Understanding the boundaries between Halal and Haram in relationships ensures alignment with Islamic teachings and promotes ethical conduct. Explore deeper insights about maintaining Halal relationships and avoiding Haram practices in this article.
Table of Comparison
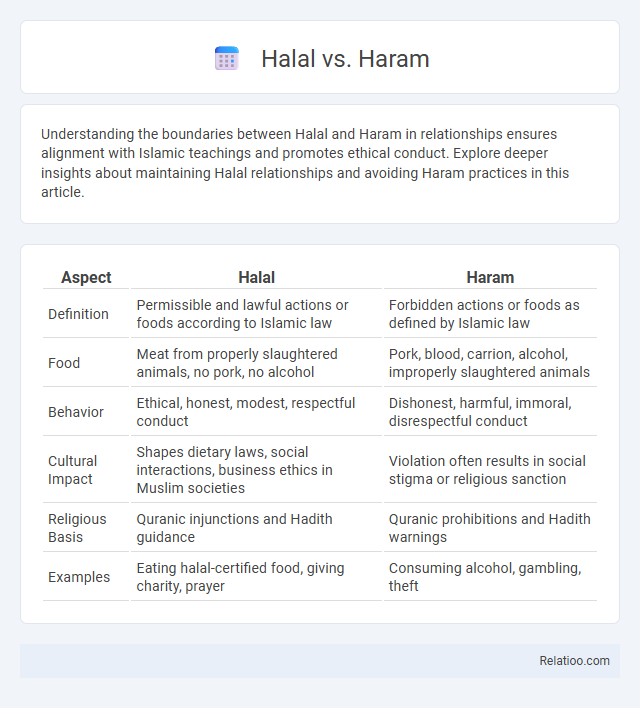
| Aspect | Halal | Haram |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permissible and lawful actions or foods according to Islamic law | Forbidden actions or foods as defined by Islamic law |
| Food | Meat from properly slaughtered animals, no pork, no alcohol | Pork, blood, carrion, alcohol, improperly slaughtered animals |
| Behavior | Ethical, honest, modest, respectful conduct | Dishonest, harmful, immoral, disrespectful conduct |
| Cultural Impact | Shapes dietary laws, social interactions, business ethics in Muslim societies | Violation often results in social stigma or religious sanction |
| Religious Basis | Quranic injunctions and Hadith guidance | Quranic prohibitions and Hadith warnings |
| Examples | Eating halal-certified food, giving charity, prayer | Consuming alcohol, gambling, theft |
Understanding Halal and Haram: Basic Definitions
Halal refers to foods and practices permitted under Islamic law, ensuring items are pure, clean, and ethically sourced. Haram denotes foods and actions explicitly forbidden, such as pork and alcohol, which violate religious guidelines. Food taboos extend beyond halal and haram, encompassing cultural restrictions that vary globally based on tradition and social norms.
Historical Origins of Halal and Haram in Islam
The historical origins of halal and haram in Islam trace back to the Quran and Hadith, which prescribe specific dietary laws to distinguish permissible (halal) from forbidden (haram) foods. These laws emerged in the 7th century Arabian Peninsula to ensure spiritual purity, hygiene, and social cohesion within the Muslim community. The concept of halal and haram extends beyond food, symbolizing a comprehensive ethical framework rooted in Islamic jurisprudence (fiqh) and tradition.
Religious Significance: Why Halal and Haram Matter
Halal and Haram classifications carry profound religious significance in Islam, guiding Muslim dietary practices to ensure obedience to Quranic commandments and prophetic teachings. These distinctions help You maintain spiritual purity and ethical consumption by avoiding Haram foods that are explicitly forbidden, such as pork and intoxicants, while embracing Halal items prepared according to prescribed rituals. Food taboos across various religions similarly reflect cultural values and divine mandates, reinforcing identity and moral discipline within communities.
Halal vs Haram in Dietary Laws
Halal and Haram are essential concepts in Islamic dietary laws, defining what is permissible and forbidden for consumption. Halal foods comply with Islamic guidelines, including the humane slaughter of animals and the absence of prohibited substances like pork and alcohol. Understanding these distinctions helps you adhere to religious practices and avoid foods that are considered Haram or taboo in Muslim communities.
Common Misconceptions about Halal and Haram
Common misconceptions about halal and haram often stem from confusing cultural practices with Islamic dietary laws, leading to the false belief that all non-halal practices are haram. Halal strictly refers to what is permissible under Islamic law, primarily concerning food cleanliness, slaughter methods, and ingredient sources, whereas haram denotes prohibited items like pork and alcohol. Food taboos in various cultures may not align with halal or haram rules, causing misunderstandings about what Muslims can consume.
Halal and Haram in Modern Lifestyle Choices
Halal and Haram dietary guidelines, rooted in Islamic law, significantly influence modern lifestyle choices by defining permissible and prohibited foods for Muslims globally. Halal foods ensure ethical sourcing, cleanliness, and specific slaughtering methods, aligning with health-conscious and sustainable eating trends. Haram foods, including pork and alcohol, are strictly avoided to comply with religious principles, affecting social dining, nutrition, and global food industry practices.
Impact of Halal and Haram on Global Markets
Halal and Haram designations significantly influence global markets by shaping consumer demand and supply chains, especially in Muslim-majority regions and increasingly in non-Muslim countries with growing Muslim populations. Your business must navigate complex certification standards and ethical considerations to meet Halal requirements, ensuring access to lucrative markets while avoiding Haram products that can lead to consumer rejection and regulatory sanctions. Food taboos further affect import/export dynamics, driving companies to adapt product formulations and marketing strategies to align with cultural and religious sensitivities worldwide.
Certification and Regulation: Ensuring Halal Compliance
Halal certification involves rigorous inspection and documentation to ensure that food products comply with Islamic dietary laws, focusing on permissible ingredients and hygienic preparation. Regulatory bodies and certification authorities implement strict guidelines and auditing processes to verify that businesses meet halal standards, protecting Your dietary requirements and faith. This formal certification distinguishes halal foods from haram or taboo items, fostering trust in food safety and religious adherence.
Social and Cultural Influences on Halal and Haram Practices
Halal and Haram food practices are deeply rooted in Islamic law, shaping social behaviors and cultural identities within Muslim communities worldwide. Your dietary choices reflect a complex interplay of religious doctrines, local customs, and social norms that reinforce group cohesion and spiritual adherence. Food taboos beyond Islamic contexts demonstrate how cultural influences govern acceptable and prohibited foods, impacting social interactions and collective values.
The Future of Halal and Haram in a Changing World
The future of halal and haram food practices is shaped by evolving global diets, technological advancements, and increasing demand for ethical and sustainable food sources. Your choices in halal consumption are influenced by innovations such as lab-grown meat and blockchain for halal certification, ensuring authenticity and transparency. Growing awareness and cross-cultural exchanges challenge traditional food taboos, encouraging a dynamic reinterpretation of halal and haram standards in a changing world.
Infographic: Halal vs Haram
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com