Repudiation involves the outright rejection of a relationship's validity, while denial refers to refusing to acknowledge the emotional or factual reality within the relationship. Explore the differences and impacts of repudiation versus denial on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
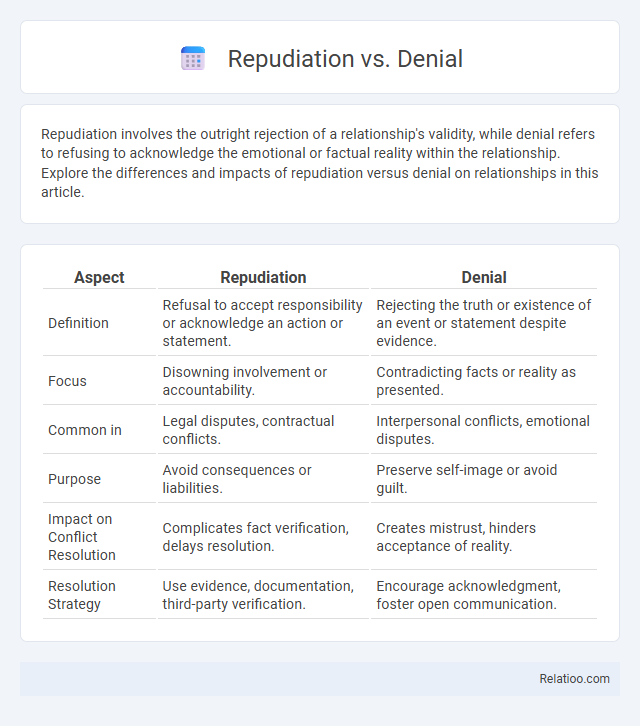
| Aspect | Repudiation | Denial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Refusal to accept responsibility or acknowledge an action or statement. | Rejecting the truth or existence of an event or statement despite evidence. |
| Focus | Disowning involvement or accountability. | Contradicting facts or reality as presented. |
| Common in | Legal disputes, contractual conflicts. | Interpersonal conflicts, emotional disputes. |
| Purpose | Avoid consequences or liabilities. | Preserve self-image or avoid guilt. |
| Impact on Conflict Resolution | Complicates fact verification, delays resolution. | Creates mistrust, hinders acceptance of reality. |
| Resolution Strategy | Use evidence, documentation, third-party verification. | Encourage acknowledgment, foster open communication. |
Introduction to Repudiation and Denial
Repudiation refers to the rejection or refusal to acknowledge a contract, agreement, or claim, often seen in legal and cybersecurity contexts where a party denies having performed an action. Denial involves outright refusing the truth or existence of an event or fact, commonly used in psychological or security scenarios where someone denies involvement or responsibility. Understanding the nuances between repudiation and denial helps you accurately identify and address disputes, ensuring effective resolution in legal, digital, or interpersonal conflicts.
Defining Repudiation
Repudiation is the act of rejecting or refusing to acknowledge the validity of a contract, agreement, or statement, which can lead to legal disputes. Denial involves outright refusing a claim or accusation, often without addressing the underlying evidence or contract terms. Your understanding of repudiation is crucial in distinguishing it from simple denial because repudiation implies a breach or refusal to perform contractual obligations.
Defining Denial
Denial is the outright rejection of an action, statement, or accusation as untrue or false, often without providing evidence or justification. In contrast, repudiation involves formally disavowing or rejecting responsibility or association with a transaction or agreement, typically within legal or contractual contexts. Understanding denial helps differentiate it from repudiation, as denial centers on refusing acknowledgment, while repudiation implies a deliberate disowning or renunciation.
Key Differences Between Repudiation and Denial
Repudiation refers to the rejection of an action or contract, often asserting that the party never agreed to it, whereas denial involves refusing to acknowledge the occurrence of an event or responsibility. Key differences include repudiation's legal context, where a party disavows obligations, contrasting with denial's broader psychological or factual refusal to accept facts. In cybersecurity, repudiation attacks occur when a user denies performing an action, highlighting the importance of non-repudiation controls to prevent disputes.
Semantic Nuances: Repudiation vs Denial
Repudiation involves formally rejecting authority or responsibility, often in legal or contractual contexts, whereas denial refers to the outright refusal to accept reality or truth, typically in psychological or everyday situations. Repudiation carries a connotation of intentional disavowal against obligations, while denial emphasizes cognitive or emotional refusal to acknowledge facts. Understanding the semantic nuance between repudiation's formal rejection and denial's psychological rejection is essential for precise communication in legal, social, and interpersonal discourse.
Legal Implications of Repudiation and Denial
Repudiation involves a clear rejection or refusal to fulfill contractual obligations, leading to potential legal consequences such as breach of contract claims and damages. Denial, in a legal context, is the refusal to admit the truth of an allegation, often used as a defense mechanism without necessarily impacting contractual duties. Understanding the distinctions between repudiation and denial is crucial for Your legal strategy, as repudiation can trigger immediate remedies, while denial affects the burden of proof in litigation.
Psychological Perspectives on Repudiation and Denial
Psychological perspectives on repudiation emphasize the conscious rejection of reality or facts to protect the ego from distress, often manifesting as a defense mechanism in trauma or cognitive dissonance situations. Denial involves an unconscious refusal to accept painful truths, serving as a temporary buffer against emotional overload and enabling gradual adjustment to reality. Understanding these mental processes helps clarify how individuals manage conflicting information and emotional pain, highlighting the nuanced differences between deliberate repudiation and unconscious denial.
Real-World Examples of Repudiation and Denial
Repudiation involves denying the authenticity of a statement, contract, or transaction, often seen when a customer disputes a credit card charge claiming it wasn't authorized, while denial typically refers to refusing responsibility or involvement, such as an employee denying knowledge of data breaches in cybersecurity incidents. Real-world examples include banks handling repudiation claims where customers reject fraudulent transactions to avoid financial loss, and companies facing denial scenarios where individuals refuse accountability during internal investigations of compliance issues. Understanding these distinctions helps you effectively manage liability and implement proper legal or security responses in business contexts.
Common Misconceptions
Repudiation often gets confused with denial, but repudiation specifically involves rejecting a claim or contract's validity, whereas denial refers to simply refusing to acknowledge an event or fact. Common misconceptions arise when people use denial to imply legal renouncement like repudiation, which can lead to misunderstandings in contractual or cybersecurity contexts. Your clarity on these terms ensures accurate communication and legal interpretation, particularly in scenarios involving disputes or authentication challenges.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Repudiation and Denial
Choosing between repudiation and denial depends on the context of your legal or contractual dispute, as repudiation involves rejecting the validity of a contract or agreement, whereas denial simply disputes or refuses acceptance of a specific claim or accusation. Your decision should consider the strength of evidence available and the potential legal implications, with repudiation often leading to contract termination and denial serving as a defensive response to factual allegations. Understanding these distinctions ensures you select the most effective strategy for protecting your rights and interests.
Infographic: Repudiation vs Denial
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com