Atheism denies the existence of deities, while agnosticism maintains that the existence or non-existence of deities is unknown or unknowable. Explore the nuances and implications of both beliefs in this detailed article.
Table of Comparison
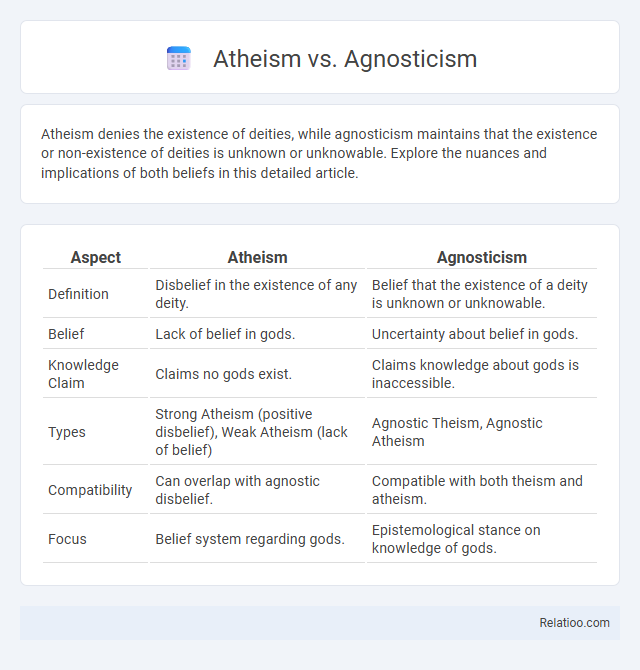
| Aspect | Atheism | Agnosticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disbelief in the existence of any deity. | Belief that the existence of a deity is unknown or unknowable. |
| Belief | Lack of belief in gods. | Uncertainty about belief in gods. |
| Knowledge Claim | Claims no gods exist. | Claims knowledge about gods is inaccessible. |
| Types | Strong Atheism (positive disbelief), Weak Atheism (lack of belief) | Agnostic Theism, Agnostic Atheism |
| Compatibility | Can overlap with agnostic disbelief. | Compatible with both theism and atheism. |
| Focus | Belief system regarding gods. | Epistemological stance on knowledge of gods. |
Understanding Atheism: Definition and Origins
Atheism is defined as the absence of belief in any deities, originating from the Greek word "atheos," meaning "without gods," and has roots in ancient philosophical skepticism. Unlike agnosticism, which centers on the uncertainty of God's existence, atheism asserts a position of disbelief, focusing on empirical evidence and reason. Your understanding of atheism deepens by exploring its historical evolution from early philosophical debates to modern secular movements.
What Is Agnosticism? Perspectives and Meaning
Agnosticism is the philosophical position that the existence or nonexistence of deities is unknown or unknowable, emphasizing uncertainty rather than belief or disbelief. It differs from atheism, which denies the existence of gods, and theism, which affirms it, by maintaining a neutral stance on core belief in divinity. Agnosticism often focuses on epistemological limits, asserting that human knowledge is insufficient to make definitive claims about supernatural entities.
Historical Evolution of Atheist and Agnostic Thought
Atheism and agnosticism both evolved significantly during the Enlightenment, with atheism emphasizing the rejection of deities based on empirical evidence while agnosticism focused on the limits of human knowledge regarding divine existence. Early philosophers like David Hume contributed to agnostic skepticism, whereas figures like Ludwig Feuerbach and Friedrich Nietzsche advanced atheistic critique of religion as a social construct. Understanding this historical evolution can help you grasp the nuanced core beliefs that distinguish atheism's assertion of no gods from agnosticism's suspension of judgment.
Core Differences Between Atheism and Agnosticism
Atheism is defined by the explicit lack of belief in any deities, asserting that gods do not exist, while agnosticism centers on the belief that the existence or non-existence of deities is unknown or inherently unknowable. Your understanding of these core differences highlights atheism's definitive stance against theism contrasted with agnosticism's acknowledgment of uncertainty and the limits of human knowledge. Core belief distinctions involve atheism's rejection of divine claims versus agnosticism's suspension of judgment until evidence is conclusive.
Philosophical Arguments Surrounding Belief and Doubt
Philosophical arguments surrounding atheism and agnosticism often revolve around the nature of belief and doubt, where atheism asserts a lack of belief in deities, while agnosticism emphasizes the uncertainty or unknowability of such existence. Core beliefs underpin each stance, with atheism focusing on empirical evidence and skepticism, and agnosticism prioritizing intellectual humility and the limitation of human knowledge. Your exploration of these perspectives can illuminate how belief systems handle evidence, faith, and the boundaries of certainty.
Common Misconceptions About Atheism and Agnosticism
Common misconceptions about atheism include the belief that atheists lack morals or meaning in life, while many atheists base their ethics on secular humanism and reason. Agnosticism is often misunderstood as indecision or apathy towards belief, yet it specifically refers to the position that the existence of deities is unknown or unknowable. Both atheism and agnosticism differ significantly from core religious beliefs, which typically assert definitive claims about divinity and purpose.
Social and Cultural Impact of Nonbelief
Atheism and agnosticism shape diverse social and cultural landscapes by challenging traditional religious norms and promoting secular values. Core beliefs within these groups often emphasize reason, scientific inquiry, and individual autonomy, fostering communities that prioritize human rights and ethical pluralism. The rise of nonbelief influences public discourse, education policies, and interfaith dialogues, contributing to greater acceptance of religious diversity and skepticism.
Famous Atheists and Agnostics Throughout History
Famous atheists such as Richard Dawkins and Christopher Hitchens have profoundly influenced contemporary discourse by openly rejecting the existence of deities based on scientific reasoning and empirical evidence. Notable agnostics like Thomas Huxley and Bertrand Russell emphasize the uncertainty of divine knowledge, advocating for skepticism regarding metaphysical claims without definitive proof. Understanding your position within atheism, agnosticism, or core belief perspectives can clarify your approach to spirituality and critical inquiry in historical and philosophical contexts.
Atheism, Agnosticism, and Modern Science
Atheism rejects belief in deities, emphasizing evidence-based understanding aligned with modern scientific principles, while agnosticism maintains that the existence of gods is unknown or unknowable, reflecting a position of skepticism and open inquiry in light of scientific uncertainties. Modern science relies on empirical data and falsifiable hypotheses, often influencing atheistic perspectives by prioritizing natural explanations over supernatural claims. Your exploration of these viewpoints can clarify how evidence and skepticism shape contemporary beliefs and challenge traditional core beliefs.
Navigating Spirituality: Choosing Between Atheism and Agnosticism
Navigating spirituality involves understanding the distinctions between atheism and agnosticism, where atheism asserts the absence of belief in deities, and agnosticism maintains that the existence of gods is unknown or unknowable. Core beliefs in atheism rely on empirical evidence and skepticism, while agnosticism prioritizes inquiry and open-ended exploration of metaphysical questions. This nuanced difference impacts spiritual identity and personal philosophies, shaping how individuals relate to faith, doubt, and existential meaning.
Infographic: Atheism vs Agnosticism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com