Arranged marriages involve families selecting partners based on compatibility factors, while courtship allows individuals to choose partners through personal interaction and emotional connection. Explore the key differences and cultural impacts of arranged marriages versus courtship in this article.
Table of Comparison
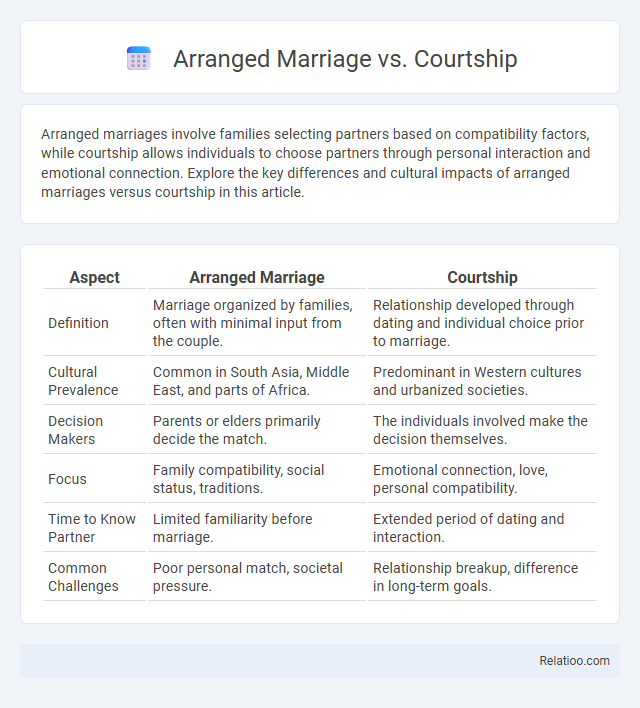
| Aspect | Arranged Marriage | Courtship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marriage organized by families, often with minimal input from the couple. | Relationship developed through dating and individual choice prior to marriage. |
| Cultural Prevalence | Common in South Asia, Middle East, and parts of Africa. | Predominant in Western cultures and urbanized societies. |
| Decision Makers | Parents or elders primarily decide the match. | The individuals involved make the decision themselves. |
| Focus | Family compatibility, social status, traditions. | Emotional connection, love, personal compatibility. |
| Time to Know Partner | Limited familiarity before marriage. | Extended period of dating and interaction. |
| Common Challenges | Poor personal match, societal pressure. | Relationship breakup, difference in long-term goals. |
Introduction to Arranged Marriage and Courtship
Arranged marriage is a traditional practice where families or matchmakers select partners based on social, cultural, and economic compatibility, often emphasizing family background and community values. Courtship involves individuals independently seeking romantic partners through dating and personal interactions, prioritizing emotional connection and individual choice. Both approaches reflect diverse cultural frameworks and social expectations in forming lifelong partnerships.
Historical Roots and Cultural Contexts
Arranged marriage has deep historical roots in many cultures, serving as a means to strengthen family alliances and social status, particularly in South Asia and the Middle East. Courtship, prevalent in Western societies, emerged as a practice emphasizing individual choice and romantic compatibility, evolving with changing social norms and increased personal autonomy. Your understanding of these marital traditions reflects the diverse cultural contexts that shape how relationships are formed across different societies.
Key Principles and Practices
Arranged marriage emphasizes family involvement and social compatibility, prioritizing factors like caste, religion, and economic status, while courtship centers on individual choice and mutual attraction developed over time. Arranged marriages follow traditional matchmaking practices and parental approval, contrasting with courtship's emphasis on personal interaction and emotional bonding before commitment. Both approaches aim for marital stability, but arranged marriage relies on structured social frameworks, whereas courtship depends on gradual relationship development and personal decision-making.
Decision-Making: Family vs. Individual Autonomy
Arranged marriage often involves family decision-making, where elders play a significant role in selecting a compatible partner based on cultural, religious, or social criteria. In contrast, courtship emphasizes individual autonomy, allowing you to make personal choices about your partner through mutual attraction and personal compatibility. Understanding these differences highlights the balance between respecting family input and exercising your own freedom in choosing a life partner.
Compatibility and Emotional Bonding
Arranged marriages often prioritize compatibility through family background, social status, and cultural alignment, creating a structured foundation for emotional bonding to develop over time. Courtship emphasizes personal choice and emotional connection before commitment, allowing couples to build a deep understanding and shared experiences prior to marriage. Hybrid models combine arranged compatibility factors with opportunities for emotional bonding, aiming to balance tradition and personal connection for long-term relationship success.
Social Stigma and Perceptions
Arranged marriage often faces social stigma due to stereotypes of lack of personal choice, while courtship is perceived as a process promoting romantic compatibility and individual autonomy. Courtship is commonly idealized in modern societies, emphasizing emotional connection and mutual consent, whereas arranged marriages may be viewed as traditional or restrictive despite their prevalence in various cultures. Social perceptions can shift with increasing intercultural understanding and recognition of diverse relationship dynamics beyond simplistic judgments.
Success Rates and Psychological Impacts
Arranged marriages often report higher long-term success rates due to familial support and shared cultural values, fostering stability and commitment. Courtship marriages tend to emphasize individual choice and emotional compatibility, which can lead to higher initial satisfaction but sometimes face challenges in long-term adjustment. Psychological impacts in arranged marriages may include lower relationship anxiety and higher social integration, while courtship marriages often show greater personal autonomy but increased risk of relationship uncertainty and stress.
Challenges and Common Misconceptions
Arranged marriages often face challenges related to limited personal choice and pressure from family expectations, while courtship emphasizes individual compatibility but can encounter misunderstandings about commitment and intentions. Common misconceptions about arranged marriages include assumptions of lack of love or freedom, whereas courtship is sometimes idealized as purely romantic without acknowledging practical challenges. Both approaches require clear communication and mutual respect to overcome societal stereotypes and build successful relationships.
Modern Trends and Evolving Attitudes
Modern trends in arranged marriage increasingly incorporate elements of courtship, where individuals are given more autonomy in partner selection, reflecting evolving attitudes toward personal choice and compatibility. Courtship emphasizes emotional connection and mutual consent, contrasting traditional arranged marriages that often prioritized family involvement and social alliances. The blending of these approaches highlights a shift towards hybrid models balancing cultural heritage with contemporary values of individualism and romantic affection.
Conclusion: Navigating Love and Tradition
Navigating love and tradition involves understanding that arranged marriages prioritize family involvement and cultural values, while courtship emphasizes personal choice and emotional connection. Your decision should balance respect for heritage with individual happiness, ensuring a relationship built on mutual understanding and trust. Both paths offer unique strengths that can lead to fulfilling partnerships when aligned with your personal beliefs and goals.
Infographic: Arranged marriage vs Courtship
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com