Closed communication limits emotional expression and hinders problem-solving in relationships, while passive communication avoids confrontation but often leads to unresolved issues and resentment. Discover how these communication styles impact your connection and ways to improve by reading this article.
Table of Comparison
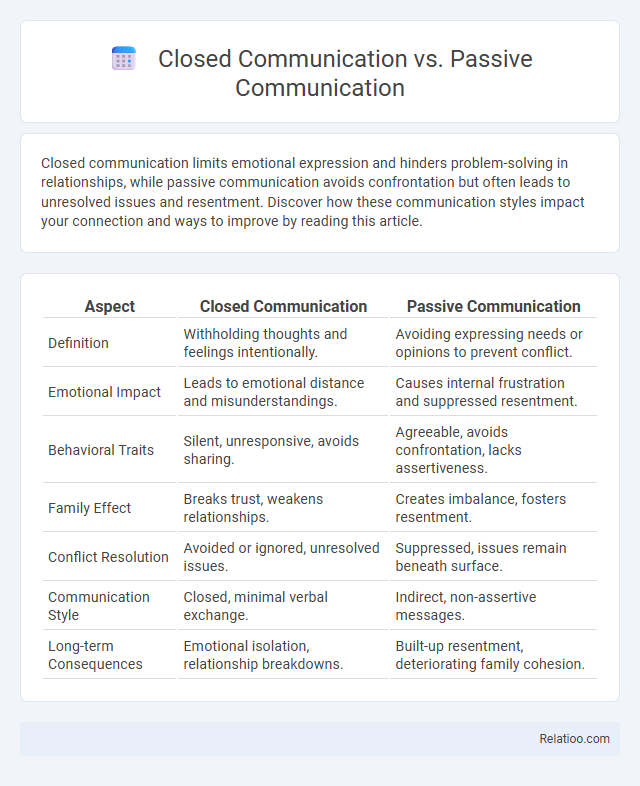
| Aspect | Closed Communication | Passive Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Withholding thoughts and feelings intentionally. | Avoiding expressing needs or opinions to prevent conflict. |
| Emotional Impact | Leads to emotional distance and misunderstandings. | Causes internal frustration and suppressed resentment. |
| Behavioral Traits | Silent, unresponsive, avoids sharing. | Agreeable, avoids confrontation, lacks assertiveness. |
| Family Effect | Breaks trust, weakens relationships. | Creates imbalance, fosters resentment. |
| Conflict Resolution | Avoided or ignored, unresolved issues. | Suppressed, issues remain beneath surface. |
| Communication Style | Closed, minimal verbal exchange. | Indirect, non-assertive messages. |
| Long-term Consequences | Emotional isolation, relationship breakdowns. | Built-up resentment, deteriorating family cohesion. |
Understanding Closed Communication
Closed communication involves withholding information, emotions, or thoughts, leading to limited interaction and potential misunderstandings. It contrasts with passive communication, which often involves avoiding confrontation and expressing needs indirectly. Understanding closed communication is crucial for improving transparency, enhancing trust, and fostering more effective interpersonal relationships.
Defining Passive Communication
Passive communication is characterized by an avoidance of expressing thoughts, needs, or feelings directly, often leading to misunderstandings and unmet personal boundaries. Unlike closed communication, which restricts information flow sharply, passive communication involves silence or submissiveness that may mask true emotions. This communication style can result in internalized stress and a lack of assertiveness, impacting relationships and effective collaboration.
Key Differences Between Closed and Passive Communication
Closed communication involves withholding information and limiting interaction, creating barriers to understanding, while passive communication is characterized by avoiding conflict, yielding to others, and often suppressing one's own needs. The key difference lies in intent: closed communication restricts exchange deliberately, whereas passive communication avoids expression due to fear or discomfort. Your awareness of these distinctions can improve interpersonal relationships and enhance effective communication strategies.
Characteristics of Closed Communication
Closed communication is characterized by limited information exchange, a lack of openness, and minimal feedback between parties; it typically involves withholding thoughts or feelings to avoid conflict or maintain control. This communication style often results in misunderstandings, reduced trust, and decreased collaboration within teams or relationships. Unlike passive communication, which is marked by submissiveness and avoidance, closed communication deliberately restricts dialogue and transparency.
Traits of Passive Communication
Passive communication traits include reluctance to express opinions or needs, avoidance of confrontation, and a tendency to yield to others to maintain harmony. You may experience difficulty asserting yourself, often resulting in unmet needs and suppressed emotions. This communication style contrasts with closed communication, which is marked by withholding information, and aggressive communication, characterized by forceful and dominating behavior.
Impacts on Personal Relationships
Closed communication, characterized by withholding information and emotions, often leads to misunderstandings and emotional distance in personal relationships, undermining trust and intimacy. Passive communication, where individuals avoid expressing their needs or opinions, can result in resentment and unfulfilled expectations, weakening relationship satisfaction. In contrast, open and direct communication fosters transparency and emotional connection, promoting healthier and more resilient personal relationships.
Effects in Professional Environments
Closed communication limits the flow of information, leading to misunderstandings and reduced collaboration in professional environments. Passive communication can cause unresolved conflicts and lowered team morale due to a lack of assertiveness and clear expression of ideas. Compared to open communication, both closed and passive communication hinder decision-making processes and negatively impact productivity and employee engagement.
Strategies to Overcome Closed Communication
Overcoming closed communication requires adopting open dialogue strategies such as active listening, expressing thoughts clearly, and encouraging feedback to build trust and transparency. Implementing nonverbal cues like maintaining eye contact and using affirmative gestures helps break barriers in passive and closed communication styles. Cultivating a safe environment where individuals feel valued reduces fear and resistance, fostering more effective and open interactions.
Tips for Addressing Passive Communication
Addressing passive communication requires clear boundary-setting and encouraging open expression to prevent misunderstandings and resentment. You can improve interactions by asking direct questions and validating feelings to empower others to share their thoughts honestly. Recognizing the differences between closed, passive, and active communication styles allows you to tailor your approach for more effective and transparent dialogue.
Choosing Effective Communication Styles
Choosing effective communication styles depends on context and desired outcomes; closed communication limits information exchange and often leads to misunderstandings, while passive communication minimizes personal expression and may result in unmet needs. Open communication fosters transparency and active listening, promoting mutual understanding and problem-solving. Analyzing audience needs and communication goals helps in selecting the optimal style for clarity and relationship building.
Infographic: Closed Communication vs Passive Communication
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com