Validation affirms an individual's feelings and experiences, fostering emotional connection and trust in relationships. Understanding the difference between validation and feedback can improve communication and strengthen bonds; discover more in this article.
Table of Comparison
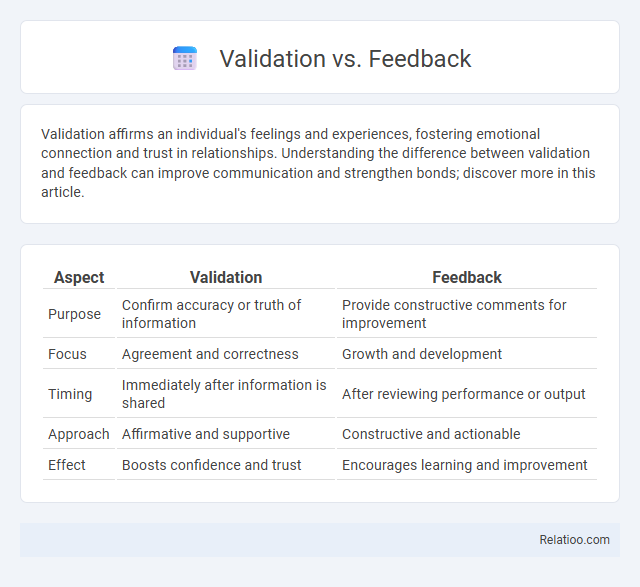
| Aspect | Validation | Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Confirm accuracy or truth of information | Provide constructive comments for improvement |
| Focus | Agreement and correctness | Growth and development |
| Timing | Immediately after information is shared | After reviewing performance or output |
| Approach | Affirmative and supportive | Constructive and actionable |
| Effect | Boosts confidence and trust | Encourages learning and improvement |
Understanding Validation and Feedback
Validation involves recognizing and affirming an individual's feelings or experiences to promote emotional acceptance and trust. Feedback provides specific, constructive information aimed at improving performance or understanding, often linked to actions or outcomes. Understanding the distinction between validation, which supports emotional well-being, and feedback, which guides behavior, helps foster effective communication and personal growth.
Key Differences Between Validation and Feedback
Validation confirms the accuracy or truth of information, ensuring that Your data or input meets specific standards or criteria. Feedback provides evaluative or corrective information aimed at improving performance or outcomes, focusing on suggestions rather than confirmation. The key difference lies in validation verifying correctness, whereas feedback offers guidance for enhancement.
The Role of Validation in Communication
Validation in communication confirms the feelings and experiences of You, strengthening trust and emotional connection. Unlike feedback, which offers constructive critique to improve behavior, validation acknowledges and respects Your perspective without judgment. This empathetic practice fosters open dialogue, encouraging honesty and mutual understanding.
Feedback: Definition and Importance
Feedback is the process of providing information about performance or behavior to promote improvement and learning, essential in educational, professional, and personal contexts. It enables individuals and organizations to identify strengths and areas for development, fostering continuous growth and informed decision-making. Unlike validation, which confirms correctness or acceptance, feedback offers constructive insights that drive progress and enhance effectiveness.
Benefits of Providing Validation
Providing validation reinforces your audience's feelings and experiences, fostering trust and emotional connection. It enhances communication by affirming the value of their input, leading to increased engagement and satisfaction. Validation supports positive relationships by acknowledging perspectives, which encourages openness and mutual respect.
Advantages of Constructive Feedback
Constructive feedback enhances learning and performance by providing specific, actionable insights that guide improvement and skill development. Unlike validation, which confirms feelings or efforts, and general feedback, which may be vague, constructive feedback targets behaviors and outcomes, fostering growth and motivation. This type of feedback builds trust and encourages open communication, ultimately leading to higher productivity and more effective teamwork.
When to Use Validation vs. Feedback
Validation occurs when you confirm the accuracy or acceptability of information, ensuring Your data meets established standards or criteria. Feedback provides constructive insights or suggestions aimed at improving performance or understanding, rather than simply confirming correctness. Use validation when accuracy and compliance are critical, and feedback when fostering growth or correcting behavior is the primary goal.
Common Mistakes in Validation and Feedback
Common mistakes in validation and feedback often include confusing validation with agreement, where you assume validating someone's feelings means endorsing their viewpoint, leading to misunderstandings. Feedback errors frequently occur when responses lack specificity, focus on the person rather than behavior, or fail to be timely, reducing their effectiveness. You can enhance communication by clearly distinguishing validation as acknowledging emotions without judgment and feedback as constructive information aimed at improvement.
Best Practices for Effective Communication
Effective communication relies on clear differentiation between validation, feedback, and acknowledgment to foster understanding and growth. Validation involves recognizing and accepting Your feelings or perspectives to build trust and empathy, while feedback provides constructive information aimed at improvement or adjustment. Best practices include being specific, timely, and sincere, ensuring your message supports positive engagement and encourages open dialogue.
Integrating Validation and Feedback for Growth
Integrating validation and feedback fosters personal and professional growth by combining external affirmations with constructive insights to build self-awareness and improve performance. Validation reassures individuals by acknowledging their efforts, while feedback provides actionable guidance for development, creating a balanced approach to learning. This synergy enhances motivation and accelerates skill acquisition, driving continuous improvement in various contexts.
Infographic: Validation vs Feedback
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com