritizing children's well-being and open communication remains essential regardless of the family type.
Infographic: Single-Parent Family vs Blended Family
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com