Science relies on empirical evidence and testable hypotheses to explain natural phenomena, while religion is grounded in faith and spiritual beliefs. Explore the complex interaction between science and religion in this article to understand their roles in shaping human understanding.
Table of Comparison
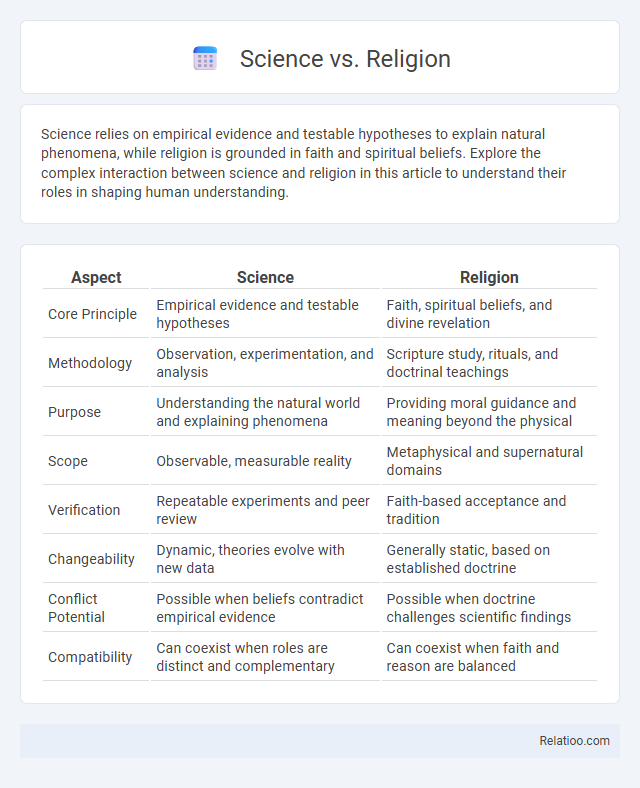
| Aspect | Science | Religion |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Empirical evidence and testable hypotheses | Faith, spiritual beliefs, and divine revelation |
| Methodology | Observation, experimentation, and analysis | Scripture study, rituals, and doctrinal teachings |
| Purpose | Understanding the natural world and explaining phenomena | Providing moral guidance and meaning beyond the physical |
| Scope | Observable, measurable reality | Metaphysical and supernatural domains |
| Verification | Repeatable experiments and peer review | Faith-based acceptance and tradition |
| Changeability | Dynamic, theories evolve with new data | Generally static, based on established doctrine |
| Conflict Potential | Possible when beliefs contradict empirical evidence | Possible when doctrine challenges scientific findings |
| Compatibility | Can coexist when roles are distinct and complementary | Can coexist when faith and reason are balanced |
Introduction: Defining Science and Religion
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge through testable explanations and predictions about the natural world, relying on empirical evidence and the scientific method. Religion encompasses organized systems of beliefs, rituals, and moral codes centered on spirituality, faith, and the divine, often addressing questions beyond empirical observation. Core beliefs serve as foundational principles or convictions that shape individual or collective understanding, influencing perspectives in both scientific inquiry and religious practice.
Historical Context: The Evolution of the Debate
The debate between science, religion, and core belief has evolved significantly since the Scientific Revolution of the 16th century, which challenged traditional religious explanations of natural phenomena. Key historical events such as Galileo's conflict with the Catholic Church and Darwin's theory of evolution catalyzed shifts in how societies reconcile empirical evidence with spiritual doctrines. This ongoing discourse reflects the dynamic interplay between scientific progress, theological interpretation, and deeply held cultural convictions.
Core Principles: Scientific Method vs Faith-Based Beliefs
The core principles of the scientific method emphasize empirical evidence, rigorous experimentation, and falsifiability to establish knowledge, contrasting with faith-based beliefs rooted in spiritual conviction and doctrinal teachings without requiring empirical proof. Science prioritizes reproducibility and objective analysis, enabling continuous refinement of understanding through observable data and logical reasoning. Faith-based systems rely on personal or communal trust in sacred texts, rituals, and spiritual experiences as foundational truths guiding morality and existence.
Areas of Conflict: Creation, Evolution, and Cosmology
Conflicts between science and religion often emerge in areas like creation, evolution, and cosmology, where scientific evidence from fields such as genetics and astrophysics challenges traditional religious narratives. Core beliefs in many religions propose creation by a divine being, contrasting with scientific explanations based on natural processes and empirical data. These differing frameworks influence ongoing debates about the origin of life, the development of species, and the structure of the universe, highlighting fundamental clashes between faith-based doctrines and evidence-based science.
Areas of Harmony: Shared Values and Ethical Overlaps
Science, religion, and core beliefs intersect significantly in their shared commitment to ethical principles such as compassion, integrity, and the pursuit of truth. Both scientific inquiry and religious teachings emphasize the importance of humility in understanding the universe and our place within it. This harmony fosters dialogue around moral responsibility, human dignity, and the stewardship of the environment, reflecting a common ground that transcends their methodological differences.
Influential Thinkers: Key Figures in Science and Religion
Prominent thinkers such as Albert Einstein and Isaac Newton have reshaped scientific understanding with groundbreaking discoveries, while influential religious figures like Augustine of Hippo and Thomas Aquinas critically bridged faith and reason. Your exploration of core beliefs benefits from examining how these key figures challenged and harmonized the boundaries between empirical evidence and spiritual doctrine. Their legacies continue to influence contemporary debates on the compatibility and conflicts between science, religion, and fundamental worldviews.
Societal Impacts: How Science and Religion Shape Culture
Science drives technological advancement and shapes societal norms through empirical knowledge, fostering innovation and global connectivity. Religion influences cultural values, moral frameworks, and community cohesion by providing shared narratives and ethical guidance. Core beliefs rooted in either domain profoundly impact laws, education systems, and social behaviors, reflecting the interplay between scientific progress and religious traditions in shaping cultural identity.
Modern Perspectives: Dialogue and Integration
Modern perspectives on science, religion, and core beliefs emphasize dialogue and integration rather than conflict. Scholars and practitioners explore how scientific discoveries and religious values can coexist and inform each other, fostering mutual respect and complementary understanding. This approach highlights the potential for unified frameworks that incorporate empirical evidence alongside ethical and spiritual insights, enriching human knowledge and experience.
Challenges in Bridging the Divide
Science and religion often clash due to fundamentally different epistemologies, with science relying on empirical evidence and religion on faith-based doctrines. Core beliefs rooted in cultural and personal identities create psychological resistance to reconciling scientific explanations with spiritual worldviews. Challenges in bridging this divide include overcoming cognitive biases, integrating diverse knowledge systems, and fostering mutual respect to encourage constructive dialogue.
Conclusion: The Future of Science and Religion
Science and religion continue to shape human understanding, with science driving innovation and empirical knowledge while religion addresses moral values and spiritual meaning. Your personal core beliefs often result from the interplay between scientific discoveries and religious teachings, influencing how you interpret existence and purpose. The future of both domains may lie in a respectful coexistence that leverages scientific advancements to enhance life, while honoring the ethical frameworks provided by religious and philosophical traditions.
Infographic: Science vs Religion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com