Emotional mirroring involves reflecting another person's feelings through body language and expressions, while empathy is the deeper capacity to understand and share those emotions mentally and emotionally. Explore this article to discover how mastering both can transform your relationships.
Table of Comparison
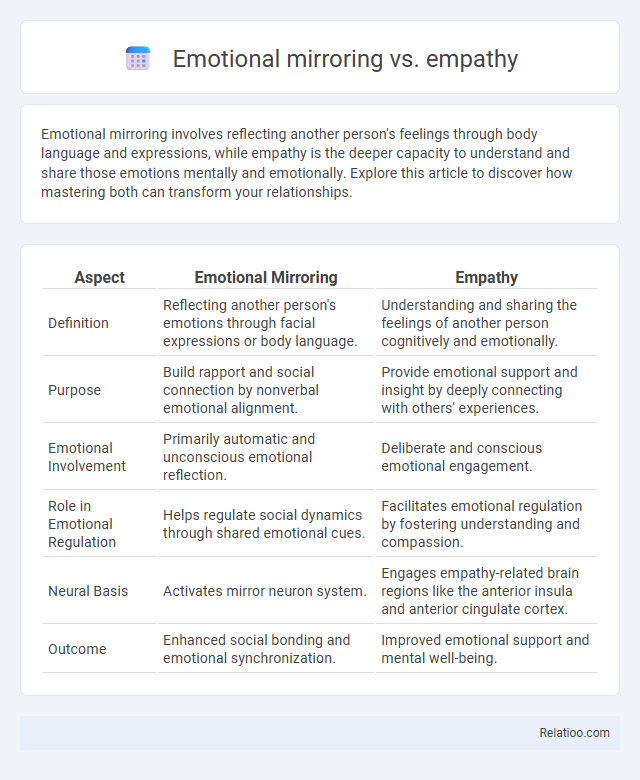
| Aspect | Emotional Mirroring | Empathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reflecting another person's emotions through facial expressions or body language. | Understanding and sharing the feelings of another person cognitively and emotionally. |
| Purpose | Build rapport and social connection by nonverbal emotional alignment. | Provide emotional support and insight by deeply connecting with others' experiences. |
| Emotional Involvement | Primarily automatic and unconscious emotional reflection. | Deliberate and conscious emotional engagement. |
| Role in Emotional Regulation | Helps regulate social dynamics through shared emotional cues. | Facilitates emotional regulation by fostering understanding and compassion. |
| Neural Basis | Activates mirror neuron system. | Engages empathy-related brain regions like the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex. |
| Outcome | Enhanced social bonding and emotional synchronization. | Improved emotional support and mental well-being. |
Introduction to Emotional Mirroring and Empathy
Emotional mirroring involves unconsciously reflecting another person's emotions through body language, facial expressions, or tone, facilitating nonverbal communication and connection. Empathy extends beyond mirroring by consciously understanding and sharing another individual's emotional experience, allowing for deeper emotional insight and compassion. Both processes are crucial in social interactions, with emotional mirroring serving as an automatic response and empathy requiring cognitive and affective engagement.
Defining Emotional Mirroring
Emotional mirroring involves unconsciously reflecting another person's emotions through facial expressions, body language, or tone, facilitating nonverbal communication and social bonding. Empathy, in contrast, is the conscious ability to understand and share someone else's emotional experience by mentally and emotionally placing oneself in their situation. Defining emotional mirroring highlights its role as an automatic, neurobiological process distinct from empathy's deliberate cognitive and affective components.
What is Empathy?
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person by mentally and emotionally placing oneself in their situation. Unlike emotional mirroring, which involves automatically reflecting another's emotions through nonverbal cues, empathy requires conscious recognition and cognitive processing of those emotions. This distinction highlights empathy as a complex, active process essential for effective social connection and emotional support.
Key Differences Between Emotional Mirroring and Empathy
Emotional mirroring involves directly reflecting another person's emotions, often through facial expressions or body language, enabling immediate emotional connection. Empathy goes deeper by understanding and sharing the feelings of others, allowing You to genuinely grasp their emotional experience. The key difference lies in emotional mirroring being a spontaneous, surface-level response, while empathy requires conscious emotional engagement and cognitive understanding.
The Psychology Behind Emotional Mirroring
Emotional mirroring involves subconsciously reflecting another person's emotions through facial expressions and body language, playing a crucial role in social bonding and nonverbal communication. Empathy, by contrast, is the conscious ability to understand and share another person's feelings, engaging higher brain functions like the prefrontal cortex. The psychology behind emotional mirroring centers on mirror neurons, specialized brain cells that activate both when experiencing an emotion and when observing it in others, facilitating emotional resonance and social connectedness.
How Empathy Works in Human Interaction
Empathy works by allowing you to understand and share the feelings of others, creating a genuine emotional connection that fosters trust and effective communication. Emotional mirroring involves automatically reflecting another person's emotions and expressions, which can help validate their experience but may lack the deeper understanding offered by empathy. Unlike empathy, emotional mirroring is often subconscious and focused on observable behaviors rather than the internal emotional state, making empathy essential for meaningful human interaction.
Emotional Mirroring in Relationships
Emotional mirroring in relationships involves reflecting a partner's emotions accurately, creating a sense of understanding and validation that strengthens emotional bonds. Unlike empathy, which entails feeling or imagining another person's emotions, emotional mirroring specifically focuses on visibly matching or echoing those emotions to enhance connection and trust. This practice helps partners feel seen and heard, fostering deeper intimacy and improving communication within the relationship.
Empathy’s Role in Conflict Resolution
Empathy plays a crucial role in conflict resolution by enabling individuals to understand and share the feelings of others, fostering mutual respect and reducing hostility. Unlike emotional mirroring, which involves reflecting another's emotions, empathy goes deeper by actively engaging with and validating those emotions to promote constructive dialogue. This empathetic approach helps de-escalate conflicts and builds stronger interpersonal connections.
Potential Pitfalls of Emotional Mirroring
Emotional mirroring involves reflecting another person's emotions non-verbally to create connection, but it can lead to misunderstandings if the mirrored feelings are misinterpreted or amplified inaccurately, causing emotional contagion. Empathy goes beyond mirroring by involving cognitive understanding and emotional resonance, allowing for more accurate emotional support without necessarily replicating the other's feelings. Relying solely on emotional mirroring risks confusing sympathy with empathy, which may hinder effective communication and emotional regulation in interpersonal relationships.
Cultivating Healthy Empathy Over Mirroring
Cultivating healthy empathy involves recognizing and understanding another person's emotions without automatically reflecting or adopting them, unlike emotional mirroring which directly echoes those feelings. Empathy encourages emotional boundaries that prevent emotional exhaustion and maintain personal well-being while fostering genuine connection. Developing this skill supports emotional intelligence, promotes compassionate interactions, and enhances mental resilience in interpersonal relationships.
Infographic: Emotional mirroring vs Empathy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com