Ancestor worship centers on honoring deceased family members through rituals, emphasizing lineage and familial bonds. Polytheism involves the belief in and worship of multiple gods, each governing different aspects of life and nature; explore their distinctions and cultural impacts in this article.
Table of Comparison
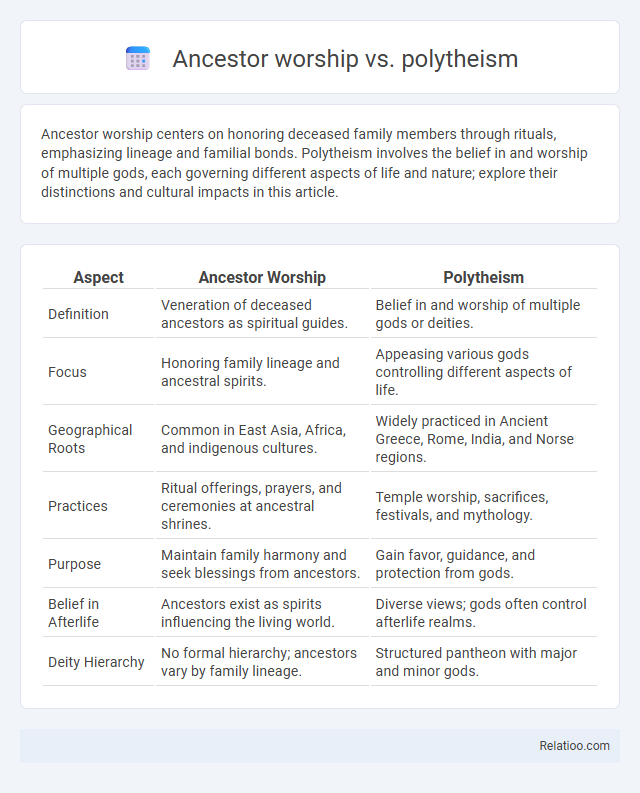
| Aspect | Ancestor Worship | Polytheism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Veneration of deceased ancestors as spiritual guides. | Belief in and worship of multiple gods or deities. |
| Focus | Honoring family lineage and ancestral spirits. | Appeasing various gods controlling different aspects of life. |
| Geographical Roots | Common in East Asia, Africa, and indigenous cultures. | Widely practiced in Ancient Greece, Rome, India, and Norse regions. |
| Practices | Ritual offerings, prayers, and ceremonies at ancestral shrines. | Temple worship, sacrifices, festivals, and mythology. |
| Purpose | Maintain family harmony and seek blessings from ancestors. | Gain favor, guidance, and protection from gods. |
| Belief in Afterlife | Ancestors exist as spirits influencing the living world. | Diverse views; gods often control afterlife realms. |
| Deity Hierarchy | No formal hierarchy; ancestors vary by family lineage. | Structured pantheon with major and minor gods. |
Understanding Ancestor Worship
Ancestor worship centers on honoring deceased forebears through rituals, offerings, and prayers to maintain familial bonds and seek guidance or protection from them. It differs from polytheism, which involves reverence for multiple gods with distinct personalities and domains, and from broader supernatural beliefs that include spirits, demons, or mystical forces beyond ancestral lineage. Understanding ancestor worship requires recognizing its role in cultural continuity, social cohesion, and moral framework within communities that emphasize lineage and filial piety.
Defining Polytheism
Polytheism is the belief system that recognizes and worships multiple gods or deities, each with distinct attributes, powers, and domains, distinguishing it from ancestor worship, which centers on venerating deceased forebears, and supernatural beliefs that encompass a broader range of spiritual or mystical entities beyond specific gods. Your understanding of polytheism involves acknowledging a complex pantheon where gods often personify natural forces, societal values, or cosmic principles. This belief shapes cultural rituals, mythologies, and religious structures, illustrating human attempts to explain and interact with the world through divine multiplicity.
