Open-mindedness fosters meaningful relationship growth by embracing diverse perspectives, while dogmatism limits understanding and creates conflict. Discover how balancing these mindsets enhances connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
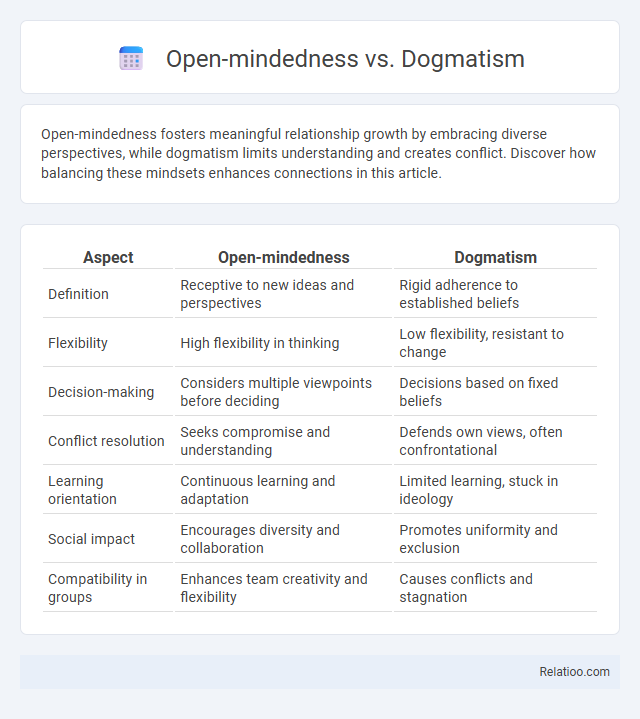
| Aspect | Open-mindedness | Dogmatism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Receptive to new ideas and perspectives | Rigid adherence to established beliefs |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in thinking | Low flexibility, resistant to change |
| Decision-making | Considers multiple viewpoints before deciding | Decisions based on fixed beliefs |
| Conflict resolution | Seeks compromise and understanding | Defends own views, often confrontational |
| Learning orientation | Continuous learning and adaptation | Limited learning, stuck in ideology |
| Social impact | Encourages diversity and collaboration | Promotes uniformity and exclusion |
| Compatibility in groups | Enhances team creativity and flexibility | Causes conflicts and stagnation |
Understanding Open-mindedness and Dogmatism
Open-mindedness fosters intellectual growth by encouraging you to consider diverse perspectives and adapt your beliefs based on new evidence, enhancing empathy and critical thinking. Dogmatism, by contrast, rigidly clings to specific moral values or ideologies, often rejecting alternative viewpoints and limiting personal and social development. Understanding the balance between open-mindedness and dogmatism is crucial for cultivating moral values that are both principled and adaptable to complex ethical situations.
Key Characteristics of Open-minded Individuals
Open-minded individuals exhibit intellectual humility, actively seek diverse perspectives, and remain adaptable to new information, fostering inclusive and critical thinking environments. Unlike dogmatism, which is characterized by rigid beliefs and resistance to change, open-mindedness encourages continuous learning and moral reflection. These traits enhance ethical decision-making by promoting empathy, tolerance, and a balanced evaluation of moral values.
Traits and Signs of Dogmatic Thinking
Dogmatic thinking is characterized by rigid beliefs and an unwillingness to consider alternative perspectives, often leading to close-mindedness and resistance to change. Signs of dogmatism include dismissing opposing views without evaluation, relying on absolute truths, and showing intolerance toward differing opinions. Your ability to recognize these traits can foster open-mindedness and promote a balanced moral value system grounded in empathy and critical thinking.
Psychological Roots of Open-mindedness
Open-mindedness stems from psychological traits such as cognitive flexibility, empathy, and a tolerance for ambiguity, promoting adaptive thinking and learning. Dogmatism, often rooted in rigid cognitive structures and fear of uncertainty, limits openness and critical evaluation of new ideas, while moral values influence the degree to which you challenge or uphold beliefs. Your capacity for open-mindedness enhances personal growth by balancing these psychological and ethical dimensions.
How Dogmatism Develops: Causes and Influences
Dogmatism develops through a combination of psychological, social, and environmental factors, including rigid upbringing, cultural indoctrination, and cognitive biases that limit exposure to alternative perspectives. Childhood experiences emphasizing obedience and authority often cultivate inflexible belief systems, while social reinforcement from like-minded groups strengthens dogmatic attitudes. Neurocognitive studies suggest that low tolerance for ambiguity and a heightened need for certainty further contribute to the development of dogmatism, contrasting sharply with the adaptive openness associated with moral value flexibility.
The Impact of Open-mindedness on Personal Growth
Open-mindedness fosters personal growth by encouraging the exploration of diverse perspectives, which leads to increased cognitive flexibility and emotional intelligence. This adaptability contrasts sharply with dogmatism, where rigid beliefs can hinder learning and moral development. Embracing open-mindedness enhances ethical understanding and promotes a balanced integration of moral values through reflective thinking and empathy.
Consequences of Dogmatism in Society
Dogmatism in society often leads to entrenched beliefs that hinder open dialogue and critical thinking, reducing social cohesion and impeding progress. This rigid thinking fosters intolerance and polarization, escalating conflicts and undermining moral values that promote empathy and understanding. Your ability to cultivate open-mindedness is crucial for overcoming these negative consequences and nurturing a more inclusive and harmonious community.
Strategies to Cultivate Open-mindedness
Strategies to cultivate open-mindedness include actively seeking diverse perspectives, engaging in reflective thinking, and practicing empathy to understand others' viewpoints. You can challenge dogmatic beliefs by questioning assumptions and embracing uncertainty, which fosters intellectual humility and moral development. Prioritizing open-mindedness enhances your ability to navigate complex moral values with greater tolerance and flexibility.
Overcoming Dogmatic Beliefs: Practical Steps
Overcoming dogmatic beliefs requires cultivating open-mindedness through critical self-reflection and exposure to diverse perspectives, which challenges rigid thought patterns and entrenched biases. Engaging in active listening and empathy promotes understanding of conflicting moral values, facilitating cognitive flexibility and reducing ideological polarization. Regular practice of questioning assumptions and seeking evidence-based information supports moral development and ethical reasoning, enabling individuals to prioritize nuanced, inclusive values over dogmatic certainty.
Open-mindedness vs Dogmatism: Finding a Healthy Balance
Open-mindedness fosters critical thinking and adaptability by encouraging the evaluation of diverse perspectives, while dogmatism rigidly adheres to fixed beliefs, limiting growth and understanding. Striking a healthy balance involves embracing open-minded inquiry without abandoning core moral values, ensuring ethical consistency alongside intellectual flexibility. Research shows that individuals who balance open-mindedness with principled convictions tend to exhibit better decision-making and stronger interpersonal relationships.
Infographic: Open-mindedness vs Dogmatism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com