Windows offers a user-friendly interface and widespread software compatibility, while Linux provides enhanced security and customization for advanced users. Discover the key differences between Windows and Linux to choose the best operating system for your needs in this article.
Table of Comparison
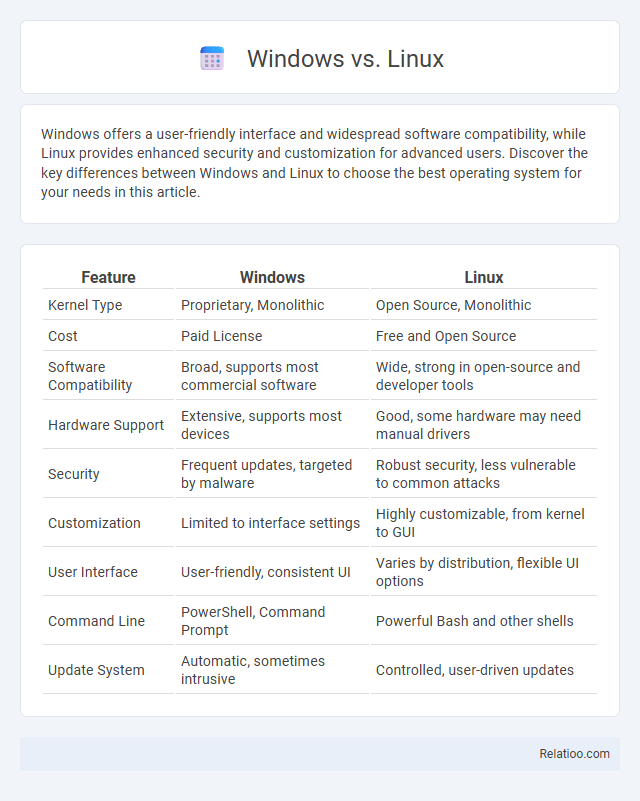
| Feature | Windows | Linux |
|---|---|---|
| Kernel Type | Proprietary, Monolithic | Open Source, Monolithic |
| Cost | Paid License | Free and Open Source |
| Software Compatibility | Broad, supports most commercial software | Wide, strong in open-source and developer tools |
| Hardware Support | Extensive, supports most devices | Good, some hardware may need manual drivers |
| Security | Frequent updates, targeted by malware | Robust security, less vulnerable to common attacks |
| Customization | Limited to interface settings | Highly customizable, from kernel to GUI |
| User Interface | User-friendly, consistent UI | Varies by distribution, flexible UI options |
| Command Line | PowerShell, Command Prompt | Powerful Bash and other shells |
| Update System | Automatic, sometimes intrusive | Controlled, user-driven updates |
Introduction to Windows and Linux
Windows and Linux are two of the most widely used operating systems, each offering distinct features and benefits tailored to different user needs. Windows, developed by Microsoft, is known for its user-friendly interface, extensive software compatibility, and strong support for gaming and enterprise applications, making it a popular choice among general consumers and businesses. Linux, an open-source operating system, provides high customization, security, and performance advantages, favored by developers, system administrators, and organizations seeking cost-effective and flexible solutions.
User Interface Comparison
Windows offers a polished, user-friendly interface with a consistent Start menu and taskbar, emphasizing ease of navigation and accessibility for mainstream users. Linux provides a diverse range of customizable desktops like GNOME, KDE, and XFCE, catering to power users who prefer flexibility in appearance and workflow. Value-wise, Linux is often preferred for its free, open-source desktop environments, while Windows incurs licensing costs but provides a standardized experience ideal for general consumers and enterprise environments.
Performance and System Requirements
Windows demands higher system resources, often requiring more RAM and CPU power, which can impact performance on older hardware. Linux operates efficiently with lower system requirements, making it ideal for running smoothly on modest or legacy devices while maintaining high performance. Value-wise, Linux offers cost benefits due to its open-source nature and flexibility, whereas Windows may entail licensing costs but provides extensive software compatibility and support.
Security Features and Vulnerabilities
Windows and Linux differ significantly in security features and vulnerabilities, with Linux offering robust open-source security controls and frequent patches, making it a preferred choice for cybersecurity professionals. Windows provides comprehensive built-in security tools like Windows Defender and advanced malware protection but faces more frequent targeted attacks and vulnerabilities due to its larger user base. Your choice between these platforms should depend on the specific security needs and risk tolerance for the environment in which they will be deployed.
Software Availability and Compatibility
Windows offers extensive software availability with broad compatibility for most commercial and gaming applications, making it ideal for users requiring diverse and specialized software. Linux provides a growing ecosystem of open-source and developer tools, but compatibility with mainstream software can be limited, often requiring alternatives or emulation. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize access to a wide range of proprietary software with seamless integration (Windows) or prefer cost-effective, customizable solutions with strong support for programming and server environments (Linux).
Customization and Flexibility
Windows offers a user-friendly interface with limited customization options, suitable for those seeking consistency and ease of use. Linux provides unparalleled flexibility and customization, allowing You to tailor your operating system through open-source tools and diverse distributions. This value in adaptability makes Linux ideal for developers and power users who prioritize control over their computing environment.
Cost and Licensing Differences
Windows typically requires paid licenses for each user or device, increasing overall costs for businesses and individuals. Linux offers open-source distributions that are free to use, significantly reducing expenses while providing flexibility in customization and deployment. Your choice impacts the total cost of ownership, with Linux being more cost-effective due to its licensing model compared to the proprietary licensing fees of Windows.
Community Support and Documentation
Linux offers extensive community support and comprehensive documentation maintained by a global network of developers and users, fostering rapid problem resolution and continuous improvement. Windows provides structured, professional support channels alongside official Microsoft documentation, ensuring reliable help for enterprise users and mainstream applications. Value-wise, Linux's open-source nature delivers cost-effective solutions with robust communal resources, whereas Windows requires licensing fees but benefits from extensive, centralized support tailored for business environments.
Use Cases: Home, Business, and Server
Windows excels in home and business environments with user-friendly interfaces and broad software compatibility, while Linux offers cost-effective, customizable solutions ideal for servers and tech-savvy home users. Your choice depends on specific use cases: Windows supports productivity and multimedia, Linux provides robust security and performance for servers, and value considerations highlight Linux's open-source nature versus Windows' licensing costs. Businesses often deploy Windows for desktops and Linux for backend servers to balance usability and efficiency.
Which Operating System Should You Choose?
Windows offers widespread software compatibility and a user-friendly interface, making it ideal for gaming, professional applications, and general use. Linux provides a highly customizable, secure, and cost-effective solution preferred by developers, system administrators, and those seeking open-source flexibility. Choosing between Windows, Linux, or a value-based OS depends on your specific needs for software availability, customization, security, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Windows vs Linux
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com