Historical Roots of Ancestor Worship
Ancestor worship traces back to ancient agrarian societies where honoring forebears ensured protection and continuity of family lineage. Polytheism, involving the veneration of multiple deities, often coexisted with ancestor worship but emphasized divine beings beyond human ancestry. Your understanding of these beliefs highlights how ancestor worship uniquely centers on familial spirits, distinguishing it from broader supernatural belief systems rooted in deities and mystical forces.
Origins and Spread of Polytheism
Polytheism originated in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley, where multiple gods represented natural forces and societal roles, reflecting early human attempts to explain complex environments through diverse deities. Ancestor worship, prevalent in East Asia and Africa, centers on revering deceased forebears to maintain familial and social harmony, while supernatural beliefs encompass a broad spectrum of entities beyond gods, including spirits and magical forces, across many cultures. The spread of polytheism occurred through trade, conquest, and cultural exchange, evolving into complex pantheons that shaped art, politics, and religious practices across regions like Greece, Rome, and India.
Core Beliefs and Practices in Ancestor Worship
Ancestor worship centers on honoring deceased family members through rituals, offerings, and prayers to maintain a spiritual connection and seek guidance or protection. Core beliefs emphasize the continued influence of ancestors on your fate, well-being, and prosperity, with practices often involving ancestral altars, festivals, and memorial ceremonies. Unlike polytheism, which involves worshipping multiple deities, and broader supernatural beliefs that may include spirits or magical forces, ancestor worship specifically vests reverence in familial lineage and its ongoing spiritual presence.
Rituals and Deities in Polytheistic Traditions
Polytheistic traditions feature diverse rituals dedicated to multiple deities, each embodying specific aspects of nature or human experience, such as Zeus in Greek mythology or Vishnu in Hinduism. Rituals often include offerings, prayers, and festivals aimed at gaining favor or appeasing gods, reflecting a complex pantheon where deities interact with humans and each other. Ancestor worship centers on honoring familial spirits through rites that maintain lineage and protection, while supernatural beliefs encompass broader practices involving spirits or forces beyond polytheistic gods.
Social and Cultural Roles
Ancestor worship reinforces family bonds and social cohesion by honoring the lineage and maintaining a connection to past generations, serving as a moral guide within communities. Polytheism supports diverse cultural identities through a pantheon of gods representing various aspects of life and nature, influencing rituals, festivals, and societal values. Your understanding of supernatural beliefs reveals how these frameworks address existential questions and regulate social behavior, embedding spiritual significance into everyday cultural practices.
Ancestor Worship vs Polytheism: Key Differences
Ancestor worship centers on venerating deceased family members to maintain a spiritual connection, whereas polytheism involves believing in multiple gods with distinct roles and powers. Ancestor worship often emphasizes rituals and offerings to honor lineage and seek guidance, while polytheism includes diverse mythologies and deities governing natural and moral order. Your understanding of these differences helps clarify cultural practices and religious beliefs unique to various societies.
Modern Perspectives and Adaptations
Modern perspectives on ancestor worship emphasize its role in preserving cultural identity and fostering familial continuity, often integrating contemporary values with traditional rituals. Polytheism adapts by evolving its pantheon narratives to resonate with current social and environmental themes, reflecting humanity's diverse spiritual needs. Your understanding of supernatural belief shifts as these practices blend ancient reverence with modern interpretations, highlighting a dynamic interplay between faith, culture, and identity.
Influence on Contemporary Spirituality
Ancestor worship, polytheism, and supernatural beliefs each shape contemporary spirituality by influencing practices, rituals, and worldviews. Ancestor worship emphasizes reverence for familial lineage and guides ethical behavior through honoring predecessors, fostering community continuity. Polytheism introduces diverse deities representing natural and social forces, enriching spiritual narratives and offering multiple pathways for personal devotion, while supernatural beliefs broadly support faith in forces beyond empirical understanding, contributing to modern metaphysical and mystical explorations.
Infographic: Ancestor Worship vs Polytheism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com