Masculine cultures emphasize competition, assertiveness, and achievement, while feminine cultures prioritize cooperation, care, and quality of life. Explore the nuances of these cultural dynamics and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
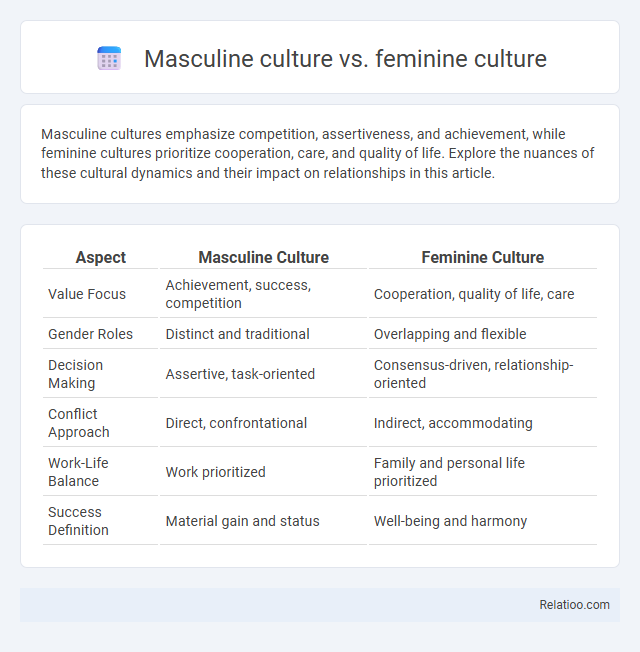
| Aspect | Masculine Culture | Feminine Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Value Focus | Achievement, success, competition | Cooperation, quality of life, care |
| Gender Roles | Distinct and traditional | Overlapping and flexible |
| Decision Making | Assertive, task-oriented | Consensus-driven, relationship-oriented |
| Conflict Approach | Direct, confrontational | Indirect, accommodating |
| Work-Life Balance | Work prioritized | Family and personal life prioritized |
| Success Definition | Material gain and status | Well-being and harmony |
Understanding Masculine and Feminine Cultures
Masculine cultures emphasize values such as competitiveness, assertiveness, and achievement, whereas feminine cultures prioritize care, cooperation, and quality of life. Understanding these cultural dimensions helps you navigate social interactions by recognizing how gender roles and cultural background influence communication styles and workplace behavior. Awareness of these differences fosters empathy and effectiveness in diverse environments.
Defining Key Characteristics of Masculine Cultures
Masculine cultures prioritize achievement, assertiveness, and material success, emphasizing competition and ambition as core values. In these societies, gender roles tend to be clearly defined, with men expected to be assertive and women nurturing, reflecting traditional social structures. Cultural backgrounds influence the extent to which masculinity shapes behavior, communication styles, and workplace dynamics, often contrasting with feminine cultures that value cooperation and quality of life.
Core Traits of Feminine Cultures
Feminine cultures emphasize cooperation, care for others, and quality of life, often valuing empathy and nurturing behaviors over competitiveness. Core traits include prioritizing social support, environmental concern, and work-life balance, contrasting with masculine cultures that highlight achievement, assertiveness, and material success. Understanding these cultural backgrounds aids in navigating interpersonal dynamics and fostering inclusive environments sensitive to diverse value systems.
Origins and Theories Behind Cultural Dimensions
Masculine and feminine cultures, defined by Geert Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory, originate from societal values prioritizing competition and achievement versus cooperation and care, respectively. Masculine cultures emphasize assertiveness, material success, and traditional gender roles, while feminine cultures value quality of life, interpersonal relationships, and gender equality. These cultural dimensions derive from social psychology and anthropology, providing a framework to analyze how cultural background shapes behavior, communication styles, and societal norms.
Workplace Dynamics: Masculine vs Feminine Societies
Masculine cultures in workplace dynamics prioritize competition, achievement, and assertiveness, fostering environments where success is measured by tangible results and status. Feminine cultures emphasize collaboration, work-life balance, and employee well-being, encouraging support and consensus over hierarchy. Understanding these cultural backgrounds helps multinational organizations tailor management styles, enhance communication, and improve team cohesion across diverse cultural contexts.
Gender Roles and Social Expectations
Masculine cultures emphasize assertiveness, competitiveness, and traditionally male roles, valuing achievement and success, while feminine cultures prioritize nurturing, cooperation, and quality of life, promoting equality and care in gender roles. Your cultural background shapes social expectations, influencing how men and women express behaviors, responsibilities, and emotional roles within society. Understanding these cultural dimensions helps navigate gender dynamics and fosters respect for diverse social norms regarding masculinity and femininity.
Conflict Resolution and Communication Styles
Masculine cultures prioritize assertiveness and direct communication, often favoring competition and quick conflict resolution, while feminine cultures value empathy, cooperation, and indirect communication, encouraging consensus and harmony. Your approach to conflict resolution will differ significantly based on your cultural background, as masculine cultures tend to address conflicts head-on, whereas feminine cultures emphasize understanding and relationship maintenance. Recognizing these cultural nuances enhances your communication effectiveness and helps prevent misunderstandings in diverse settings.
Power, Success, and Achievement Values
Masculine cultures prioritize power, success, and achievement through competition, assertiveness, and material rewards, whereas feminine cultures value cooperation, care, and quality of life over dominance and status. Your cultural background influences how you perceive and pursue these values, shaping whether you emphasize ambition and performance or relationships and community well-being. Understanding these distinctions helps navigate cross-cultural interactions and align your goals with cultural expectations.
Impact on Family and Relationships
Masculine cultures emphasize achievement, competition, and traditional gender roles, which can lead Your family dynamics to prioritize success and clearly defined responsibilities, sometimes at the expense of emotional expression. Feminine cultures value care, cooperation, and quality of life, fostering nurturing relationships and open communication within families that strengthen emotional bonds. Cultural background shapes these attitudes by influencing societal expectations, communication styles, and conflict resolution methods, ultimately affecting how families support each other and maintain relationships.
Global Examples and Case Studies
Masculine cultures, such as Japan and Germany, emphasize achievement, competition, and material success, while feminine cultures like Sweden and the Netherlands prioritize cooperation, quality of life, and caregiving. Cultural background profoundly shapes workplace behaviors and communication styles, as seen in case studies comparing American individualism with Indian collectivism, highlighting how your approach to teamwork and leadership must adapt to diverse cultural contexts. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate global business dynamics, fostering cross-cultural competence and effective collaboration.
Infographic: Masculine culture vs Feminine culture
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com