Christian beliefs emphasize love, forgiveness, and sacrificial commitment in relationships, rooted in teachings of Jesus Christ and biblical principles. Islamic beliefs highlight compassion, mutual respect, and defined roles based on the Quran and Hadith guidance. Discover more about these perspectives in this article.
Table of Comparison
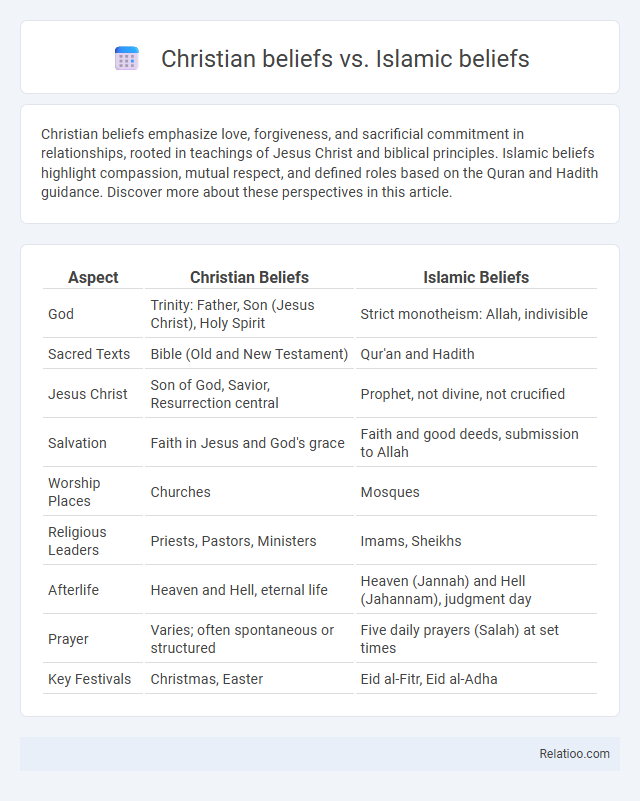
| Aspect | Christian Beliefs | Islamic Beliefs |
|---|---|---|
| God | Trinity: Father, Son (Jesus Christ), Holy Spirit | Strict monotheism: Allah, indivisible |
| Sacred Texts | Bible (Old and New Testament) | Qur'an and Hadith |
| Jesus Christ | Son of God, Savior, Resurrection central | Prophet, not divine, not crucified |
| Salvation | Faith in Jesus and God's grace | Faith and good deeds, submission to Allah |
| Worship Places | Churches | Mosques |
| Religious Leaders | Priests, Pastors, Ministers | Imams, Sheikhs |
| Afterlife | Heaven and Hell, eternal life | Heaven (Jannah) and Hell (Jahannam), judgment day |
| Prayer | Varies; often spontaneous or structured | Five daily prayers (Salah) at set times |
| Key Festivals | Christmas, Easter | Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha |
Introduction to Christian and Islamic Beliefs
Christian beliefs center on the divinity of Jesus Christ, salvation through faith, and the teachings of the Bible as the ultimate spiritual guide. Islamic beliefs emphasize the oneness of Allah, the prophethood of Muhammad, and adherence to the Quran and Hadith for moral and religious conduct. Your understanding of virginity may be influenced by these distinct religious frameworks, which shape cultural values and personal convictions differently.
Concept of God in Christianity vs Islam
Christianity centers on the belief in one God existing as a Trinity: Father, Son, and Holy Spirit, emphasizing Jesus Christ as the incarnate Son of God and the Savior of humanity. Islam strictly upholds the concept of Tawhid, the absolute oneness of Allah, rejecting any division or incarnation, and regards Muhammad as His final prophet. Both religions view God as omnipotent and merciful, yet differ significantly in the understanding of God's nature and revelation.
