Chronic anger suppression often leads to increased stress and health problems, while healthy anger expression can improve communication and emotional well-being. Discover effective strategies for balancing anger management in this article.
Table of Comparison
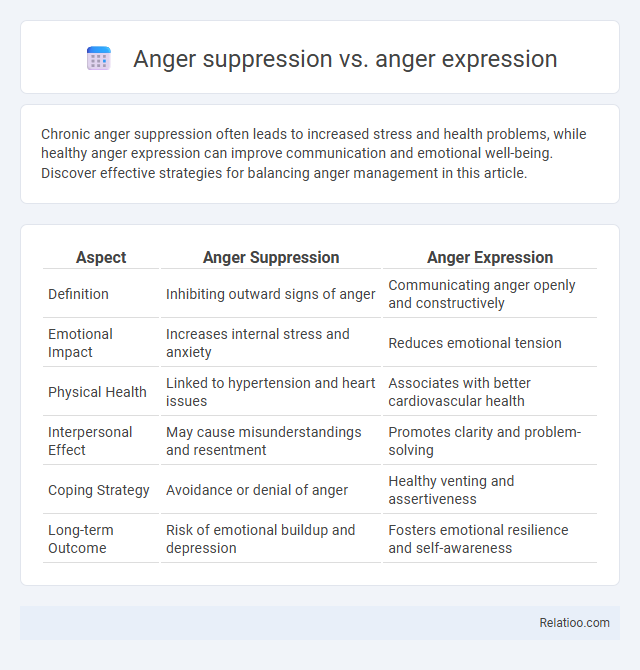
| Aspect | Anger Suppression | Anger Expression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inhibiting outward signs of anger | Communicating anger openly and constructively |
| Emotional Impact | Increases internal stress and anxiety | Reduces emotional tension |
| Physical Health | Linked to hypertension and heart issues | Associates with better cardiovascular health |
| Interpersonal Effect | May cause misunderstandings and resentment | Promotes clarity and problem-solving |
| Coping Strategy | Avoidance or denial of anger | Healthy venting and assertiveness |
| Long-term Outcome | Risk of emotional buildup and depression | Fosters emotional resilience and self-awareness |
Understanding Anger: Suppression vs. Expression
Anger suppression involves consciously inhibiting the outward display of anger, which can lead to increased internal stress, elevated blood pressure, and potential health risks. In contrast, anger expression allows individuals to communicate their feelings openly, which can promote emotional release and improve interpersonal relationships when done constructively. Effective anger management balances these approaches by recognizing triggers, implementing coping strategies, and fostering healthy expression to reduce negative psychological and physiological impacts.
Psychological Effects of Suppressing Anger
Suppressing anger is linked to increased physiological stress, elevated blood pressure, and greater risk of cardiovascular disease due to the body's prolonged fight-or-flight response. Psychological effects include heightened anxiety, depression, and impaired emotional regulation, which can exacerbate interpersonal conflicts and reduce overall well-being. In contrast, healthy anger expression and anger management strategies promote emotional balance, reduce stress-related health risks, and improve psychological resilience.
Health Consequences of Expressing Anger
Expressing anger openly can lead to elevated blood pressure, increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, and heightened stress hormone levels, negatively impacting heart health over time. Conversely, suppressing anger may cause internalized stress, contributing to anxiety, depression, and weakened immune function. Effective anger management techniques balance healthy expression and regulation, reducing physical health risks while improving psychological well-being.
Anger Suppression: Short-term Relief, Long-term Harm?
Anger suppression offers short-term relief by temporarily avoiding confrontation or emotional discomfort, but it often leads to long-term harm such as increased stress, anxiety, and physical health problems like hypertension. Expressing anger constructively allows you to address underlying issues and improve communication, while effective anger management techniques help regulate emotional responses without harm. Your ability to balance anger expression with healthy coping strategies determines the overall impact on mental and physical well-being.
Anger Expression: Constructive vs. Destructive Approaches
Anger expression involves conveying emotions either constructively, by using assertive communication and problem-solving techniques, or destructively, through aggression, passive-aggressiveness, or hostility. Constructive anger expression promotes emotional health, reduces stress, and fosters positive relationships, while destructive expression often escalates conflicts and damages mental well-being. Understanding and practicing constructive anger expression is crucial for effective anger management and improving interpersonal dynamics.
Cultural Perspectives on Anger Management
Cultural perspectives on anger management significantly influence how individuals suppress, express, or control anger, shaping social norms and acceptable behaviors. In collectivist societies, anger suppression is often encouraged to maintain group harmony, while individualistic cultures may promote controlled expression as a form of assertiveness. Understanding your cultural background helps tailor anger management techniques that respect cultural values while promoting emotional well-being.
Emotional Regulation: Finding a Healthy Balance
Anger suppression involves inhibiting emotional responses, which can lead to increased stress and negative health outcomes if chronic. Anger expression allows for releasing feelings but requires control to avoid aggression or harm in relationships. Effective anger management integrates emotional regulation strategies to balance expressing emotions healthily while avoiding suppression, promoting mental well-being and interpersonal harmony.
Coping Strategies for Managing Anger
Effective coping strategies for managing anger involve balancing anger suppression and anger expression to promote emotional health. Suppressing anger can lead to increased stress and physical tension, while expressing anger constructively helps release emotional energy and fosters better communication. Your ability to recognize triggers, practice relaxation techniques, and employ assertive communication enhances anger management for healthier interpersonal relationships.
The Role of Therapy in Anger Control
Therapy plays a critical role in distinguishing between anger suppression, anger expression, and anger management by helping You recognize unhealthy patterns and develop healthier emotional responses. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) enable individuals to process anger constructively, reducing the risks associated with suppression and uncontrolled expression. Effective anger management therapy improves emotional regulation skills, enhances self-awareness, and fosters communication strategies that promote balanced and controlled anger expression.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Path for Anger Management
Understanding the differences between anger suppression, anger expression, and anger management is crucial for emotional health. Suppressing anger can lead to internal stress and health issues, while unregulated anger expression may harm relationships. Your best path lies in mastering anger management techniques that promote healthy expression and emotional regulation, fostering both personal well-being and positive social interactions.
Infographic: Anger suppression vs Anger expression
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com