Honor culture emphasizes respect, reputation, and social standing as central to personal identity, often linked with close-knit communities and collective values. Western culture prioritizes individualism, personal freedom, and self-expression, shaping relational dynamics through autonomy and personal choice; explore the nuanced contrasts in this article.
Table of Comparison
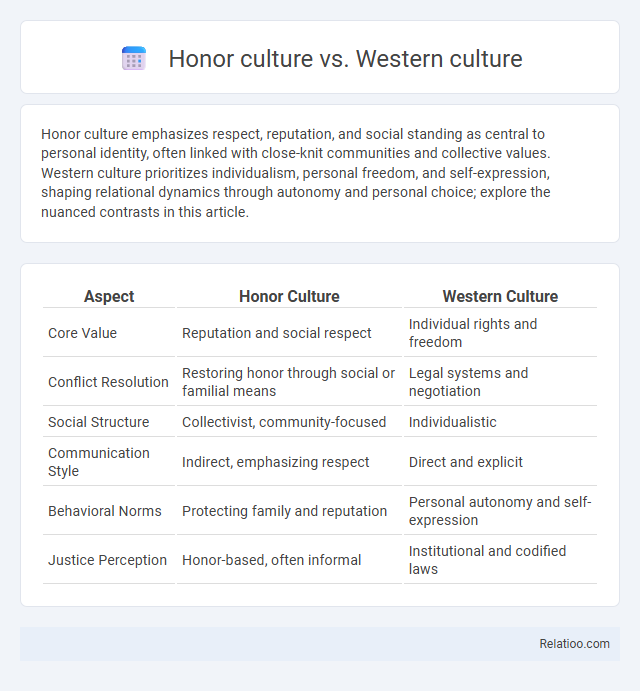
| Aspect | Honor Culture | Western Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Core Value | Reputation and social respect | Individual rights and freedom |
| Conflict Resolution | Restoring honor through social or familial means | Legal systems and negotiation |
| Social Structure | Collectivist, community-focused | Individualistic |
| Communication Style | Indirect, emphasizing respect | Direct and explicit |
| Behavioral Norms | Protecting family and reputation | Personal autonomy and self-expression |
| Justice Perception | Honor-based, often informal | Institutional and codified laws |
Understanding Honor Culture: Key Characteristics
Honor culture emphasizes reputation, family loyalty, and social status, where personal and collective honor dictate behavior and conflict resolution. Western culture generally prioritizes individualism, personal freedom, and legal justice over social reputation in defining moral conduct. Understanding honor culture involves recognizing its reliance on indirect communication, strong community ties, and the importance of restoring honor through social rituals and reparations.
Foundations of Western Culture: Core Values
Western culture is fundamentally built on individualism, rationalism, and the rule of law, emphasizing personal freedom and equality before the law, contrasting with honor cultures that prioritize reputation, social hierarchy, and collective loyalty. Your understanding of Western culture's core values--including democracy, human rights, and secular governance--highlights the focus on individual responsibility and ethical universalism. These principles shape social interactions differently from honor cultures, where social standing and respect are maintained through public recognition and adherence to traditional codes.
Social Structures and Community Roles
Honor culture emphasizes reputation and collective responsibility, where social status and family honor dictate behavior and community roles, often leading to strong kinship ties and rigid social hierarchies. Western culture prioritizes individualism and personal achievement, fostering social structures centered around individual rights, legal equality, and merit-based status. Honor cultures rely on communal enforcement of norms through social sanctions, while Western cultures emphasize institutional mechanisms and personal autonomy within community interactions.
Conflict Resolution: Shame vs. Guilt Approaches
Honor cultures emphasize conflict resolution through shame, aiming to protect social reputation and family honor by encouraging public apologies and reparations. Western cultures prioritize guilt-based approaches, focusing on individual responsibility and internal moral reflection to resolve disputes and foster reconciliation. The clash between these methods can create misunderstandings in cross-cultural interactions, as shame fosters external social enforcement while guilt promotes internal ethical change.
Family Dynamics in Honor and Western Cultures
Family dynamics in honor culture emphasize collective reputation, with loyalty, respect, and obedience to elders shaping daily interactions and decisions. Western culture prioritizes individualism, encouraging open communication and personal freedom within family roles. Understanding your family's cultural background can enhance appreciation for these differing values and improve intergenerational relationships.
Gender Roles and Expectations
Honor culture often emphasizes strict gender roles where men are expected to uphold family honor through protection and authority, while women are tasked with maintaining chastity and modesty to preserve reputation. Western culture generally promotes more egalitarian gender expectations, encouraging individual freedom and equality regardless of gender. Your understanding of these cultural differences is crucial for navigating social interactions and expectations in diverse environments.
The Role of Reputation and Social Standing
Reputation and social standing are pivotal in Honor culture, where maintaining personal and family honor influences social interactions, decision-making, and conflict resolution. Western culture often emphasizes individual achievement and personal integrity, with social standing tied to professional success and adherence to societal norms. Your understanding of these dynamics helps navigate cross-cultural relationships, recognizing that in Honor cultures, social reputation carries collective importance, whereas Western culture prioritizes individual reputation and merit.
Honor-Based Violence vs. Legal Justice
Honor culture prioritizes family reputation and social standing, often resorting to Honor-Based Violence as a method of resolving conflicts internally, bypassing formal legal systems. Western culture emphasizes individual rights and legal justice, promoting state intervention to address crimes and protect victims regardless of social or familial ties. Understanding these differences is crucial for navigating conflicts where Your safety and legal rights may be challenged by deeply ingrained honor norms.
Adaptation in a Globalized World
Honor cultures prioritize reputation, family, and social standing, influencing behavior through community-driven norms, while Western cultures emphasize individualism, legal systems, and personal achievement. Adaptation in a globalized world requires balancing these contrasting values, fostering mutual respect and effective communication across cultural boundaries. Successful cross-cultural adaptation hinges on recognizing honor culture's emphasis on relational ties alongside Western culture's focus on autonomy and rule-based interactions.
Bridging Gaps: Towards Cultural Understanding
Honor culture emphasizes reputation, family loyalty, and social hierarchy, often valuing collective honor over individual expression, while Western culture prioritizes individual rights, personal achievement, and direct communication. Bridging gaps between these cultures requires fostering empathy, recognizing the underlying values that shape behavior, and employing culturally sensitive dialogue strategies to prevent misunderstandings. Effective intercultural communication hinges on appreciating differences in conflict resolution, respect norms, and social expectations to build mutual trust and cooperation.
Infographic: Honor culture vs Western culture
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com