Empathic listening involves fully understanding and sharing the feelings of the speaker, while active listening emphasizes attentively responding and providing feedback to ensure clarity. Discover detailed comparisons and practical tips on how to apply both techniques effectively in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
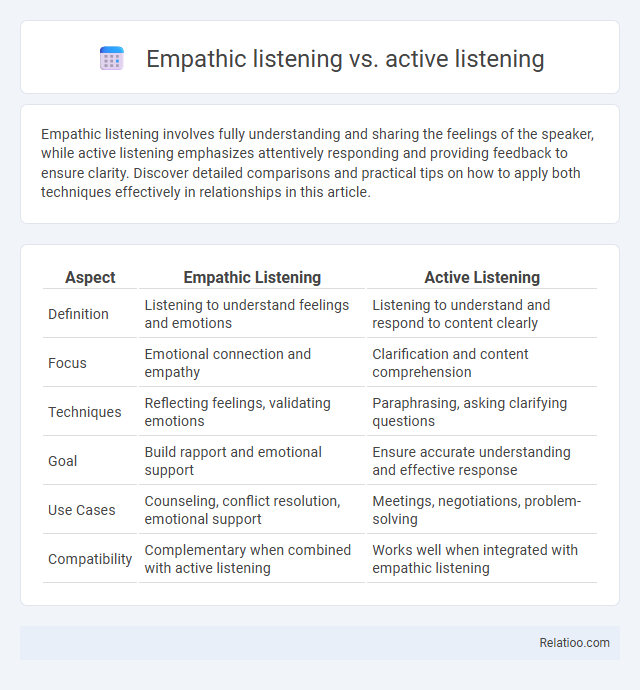
| Aspect | Empathic Listening | Active Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Listening to understand feelings and emotions | Listening to understand and respond to content clearly |
| Focus | Emotional connection and empathy | Clarification and content comprehension |
| Techniques | Reflecting feelings, validating emotions | Paraphrasing, asking clarifying questions |
| Goal | Build rapport and emotional support | Ensure accurate understanding and effective response |
| Use Cases | Counseling, conflict resolution, emotional support | Meetings, negotiations, problem-solving |
| Compatibility | Complementary when combined with active listening | Works well when integrated with empathic listening |
Understanding Empathic Listening
Empathic listening involves deeply understanding the speaker's emotions and perspectives, focusing on connecting with their feelings beyond just the words spoken. Unlike active listening, which emphasizes attention and feedback, empathic listening prioritizes emotional resonance and validation of the speaker's experience. By mastering empathic listening, you enhance your ability to build trust and foster meaningful communication in both personal and professional relationships.
Defining Active Listening
Active listening is a communication technique that involves fully concentrating, understanding, responding, and remembering what is being said. It requires the listener to provide feedback through verbal and non-verbal cues, such as nodding, summarizing, or asking clarifying questions, to demonstrate engagement. Unlike empathic listening, which emphasizes feeling and understanding the speaker's emotions, active listening prioritizes clear comprehension and accurate information exchange.
Key Differences Between Empathic and Active Listening
Empathic listening involves deeply understanding and sharing the feelings of the speaker, while active listening focuses on attentively processing and responding to the message being communicated. You can distinguish empathic listening by its emphasis on emotional connection, whereas active listening prioritizes clarity and accurate interpretation of the content. Both techniques enhance communication but differ in their primary goals, with empathic listening fostering emotional support and active listening promoting information accuracy.
Core Skills Required for Empathic Listening
Empathic listening requires core skills such as emotional attunement, nonjudgmental understanding, and responsive feedback that fosters trust and connection. Unlike active listening, which emphasizes attention and clarification, empathic listening deeply engages with the speaker's feelings and experiences to validate their emotional state. Mastery of empathic listening involves maintaining open body language, practicing patience, and reflecting emotions accurately to support genuine empathy.
Core Skills Required for Active Listening
Core skills required for active listening include focused attention, withholding judgment, reflecting back what you hear, and clarifying meaning to ensure accurate understanding. Unlike empathic listening, which centers on feeling and understanding emotions, active listening emphasizes cognitive engagement and feedback to confirm message accuracy. Developing your ability to concentrate fully and respond thoughtfully enhances communication effectiveness across personal and professional interactions.
Emotional Intelligence in Empathic Listening
Empathic listening, a core component of emotional intelligence, involves deeply understanding and resonating with the speaker's emotions, fostering genuine connection and trust. Active listening emphasizes attentiveness and accurate comprehension through verbal and non-verbal feedback but may lack the emotional depth inherent in empathic listening. The enhanced emotional awareness in empathic listening supports better interpersonal relationships and conflict resolution by recognizing and validating feelings rather than solely focusing on the content of communication.
The Role of Feedback in Active Listening
Active listening incorporates feedback as a crucial element, where the listener responds through paraphrasing, clarifying questions, and non-verbal cues to confirm understanding. In contrast, empathic listening emphasizes emotional resonance and validation without necessarily providing verbal feedback, focusing instead on genuinely feeling the speaker's emotions. The role of feedback in active listening enables a dynamic exchange that ensures accurate communication and reinforces the speaker's message.
Practical Applications in Everyday Communication
Empathic listening enhances everyday communication by allowing individuals to genuinely understand and validate emotions, fostering trust and deeper connections in personal and professional relationships. Active listening involves fully concentrating, responding, and remembering content, which improves clarity and reduces misunderstandings during conversations. Combining empathic and active listening techniques leads to more effective conflict resolution, improved teamwork, and stronger interpersonal bonds in daily interactions.
Benefits of Empathic and Active Listening
Empathic listening enhances your emotional connection by truly understanding and validating the speaker's feelings, fostering trust and deeper relationships. Active listening improves communication accuracy and problem-solving by fully concentrating, reflecting, and responding thoughtfully to the speaker's message. Combining empathic and active listening skills benefits your interactions by balancing emotional insight with clear, effective feedback.
Choosing the Right Listening Style for Different Situations
Empathic listening centers on understanding emotions and building trust, making it ideal for sensitive or conflict situations where emotional support is crucial. Active listening emphasizes comprehension and feedback, suitable for problem-solving or information exchange where clarity and accuracy matter. Choosing the right listening style depends on the context: use empathic listening to connect on a personal level, active listening for task-oriented conversations, and combine both for balanced communication in complex scenarios.
Infographic: Empathic listening vs Active listening
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com