Reappraisal involves changing the interpretation of a situation to alter emotional impact, while mindfulness emphasizes non-judgmental awareness of present experiences to manage relationship stress. Explore this article to uncover how these techniques can transform your connections.
Table of Comparison
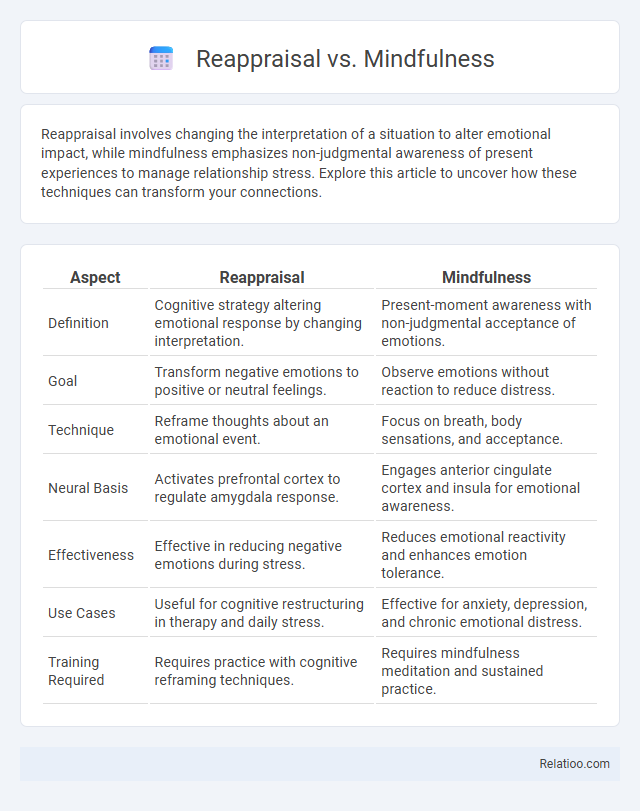
| Aspect | Reappraisal | Mindfulness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cognitive strategy altering emotional response by changing interpretation. | Present-moment awareness with non-judgmental acceptance of emotions. |
| Goal | Transform negative emotions to positive or neutral feelings. | Observe emotions without reaction to reduce distress. |
| Technique | Reframe thoughts about an emotional event. | Focus on breath, body sensations, and acceptance. |
| Neural Basis | Activates prefrontal cortex to regulate amygdala response. | Engages anterior cingulate cortex and insula for emotional awareness. |
| Effectiveness | Effective in reducing negative emotions during stress. | Reduces emotional reactivity and enhances emotion tolerance. |
| Use Cases | Useful for cognitive restructuring in therapy and daily stress. | Effective for anxiety, depression, and chronic emotional distress. |
| Training Required | Requires practice with cognitive reframing techniques. | Requires mindfulness meditation and sustained practice. |
Introduction to Reappraisal and Mindfulness
Reappraisal involves changing the way you interpret a situation to alter its emotional impact, promoting adaptive emotional regulation and reducing negative feelings. Mindfulness emphasizes non-judgmental awareness of the present moment, encouraging acceptance of thoughts and emotions without trying to change them. Understanding these distinct strategies enhances your ability to manage stress and improve psychological resilience effectively.
Defining Reappraisal: Concepts and Techniques
Reappraisal involves cognitively restructuring the meaning of an emotional stimulus to alter its impact, using techniques such as distancing or reinterpretation to shift perspective. Mindfulness emphasizes non-judgmental awareness of the present moment, allowing emotional experiences to be observed without immediate reaction. Your effective emotion regulation can benefit from reappraisal by actively changing thought patterns rather than solely focusing on awareness as in mindfulness.
Understanding Mindfulness: Core Principles
Mindfulness centers on present-moment awareness and non-judgmental observation of thoughts and feelings, fostering emotional regulation and stress reduction. Unlike cognitive reappraisal, which involves actively changing the interpretation of a situation, mindfulness encourages accepting experiences as they are, enhancing your ability to respond rather than react. This core principle supports resilience by cultivating a balanced mental state and improving overall well-being.
Key Differences Between Reappraisal and Mindfulness
Reappraisal involves actively changing the interpretation of events to alter emotional responses, while mindfulness centers on non-judgmental awareness of the present moment without attempting to change thoughts or feelings. Reappraisal engages cognitive control processes to regulate emotions, whereas mindfulness fosters acceptance and reduces reactivity by observing experiences as they are. These distinctions highlight reappraisal as an emotion regulation strategy aimed at reframing, contrasted with mindfulness's emphasis on experiential awareness and emotional acceptance.
Psychological Benefits of Reappraisal
Reappraisal, a cognitive emotion regulation strategy, effectively reduces negative emotions by changing the interpretation of a situation, leading to improved psychological well-being, reduced stress, and decreased symptoms of anxiety and depression. Unlike mindfulness, which emphasizes non-judgmental awareness of the present moment, reappraisal actively modifies emotional responses, enhancing cognitive control and resilience. Studies show reappraisal increases positive affect and adaptive coping mechanisms, contributing to long-term emotional health.
Emotional Advantages of Mindfulness Practice
Mindfulness practice enhances emotional regulation by promoting non-judgmental awareness of present experiences, reducing emotional reactivity more effectively than reappraisal techniques. Unlike reappraisal, which involves actively changing the interpretation of a situation, mindfulness fosters acceptance and reduces stress through sustained attention and detachment. Your emotional resilience improves as mindfulness supports greater self-compassion and decreases negative affect, leading to lasting emotional benefits.
Scientific Evidence: Effectiveness of Each Approach
Scientific evidence indicates that reappraisal effectively reduces negative emotions by changing cognitive interpretations of stressors, leading to improved emotional regulation and mental health outcomes. Mindfulness enhances present-moment awareness and acceptance, decreasing rumination and stress through neural changes in brain regions linked to attention and emotion control. Comparative studies reveal that combining reappraisal with mindfulness produces synergistic benefits, maximizing emotional resilience and cognitive flexibility in diverse populations.
When to Use Reappraisal vs Mindfulness
When to use reappraisal versus mindfulness depends on your goal in managing emotions: reappraisal is effective when you need to reinterpret a stressful situation to reduce negative emotions and increase positive outcomes, while mindfulness helps by promoting non-judgmental awareness of present experiences and acceptance. If you want to change your emotional response by altering your thoughts, reappraisal is best; if you aim to observe emotions without reacting or suppressing them, mindfulness is preferred. Your choice between these strategies impacts emotional regulation techniques tailored to immediate cognitive reframing or sustained emotional acceptance.
Combining Reappraisal and Mindfulness for Emotional Regulation
Combining reappraisal and mindfulness enhances emotional regulation by integrating cognitive reframing with present-moment awareness, enabling individuals to reinterpret negative experiences while maintaining non-judgmental acceptance. Research shows this synergy reduces stress and improves adaptive coping by promoting flexible emotional responses and reducing rumination. Neuroimaging studies reveal heightened activity in prefrontal cortex regions responsible for cognitive control during combined practice, supporting greater emotional resilience.
Practical Tips for Integrating Both Into Daily Life
Combining reappraisal and mindfulness enhances emotional regulation by encouraging awareness of present experiences while consciously reframing negative thoughts. Practical tips include setting daily reminders for mindfulness meditation and journaling cognitive reappraisals to identify and alter unhelpful thought patterns. Consistent practice of both methods fosters resilience, reduces stress, and promotes a balanced emotional response in everyday situations.
Infographic: Reappraisal vs Mindfulness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com