Litigation involves resolving disputes through court proceedings and public records, while arbitration offers a private, faster alternative with decisions made by neutral arbitrators. Explore this article to understand the key differences and benefits of Litigation vs Arbitration.
Table of Comparison
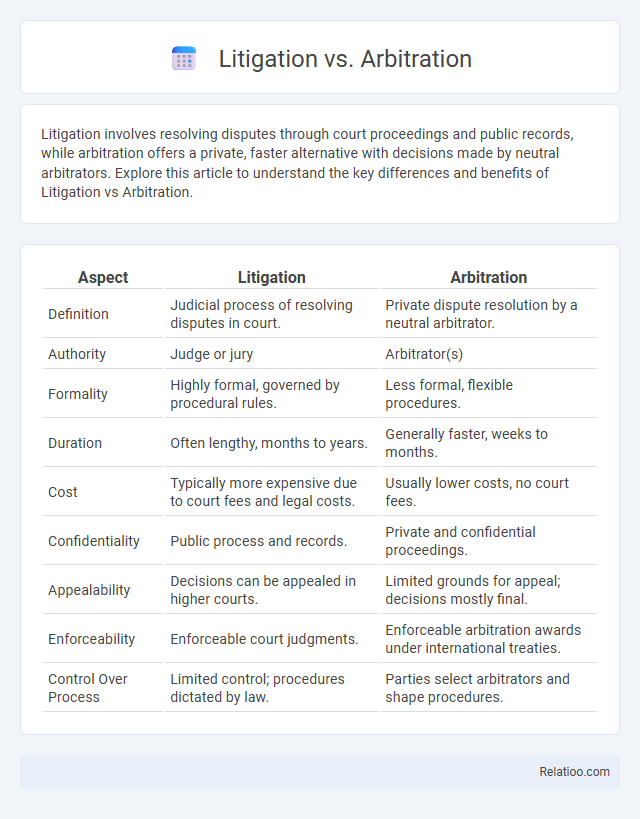
| Aspect | Litigation | Arbitration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial process of resolving disputes in court. | Private dispute resolution by a neutral arbitrator. |
| Authority | Judge or jury | Arbitrator(s) |
| Formality | Highly formal, governed by procedural rules. | Less formal, flexible procedures. |
| Duration | Often lengthy, months to years. | Generally faster, weeks to months. |
| Cost | Typically more expensive due to court fees and legal costs. | Usually lower costs, no court fees. |
| Confidentiality | Public process and records. | Private and confidential proceedings. |
| Appealability | Decisions can be appealed in higher courts. | Limited grounds for appeal; decisions mostly final. |
| Enforceability | Enforceable court judgments. | Enforceable arbitration awards under international treaties. |
| Control Over Process | Limited control; procedures dictated by law. | Parties select arbitrators and shape procedures. |
Understanding Litigation and Arbitration
Litigation involves resolving disputes through the formal court system, where a judge or jury makes binding decisions based on legal procedures and evidence. Arbitration is a private dispute resolution method where an arbitrator, chosen by the parties, issues a binding or non-binding decision outside the court system, often offering quicker and more flexible outcomes. Understanding the distinctions between litigation and arbitration helps you select the appropriate process for your legal needs, balancing formality, cost, and control over the resolution timeline.
Key Differences Between Litigation and Arbitration
Litigation involves resolving disputes through the court system, where a judge or jury makes binding decisions based on formal legal procedures, whereas arbitration is a private, less formal process where an arbitrator or panel renders a binding decision. Arbitration offers more privacy, faster resolution, and can be less costly than litigation, but it limits the right to appeal, which is typically available in courts. Understanding these key differences helps Your choice align with priorities like cost, confidentiality, and control over the dispute resolution process.
Advantages of Litigation
Litigation provides a formal, judicial process backed by legal precedent and enforceable court judgments, ensuring clear resolution and protection of your rights. The public nature of court proceedings promotes transparency and accountability, which can be beneficial in complex disputes requiring comprehensive evidence evaluation. Access to appellate courts allows for review and correction of potential errors, enhancing the fairness and thoroughness of dispute resolution.
Advantages of Arbitration
Arbitration offers a faster resolution process compared to traditional litigation, significantly reducing case backlog and court delays. It provides a confidential setting, protecting sensitive business information from public disclosure. The flexibility in selecting arbitrators with specific expertise ensures decisions are informed and tailored to the subject matter.
Disadvantages of Litigation
Litigation often involves prolonged court procedures, resulting in higher legal costs and extended timeframes compared to arbitration or submission processes. Your case may be subjected to public scrutiny, compromising confidentiality, which is typically better maintained in arbitration. Courts also have limited flexibility in procedures and rulings, potentially reducing the efficiency and adaptability that arbitration or submission offer.
Disadvantages of Arbitration
Arbitration can lead to limited grounds for appealing the decision, restricting Your ability to challenge unfavorable outcomes. It often involves high costs similar to litigation, undermining its cost-efficiency advantage. Confidentiality in arbitration may also obscure important public information, potentially affecting transparency and precedent-setting in legal matters.
Cost Comparison: Litigation vs Arbitration
Litigation typically incurs higher costs than arbitration due to extensive court fees, longer case durations, and increased attorney expenses. Arbitration offers a more cost-effective alternative with streamlined procedures, reduced discovery, and faster resolution, minimizing overall legal fees. Choosing arbitration can substantially lower financial burdens while ensuring dispute resolution outside traditional courts.
Timeframe and Efficiency Considerations
Litigation typically involves extended timeframes, often spanning months to years due to court schedules, procedural requirements, and appeals, making it less efficient for resolving disputes quickly. Arbitration offers a faster resolution by allowing parties to select arbitrators and streamline procedures, usually concluding within a few months, thus enhancing time efficiency. Submission, as a voluntary agreement to arbitrate or resolve disputes, accelerates the process by avoiding court litigation and enabling tailored, efficient conflict resolution.
Choosing Between Litigation and Arbitration
Choosing between litigation and arbitration involves evaluating factors such as cost, duration, privacy, and enforceability. Litigation offers a formal court process with public records and potential for appeals, while arbitration provides a private, often faster resolution with limited appellate options. Businesses typically prefer arbitration for confidentiality and efficiency, whereas litigation is favored when legal precedent or a public trial is necessary.
Factors Influencing Dispute Resolution Methods
Factors influencing your choice between litigation, arbitration, and submission include cost, time efficiency, confidentiality, and control over the process. Litigation often involves higher expenses and public records, while arbitration and submission provide more private and faster resolutions. The complexity of the dispute and enforceability of decisions also play critical roles in selecting the appropriate dispute resolution method.
Infographic: Litigation vs Arbitration
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com