Paraphrasing involves restating someone else's ideas in your own words while maintaining the original meaning, whereas plagiarism is the unethical practice of presenting those ideas as your own without proper attribution. Understanding the key differences between paraphrasing and plagiarism is essential for maintaining academic integrity; explore this article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
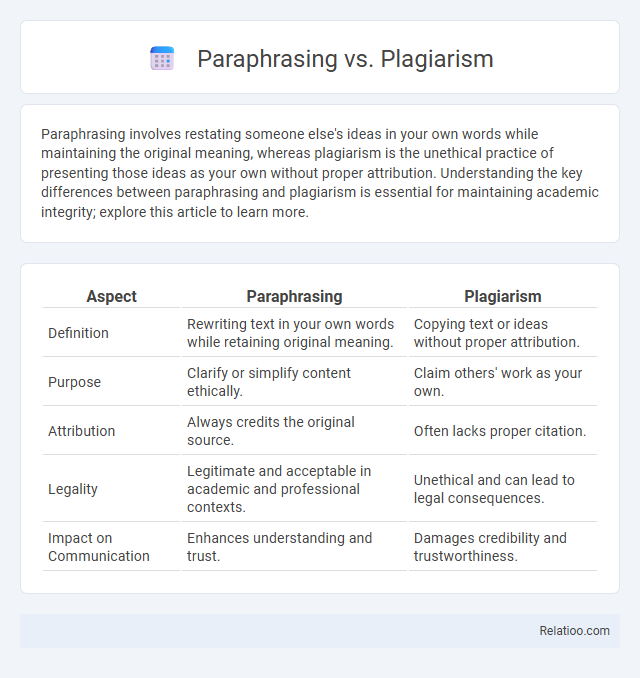
| Aspect | Paraphrasing | Plagiarism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rewriting text in your own words while retaining original meaning. | Copying text or ideas without proper attribution. |
| Purpose | Clarify or simplify content ethically. | Claim others' work as your own. |
| Attribution | Always credits the original source. | Often lacks proper citation. |
| Legality | Legitimate and acceptable in academic and professional contexts. | Unethical and can lead to legal consequences. |
| Impact on Communication | Enhances understanding and trust. | Damages credibility and trustworthiness. |
Understanding Paraphrasing: Definition and Purpose
Understanding paraphrasing involves recognizing it as the process of rewording or rephrasing text while preserving the original meaning, which differs significantly from plagiarism, the unethical act of copying someone else's work without proper attribution. Effective paraphrasing enhances clarity, demonstrates comprehension, and supports your unique voice in writing, ensuring academic integrity and originality. Mastering this skill allows you to incorporate external ideas respectfully and creatively, fostering stronger communication and credibility.
What Constitutes Plagiarism?
Plagiarism constitutes presenting someone else's ideas, words, or work as your own without proper attribution, violating ethical and legal standards. Paraphrasing involves rewording original content while maintaining the core meaning and crediting the original source, which distinguishes it from plagiarism. Understanding the boundaries of paraphrasing ensures your writing remains original and avoids the serious consequences of plagiarism.
Key Differences Between Paraphrasing and Plagiarism
Paraphrasing involves restating someone else's ideas in your own words while maintaining the original meaning, coupled with proper citation to avoid plagiarism. Plagiarism, by contrast, occurs when someone presents another's work or ideas as their own without appropriate acknowledgment, whether by copying text verbatim or insufficiently rewording. The key difference lies in intent and execution: accurate paraphrasing credits the source and transforms the content meaningfully, whereas plagiarism lacks citation and misrepresents authorship.
Why Is Proper Paraphrasing Important in Academic Writing?
Proper paraphrasing is crucial in academic writing because it demonstrates your understanding of the source material while avoiding plagiarism, which is the unethical practice of presenting someone else's ideas as your own. Effective paraphrasing allows you to integrate evidence smoothly into your work, providing clarity and enhancing originality without altering the original meaning. Mastering proper paraphrasing ensures your academic integrity is maintained and your arguments are both credible and persuasive.
Common Paraphrasing Mistakes That Lead to Plagiarism
Common paraphrasing mistakes that lead to plagiarism include inadequate rewriting of the original text, which results in closely mimicking sentence structure and vocabulary, and failing to properly cite the original source. Many writers inadvertently copy phrases verbatim or change only a few words, creating high textual similarity that plagiarism checkers detect. Proper paraphrasing requires thorough understanding, substantial rephrasing, and accurate attribution to avoid academic dishonesty.
Effective Techniques for Paraphrasing Without Plagiarizing
Effective techniques for paraphrasing without plagiarizing involve thoroughly understanding the original text and expressing the ideas in your own unique voice while maintaining the original meaning. Utilizing tools like synonym replacement, restructuring sentences, and integrating your own analysis ensures originality and clarity. Properly citing sources, even when paraphrased, is essential to avoid plagiarism and uphold academic integrity.
Citation Rules: Giving Proper Credit When Paraphrasing
Proper citation is essential when paraphrasing to avoid plagiarism by crediting the original author's ideas. Paraphrasing involves rewording source material while maintaining the original meaning, and failing to cite the source constitutes plagiarism. Following citation rules, such as including in-text citations and a full reference, ensures ethical writing and intellectual property respect.
Tools and Resources for Checking Plagiarism
Advanced plagiarism detection tools such as Turnitin, Grammarly, and Copyscape provide comprehensive analysis by scanning vast databases to identify potential unoriginal content. Paraphrasing tools like QuillBot and Spinbot assist in rewriting text while maintaining original meaning but require users to verify content originality through dedicated plagiarism checkers. Combining these resources ensures content authenticity by enabling thorough comparison against existing sources and refining paraphrased material to avoid inadvertent plagiarism.
The Consequences of Plagiarism in Academia and Beyond
Plagiarism in academia can lead to severe consequences such as academic probation, suspension, or expulsion, severely damaging a student's academic record and future opportunities. Beyond educational settings, plagiarism can result in legal actions, loss of professional reputation, and diminished trust within industries like publishing, journalism, and scientific research. Understanding proper paraphrasing techniques is essential to avoid these repercussions and uphold academic integrity.
Best Practices for Ethical Writing and Research
Paraphrasing involves rewriting source material in your own words while maintaining the original meaning, which supports ethical writing by demonstrating comprehension and proper citation. Plagiarism occurs when ideas or wording are used without acknowledgment, undermining academic integrity and intellectual honesty. Best practices for ethical research include accurately citing all sources, using quotation marks for direct quotes, and ensuring paraphrased content reflects genuine understanding rather than superficial changes.
Infographic: Paraphrasing vs Plagiarism
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com