Shared ownership allows multiple parties to co-manage assets, distributing responsibilities and benefits, while sole ownership grants complete control and singular accountability to one individual. Explore the advantages and challenges of both shared and sole ownership models in this article.
Table of Comparison
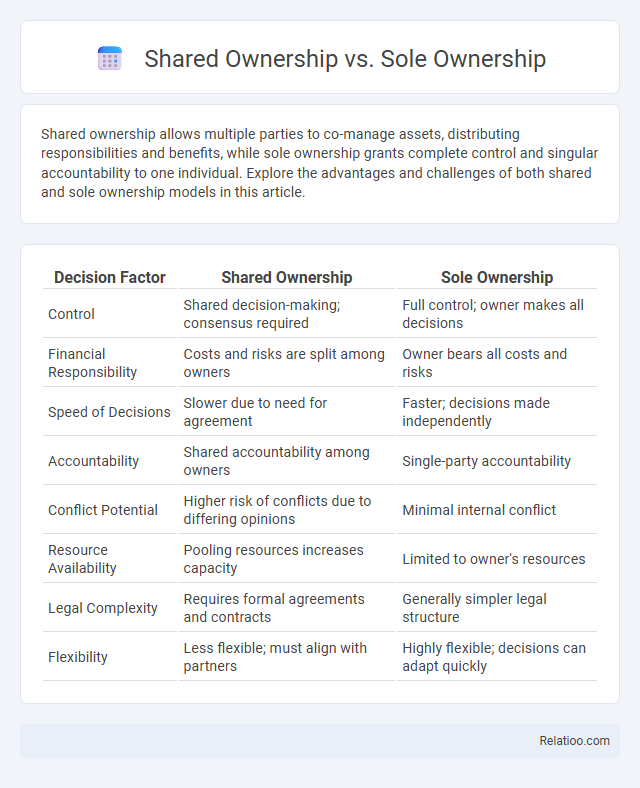
| Decision Factor | Shared Ownership | Sole Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Shared decision-making; consensus required | Full control; owner makes all decisions |
| Financial Responsibility | Costs and risks are split among owners | Owner bears all costs and risks |
| Speed of Decisions | Slower due to need for agreement | Faster; decisions made independently |
| Accountability | Shared accountability among owners | Single-party accountability |
| Conflict Potential | Higher risk of conflicts due to differing opinions | Minimal internal conflict |
| Resource Availability | Pooling resources increases capacity | Limited to owner's resources |
| Legal Complexity | Requires formal agreements and contracts | Generally simpler legal structure |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; must align with partners | Highly flexible; decisions can adapt quickly |
Introduction to Property Ownership Models
Property ownership models determine your legal rights and responsibilities regarding real estate assets. Shared ownership involves multiple parties holding title to a property, which allows you to share costs and benefits but requires joint decision-making. Sole ownership grants exclusive control and responsibility to one individual, while general ownership refers to any recognized legal claim or interest in property under local laws.
Defining Shared Ownership
Shared ownership involves multiple individuals or entities holding legal rights and responsibilities over a property, enabling shared decision-making and financial contributions. Sole ownership grants exclusive control and full liability to a single person, providing complete autonomy over the asset. Understanding shared ownership is crucial for real estate investors and co-owners to navigate complexities in rights, responsibilities, and profit distribution.
Understanding Sole Ownership
Sole ownership refers to a property being owned entirely by one individual, granting full control over decisions, use, and transfer of the asset without requiring consent from others. This form of ownership simplifies legal responsibilities and liabilities since the sole owner assumes all risks and benefits associated with the property. Understanding sole ownership is crucial for individuals seeking complete autonomy in managing real estate or other assets without joint obligations.
Key Differences Between Shared and Sole Ownership
Shared ownership involves multiple individuals holding legal rights to a property, each with an undivided interest, whereas sole ownership grants full control and responsibility to a single owner. In shared ownership, decisions and profits require consensus or predefined agreements, contrasting with sole ownership where the individual makes unilateral decisions. Liability and financial obligations differ notably: shared owners share costs and risks proportionally, while sole owners bear all expenses and risks independently.
Financial Implications of Shared vs Sole Ownership
Shared ownership divides financial responsibility and risk between co-owners, reducing your initial investment but potentially limiting control and profit share. Sole ownership requires full financial commitment, offering complete control over assets and profits while exposing you to all financial risks. Understanding these differences helps optimize your investment strategy based on risk tolerance and capital availability.
Legal Responsibilities and Rights
Shared ownership involves multiple parties holding legal rights to the property, each responsible for a proportionate share of obligations such as mortgage payments and maintenance, while your decisions often require consensus. Sole ownership grants a single individual full legal rights and responsibilities, providing complete control but also bearing the entire burden of liabilities and financial duties. Ownership rights define the legal ability to use, sell, lease, or transfer the property, with responsibilities varying according to the ownership structure and local laws.
Pros and Cons of Shared Ownership
Shared ownership allows multiple individuals to hold property rights, reducing individual financial burden and increasing purchasing power, which can make property more accessible for You. However, shared ownership can lead to complications in decision-making, potential conflicts among owners, and difficulties in selling or transferring shares. Sole ownership provides full control and streamlined decision processes, but places all financial responsibility and risk on a single person, while the general concept of ownership defines legal rights and responsibilities regardless of the structure.
Pros and Cons of Sole Ownership
Sole ownership offers complete control and decision-making power, allowing for quick and independent management of assets without the need for consensus. It also simplifies tax reporting and reduces conflicts since there is only one owner responsible for liabilities and benefits. However, the sole owner bears full financial risk and liability, which can lead to personal asset exposure and potential difficulties in raising capital compared to shared or joint ownership structures.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Shared or Sole Ownership?
Shared ownership suits individuals seeking collaborative decision-making, risk distribution, and shared financial responsibility, such as business partners or family members. Sole ownership benefits those desiring full control, simplicity in management, and complete profit retention, often ideal for solo entrepreneurs or personal property holders. Choosing between shared and sole ownership depends on the need for control, risk tolerance, and the nature of the investment or asset involved.
Conclusion: Making the Right Ownership Choice
Choosing the right ownership structure depends on Your financial goals, risk tolerance, and management preferences. Shared ownership offers collaborative decision-making and risk-sharing, while sole ownership grants full control and simplicity but also full liability. Evaluating these factors ensures the ownership model aligns with Your long-term business or property objectives.
Infographic: Shared Ownership vs Sole Ownership
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com