Family-centered upbringing prioritizes collective values, emphasizing strong family bonds and shared responsibilities, while child-centered upbringing focuses on nurturing individual needs and personal growth of the child. Discover in this article how these contrasting approaches impact child development and family dynamics.
Table of Comparison
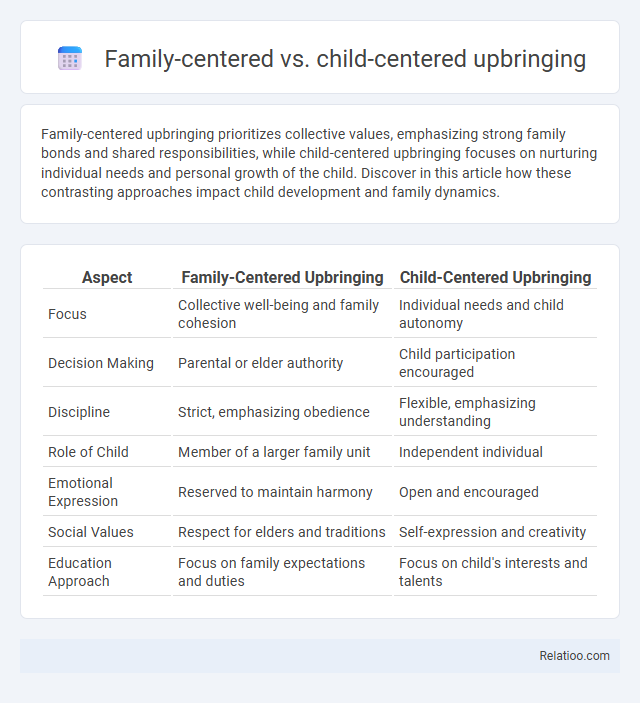
| Aspect | Family-Centered Upbringing | Child-Centered Upbringing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Collective well-being and family cohesion | Individual needs and child autonomy |
| Decision Making | Parental or elder authority | Child participation encouraged |
| Discipline | Strict, emphasizing obedience | Flexible, emphasizing understanding |
| Role of Child | Member of a larger family unit | Independent individual |
| Emotional Expression | Reserved to maintain harmony | Open and encouraged |
| Social Values | Respect for elders and traditions | Self-expression and creativity |
| Education Approach | Focus on family expectations and duties | Focus on child's interests and talents |
Introduction to Upbringing Approaches
Family-centered upbringing emphasizes collective decision-making and prioritizing the family unit's values and needs, fostering interdependence among members. Child-centered upbringing focuses on the individual child's development, autonomy, and personal interests, promoting self-expression and tailored support. Your choice between these approaches influences child-rearing practices, shaping how responsibilities, discipline, and nurturing are managed within the family context.
Defining Family-centered Upbringing
Family-centered upbringing emphasizes the collective needs, values, and roles of the entire family unit over individual preferences, fostering interdependence and shared responsibilities. This approach contrasts with child-centered upbringing, which prioritizes the child's autonomy, interests, and emotional development as central to parenting decisions. Child-rearing practices within a family-centered framework often involve collaborative decision-making, respect for extended family influence, and reinforcement of cultural traditions that support family cohesion.
Understanding Child-centered Upbringing
Understanding child-centered upbringing emphasizes the development of a child's individuality, autonomy, and emotional well-being by prioritizing their needs and preferences within the family dynamic. This approach contrasts with family-centered upbringing, which focuses on collective family values and roles, and traditional child-rearing practices that often emphasize obedience and structure. You can foster a child-centered upbringing by encouraging open communication, nurturing creativity, and supporting your child's unique personality and interests.
Core Values and Philosophies
Family-centered upbringing emphasizes collective well-being, prioritizing interdependence, respect for elders, and the transmission of cultural traditions as core values. Child-centered upbringing focuses on nurturing individual autonomy, creativity, and self-expression, fostering environments where children's interests and developmental needs are paramount. Child-rearing practices incorporate these philosophies through balanced approaches that promote both social responsibility within the family unit and the child's personal growth, adapting strategies to cultural and contextual factors.
Roles of Parents and Caregivers
Family-centered upbringing emphasizes the collective role of parents and caregivers in nurturing children's social, emotional, and cultural development, fostering strong family bonds. Child-centered upbringing prioritizes the child's individual needs, preferences, and autonomy, encouraging parents and caregivers to adapt their roles to support personalized growth and decision-making. Child-rearing practices involve specific strategies and routines by parents and caregivers to promote discipline, education, and well-being, balancing both family values and child-focused approaches to optimize developmental outcomes.
Impact on Child Development
Family-centered upbringing emphasizes collective decision-making and emotional support, fostering a strong sense of belonging and security that positively influences Your child's social and emotional development. Child-centered upbringing prioritizes the child's individuality and autonomy, encouraging self-expression and independence, which enhances cognitive growth and problem-solving skills. Child-rearing practices that balance these approaches promote holistic development by integrating emotional bonding with nurturing autonomy, resulting in well-rounded and resilient children.
Social and Emotional Outcomes
Family-centered upbringing emphasizes collective decision-making and nurturing supportive relationships, which fosters your child's sense of belonging and emotional security. Child-centered upbringing prioritizes the individual needs and autonomy of the child, promoting self-esteem and emotional intelligence through personalized attention. Child-rearing practices that balance both approaches tend to yield optimal social competence and emotional resilience in children, enhancing their ability to form healthy relationships and manage stress effectively.
Challenges and Criticisms
Family-centered upbringing often faces challenges related to balancing collective family values with individual child needs, which can limit personal autonomy and lead to emotional stress. Child-centered upbringing is criticized for fostering entitlement and insufficient discipline, as it prioritizes the child's preferences sometimes at the expense of broader family or societal expectations. Your choice between these practices must weigh the potential for over-dependence in family-centered models against the risk of underdeveloped resilience in child-centered approaches.
Cultural Influences on Upbringing Styles
Family-centered upbringing emphasizes collective decision-making and interdependence within the household, deeply rooted in cultures valuing communal harmony and respect for elders. Child-centered upbringing prioritizes the individual needs, autonomy, and emotional development of the child, often seen in Western societies that promote independence and self-expression. Your understanding of child-rearing practices can be enhanced by recognizing how cultural influences shape whether a family leans towards collective values or prioritizes the child's personal growth.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Family
Choosing the right approach for your family involves understanding the distinctions between family-centered, child-centered upbringing, and child-rearing practices. Family-centered upbringing emphasizes the roles and relationships within the entire family system, promoting collective decision-making and mutual support. Child-centered approaches prioritize the individual needs and development of the child, while child-rearing practices encompass specific strategies and routines tailored to nurture growth, discipline, and well-being, allowing families to balance these methods based on cultural values and individual child requirements.
Infographic: Family-centered vs Child-centered upbringing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com