Shared responsibility in relationships promotes mutual support, better communication, and balanced decision-making, while sole responsibility often leads to stress and imbalance. Discover practical strategies to navigate these dynamics effectively in this article.
Table of Comparison
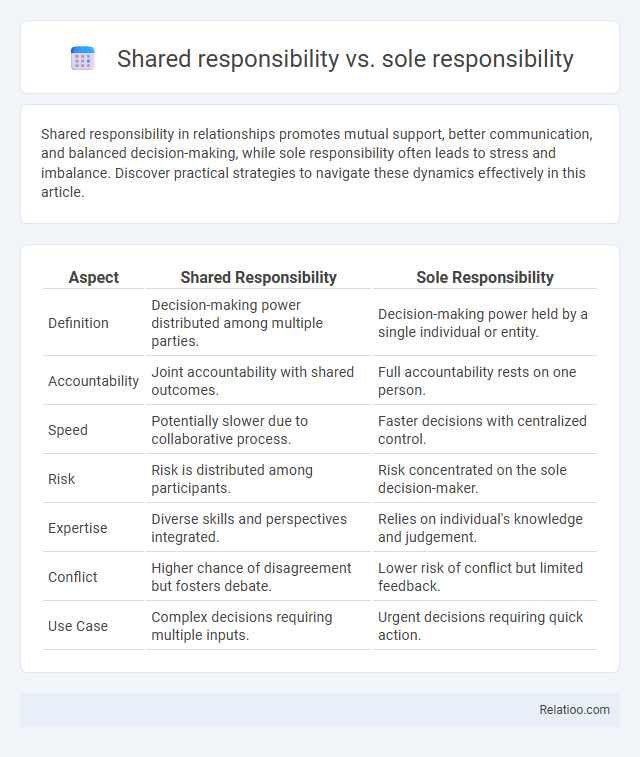
| Aspect | Shared Responsibility | Sole Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decision-making power distributed among multiple parties. | Decision-making power held by a single individual or entity. |
| Accountability | Joint accountability with shared outcomes. | Full accountability rests on one person. |
| Speed | Potentially slower due to collaborative process. | Faster decisions with centralized control. |
| Risk | Risk is distributed among participants. | Risk concentrated on the sole decision-maker. |
| Expertise | Diverse skills and perspectives integrated. | Relies on individual's knowledge and judgement. |
| Conflict | Higher chance of disagreement but fosters debate. | Lower risk of conflict but limited feedback. |
| Use Case | Complex decisions requiring multiple inputs. | Urgent decisions requiring quick action. |
Introduction to Shared vs Sole Responsibility
Shared responsibility involves multiple parties collaboratively managing tasks and accountability, enhancing resource pooling and diverse expertise application. Sole responsibility assigns full accountability and decision-making authority to one entity, ensuring clear ownership but potentially limiting flexibility. Understanding the distinction between shared and sole responsibility is crucial for effective organizational governance and project management strategies.
Defining Shared Responsibility
Shared responsibility involves multiple parties collaboratively managing tasks and obligations, ensuring accountability is distributed according to each entity's role and capacity. This contrasts with sole responsibility, where a single individual or organization bears full accountability, and interdependency, which emphasizes mutual reliance without necessarily shared accountability. Defining shared responsibility requires clarity on each participant's duties and the mechanisms for coordination and joint decision-making.
Understanding Sole Responsibility
Sole responsibility involves a single individual or entity being fully accountable for a task or outcome, ensuring clear ownership and decision-making authority. Unlike shared responsibility or interdependency, which distribute duties among multiple parties, sole responsibility centralizes accountability, eliminating ambiguity in roles. Understanding sole responsibility helps you clearly identify who must take action and bear the consequences in critical projects or situations.
Key Differences Between Shared and Sole Responsibility
Shared responsibility involves multiple parties collaboratively managing tasks or obligations, promoting teamwork and distributed accountability. Sole responsibility assigns full ownership of a task or decision to a single individual, ensuring clear accountability but limiting collaborative input. Your choice between shared and sole responsibility impacts decision-making processes, resource allocation, and overall project outcomes significantly.
Advantages of Shared Responsibility
Shared responsibility enhances collaboration, distributing tasks and resources among team members to improve efficiency and innovation. It fosters accountability by encouraging collective ownership, reducing the risk of errors and increasing problem-solving capacity. This approach also promotes transparency and trust, enabling diverse perspectives to contribute to balanced decision-making and better outcomes.
Benefits and Challenges of Sole Responsibility
Sole responsibility offers clear accountability and swift decision-making, as You have full control over outcomes without the need for consensus, enhancing efficiency and personal growth. However, the challenge lies in the increased pressure and risk, since all consequences rest solely on Your shoulders, potentially leading to burnout or oversight. Balancing these responsibilities requires strong self-management skills and resilience to leverage the benefits while mitigating the inherent risks.
Real-world Examples of Shared Responsibility
Shared responsibility occurs when multiple parties collaboratively manage tasks, such as in healthcare where doctors, nurses, and specialists coordinate patient care to ensure optimal outcomes. In environmental protection, governments, corporations, and individuals share responsibilities by implementing policies, adopting sustainable practices, and promoting awareness to combat climate change. Interdependency creates a system where each party's actions affect the others, differentiating it from sole responsibility, which assigns an individual or entity exclusive accountability for outcomes and decision-making.
Scenarios Where Sole Responsibility Works Best
Sole responsibility works best in scenarios where decision-making speed and clear accountability are critical, such as in emergency response or high-stakes project leadership. Your ability to act quickly without needing consensus ensures efficiency and reduces potential conflicts. This model thrives when tasks are well-defined and require specialized expertise, minimizing confusion and maximizing control.
Impact on Team Performance and Collaboration
Shared responsibility fosters enhanced team performance by encouraging collaboration and mutual accountability, enabling Your team to leverage diverse skills effectively. Sole responsibility can streamline decision-making but may limit input and reduce overall team engagement, potentially hindering collaborative efforts. Interdependency strengthens collaboration through coordinated roles and trust, driving higher productivity and innovation across the team.
Choosing the Right Responsibility Model
Choosing the right responsibility model depends on the project's complexity and your team's capabilities, with shared responsibility promoting collaboration and risk distribution among stakeholders. Sole responsibility assigns clear accountability to a single party, enhancing control but increasing individual burden and risk. Interdependency balances both by fostering cooperation while maintaining distinct roles, ensuring efficient task execution aligned with your goals.
Infographic: Shared responsibility vs Sole responsibility
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com