Extended families often experience complex in-law dynamics due to multiple generations living together, which can lead to both support and conflict. Nuclear families typically face simpler in-law relationships but may lack the broader support network found in extended families; explore this article to understand these differences in family dynamics.
Table of Comparison
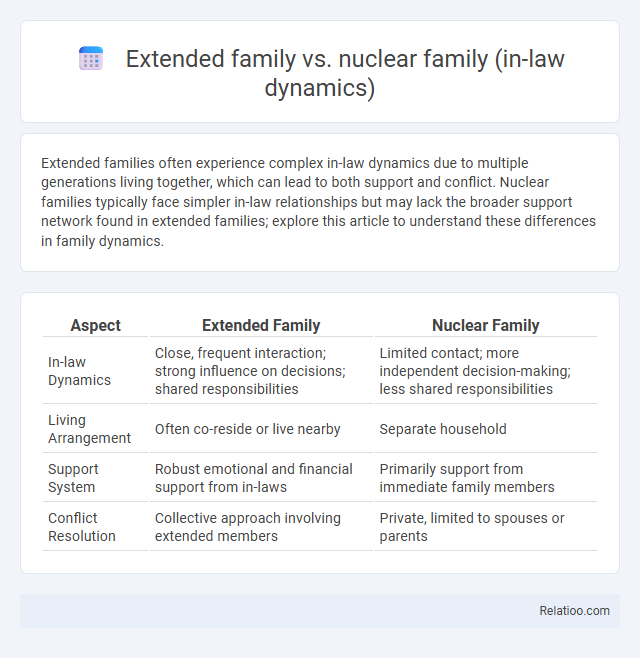
| Aspect | Extended Family | Nuclear Family |
|---|---|---|
| In-law Dynamics | Close, frequent interaction; strong influence on decisions; shared responsibilities | Limited contact; more independent decision-making; less shared responsibilities |
| Living Arrangement | Often co-reside or live nearby | Separate household |
| Support System | Robust emotional and financial support from in-laws | Primarily support from immediate family members |
| Conflict Resolution | Collective approach involving extended members | Private, limited to spouses or parents |
Understanding Extended Family and Nuclear Family Structures
Extended family structures include multiple generations living together or in close proximity, providing a rich network of support and shared responsibilities, while nuclear families consist of parents and their children living independently, emphasizing a more self-contained household dynamic. In-law relationships within extended families often involve complex, multi-generational interactions that require navigating diverse expectations and roles, whereas nuclear families typically experience simpler in-law dynamics with fewer family members directly involved. Understanding these family structures helps you manage in-law relationships effectively, fostering harmony by recognizing the distinct social and emotional frameworks at play.
Key Differences Between Extended and Nuclear Families
Extended families consist of multiple generations living together or in close proximity, fostering strong bonds and collective support among grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins, whereas nuclear families are typically composed of just parents and their children, emphasizing a more independent household structure. In-law dynamics often play a significant role in extended families, where relationships with parents-in-law and siblings-in-law are closely intertwined and influence daily interactions and decision-making. In contrast, nuclear families experience in-law relationships more distantly, often managing boundaries and autonomy with less frequent direct involvement.
The Role of In-Laws in Extended Families
In extended families, in-laws often play a crucial role in maintaining strong family bonds and facilitating support networks that benefit all members. Your relationship with in-laws in such settings typically influences household decision-making, child-rearing practices, and conflict resolution strategies. Understanding these dynamics helps foster mutual respect and cooperation, essential for the harmony and stability of the extended family unit.
In-Law Relationships in Nuclear Family Settings
In nuclear family settings, in-law relationships play a crucial role in shaping family dynamics and emotional support systems. These relationships often require active communication and boundary-setting to balance privacy with inclusion, especially when integrating spouses and managing expectations from parents-in-law. Effective management of in-law dynamics can enhance familial harmony and contribute to stronger, more resilient nuclear family bonds.
Cultural Perspectives on In-Law Dynamics
In-law dynamics vary significantly across cultural contexts, with extended families often emphasizing collective decision-making and strong intergenerational bonds, contrasting with nuclear families that prioritize privacy and autonomous family units. Cultural norms influence expectations around respect, communication, and conflict resolution between in-laws, impacting relationship quality and household harmony. Understanding these perspectives enhances cross-cultural empathy and facilitates healthier in-law interactions within diverse family structures.
Communication Challenges with In-Laws
Communication challenges with in-laws often arise from differing expectations and cultural norms between extended and nuclear family structures. In an extended family, frequent interactions can amplify misunderstandings, while nuclear families may face barriers due to limited contact and unclear boundaries. Your ability to navigate these dynamics relies on clear, respectful dialogue to bridge gaps and foster mutual understanding.
Conflict Resolution Strategies for In-Laws
In-law conflicts often arise in both extended and nuclear family structures due to differing expectations and boundaries, requiring effective communication and empathy for resolution. You can implement clear boundary-setting and active listening techniques to reduce misunderstandings and foster mutual respect. Prioritizing regular family meetings and mediation processes helps maintain harmony and strengthens in-law relationships across various family dynamics.
Impact of Family Structure on Marital Satisfaction
Extended family structures often provide a broad support network that can enhance marital satisfaction by sharing responsibilities and fostering cooperation, but may also introduce complex in-law dynamics that challenge privacy and autonomy. In contrast, nuclear families typically experience fewer in-law conflicts, promoting closer spouse bonding, though they might lack the extensive emotional support available in extended families. Understanding how your in-law relationships interact with your family structure can critically influence stress levels and overall happiness in marriage.
Emotional Boundaries with In-Laws
Emotional boundaries with in-laws differ significantly between extended and nuclear families, impacting your personal space and mental well-being. Extended families often involve closer, more frequent interactions, requiring clear communication to maintain emotional balance, while nuclear families may experience less direct in-law involvement but still need defined limits to avoid conflict. Respecting and establishing these boundaries helps foster healthy, respectful in-law relationships regardless of family structure.
Strengthening Healthy In-Law Relationships
Understanding the dynamics between extended and nuclear families is crucial for strengthening healthy in-law relationships. In extended families, regular interactions foster familiarity and support, whereas nuclear families may require deliberate effort to build these connections. You can enhance your in-law relationships by promoting open communication, respecting boundaries, and actively engaging in shared family traditions to create lasting bonds.
Infographic: Extended family vs Nuclear family (in-law dynamics)
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com