Holy Scriptures: Bible vs Quran
The Bible emphasizes virginity predominantly in the context of the Virgin Mary's purity and the call for sexual sins to be avoided, particularly in texts like 1 Corinthians 7 and Matthew 1. The Quran upholds virginity as a sign of chastity and purity, referencing virgins in both moral guidance for believers and descriptions of paradise, notably in Surah Al-Waqqi'ah and Surah An-Nahdiyah. Both scriptures underscore virginity's spiritual symbolism, but the Quran presents strict legal and ethical frameworks surrounding virginity and marriage, while the Bible often addresses it in terms of personal sanctity and divine purpose.
Jesus Christ: Son of God or Prophet?
Christian beliefs affirm Jesus Christ as the Son of God, emphasizing His divine nature and role in salvation, whereas Islamic beliefs regard Jesus (Isa) as a revered prophet and messenger, not divine but born of the Virgin Mary. The concept of virginity holds significance in both religions, highlighting purity and miraculous birth, yet interpretations differ on Jesus' identity and mission. Understanding these distinctions helps you appreciate the theological foundations shaping faith and doctrine in Christianity and Islam.
Salvation and Afterlife in Both Religions
Christian beliefs emphasize salvation through faith in Jesus Christ as the Son of God, with eternal life granted to those who accept Him, while virginity is often valued as a symbol of purity. Islamic beliefs center on submission to Allah's will and adherence to the Five Pillars, where salvation depends on both faith and righteous deeds, and virginity is associated with moral conduct and honor. Both religions teach distinct paths to the afterlife, with Christianity promising eternal heaven or hell based on grace and faith, and Islam outlining paradise or punishment determined by one's deeds and divine mercy.
Role of Prophets in Christianity and Islam
Christianity emphasizes Jesus Christ as the central prophet and Son of God, whose teachings shape the faith's moral values, including views on virginity symbolizing purity and divine grace. Islam reveres Muhammad as the final prophet, whose revelations in the Quran provide comprehensive guidelines on spirituality and social conduct, including the importance of modesty and chastity tied to virginity. Both religions regard prophets as divine messengers guiding believers toward ethical living, though their interpretations of virginity reflect distinct theological and cultural contexts.
Worship Practices: Church vs Mosque
Christian worship practices in churches often center around communal singing, prayer, and sermons focusing on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, while Islamic worship in mosques emphasizes the five daily prayers (Salah), recitation of the Quran, and the unity of the Ummah. Your understanding of spiritual discipline differs as churches typically conduct services on Sundays with rituals like the Eucharist, whereas mosques facilitate communal prayers facing Mecca, especially on Fridays during Jumu'ah. These distinct worship settings reflect deeper theological differences between Christianity and Islam concerning ritual purity, religious authority, and community participation.
Religious Holidays and Observances
Christianity and Islam both emphasize religious holidays that reflect faith and spirituality, with Christian observances like Christmas and Easter celebrating the birth and resurrection of Jesus Christ, while Islamic holidays such as Ramadan and Eid al-Fitr commemorate fasting and spiritual reflection. Views on virginity differ, with Christianity often associating it with purity and moral conduct, particularly emphasized in teachings surrounding marriage, while Islam regards virginity as a symbol of chastity and honor, linked to family and social values. These religious holidays and beliefs around virginity play key roles in shaping community practices and individual behavior in both faiths.
Moral and Ethical Teachings
Christian beliefs emphasize virginity as a symbol of purity and chastity, often associating it with moral integrity and spiritual commitment before marriage. Islamic teachings regard virginity as a significant aspect of modesty and honor, promoting sexual relations strictly within the bounds of marriage to uphold ethical conduct. Both religions underscore the importance of self-control and respect for the body, framing virginity as a reflection of moral discipline and adherence to divine commandments.
Women’s Roles and Family Structure
Christian beliefs often emphasize the sanctity of virginity, especially before marriage, and uphold traditional women's roles centered around motherhood and family caretaking within a nuclear family structure. Islamic beliefs also regard virginity as a significant moral virtue, placing strong emphasis on modesty, chastity, and the woman's role as a wife and mother within an extended family framework. Both religions promote family as a fundamental institution but differ in cultural practices and theological interpretations that shape women's roles and expectations regarding virginity and family dynamics.
Infographic: Christian beliefs vs Islamic beliefs
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com