Emotional Intelligence (EI) significantly influences relationship success by enhancing empathy, communication, and conflict resolution, while Intelligence Quotient (IQ) primarily measures cognitive abilities without addressing emotional skills. Explore how balancing EI and IQ can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
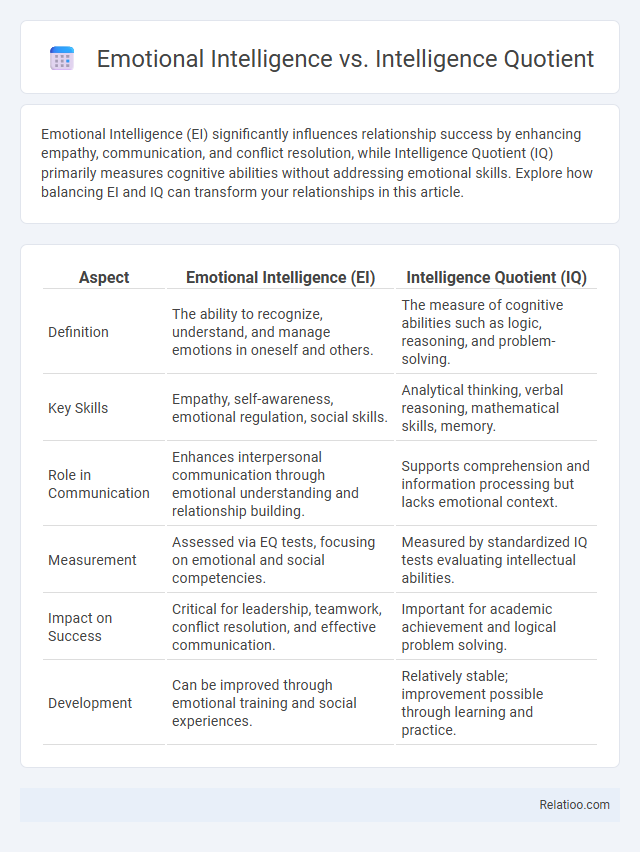
| Aspect | Emotional Intelligence (EI) | Intelligence Quotient (IQ) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions in oneself and others. | The measure of cognitive abilities such as logic, reasoning, and problem-solving. |
| Key Skills | Empathy, self-awareness, emotional regulation, social skills. | Analytical thinking, verbal reasoning, mathematical skills, memory. |
| Role in Communication | Enhances interpersonal communication through emotional understanding and relationship building. | Supports comprehension and information processing but lacks emotional context. |
| Measurement | Assessed via EQ tests, focusing on emotional and social competencies. | Measured by standardized IQ tests evaluating intellectual abilities. |
| Impact on Success | Critical for leadership, teamwork, conflict resolution, and effective communication. | Important for academic achievement and logical problem solving. |
| Development | Can be improved through emotional training and social experiences. | Relatively stable; improvement possible through learning and practice. |
Understanding Emotional Intelligence (EI)
Emotional Intelligence (EI) involves the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one's own emotions while effectively navigating interpersonal relationships through empathy and social skills. Unlike Intelligence Quotient (IQ), which measures cognitive abilities such as logical reasoning, mathematical skills, and problem-solving, EI emphasizes emotional awareness and regulation, contributing significantly to personal and professional success. Mastering EI enhances communication, leadership, and conflict resolution, making it a crucial complement to traditional intelligence metrics.
Defining Intelligence Quotient (IQ)
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) measures cognitive abilities like logical reasoning, mathematical skills, and linguistic proficiency through standardized tests. Emotional intelligence (EQ) encompasses skills such as empathy, emotional regulation, and social interaction, highlighting a person's ability to manage interpersonal relationships effectively. Understanding your IQ provides insight into your intellectual potential, while EQ reflects your capacity to navigate emotional complexities.
Key Differences Between EI and IQ
Emotional Intelligence (EI) involves the ability to recognize, understand, and manage your own emotions as well as empathize with others, whereas Intelligence Quotient (IQ) measures cognitive abilities such as logical reasoning, problem-solving, and analytical skills. EI emphasizes interpersonal skills and emotional regulation essential for social interactions, while IQ focuses on intellectual capabilities crucial for academic performance and technical tasks. Understanding the key differences helps you leverage both EI and IQ to improve personal relationships and professional success.
Components of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence (EI) encompasses five key components: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills, distinguishing it from Intelligence Quotient (IQ), which measures cognitive abilities such as logical reasoning and problem-solving. While IQ focuses on analytical and intellectual capabilities, EI emphasizes understanding and managing emotions to enhance interpersonal relationships and personal decision-making. Developing these components of EI contributes significantly to effective leadership, teamwork, and emotional resilience in diverse social and professional environments.
Measuring IQ: Methods and Metrics
Measuring Intelligence Quotient (IQ) involves standardized tests such as the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) and the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales, which evaluate cognitive abilities including logical reasoning, mathematical skills, and verbal proficiency. Emotional Intelligence (EI), assessed through tools like the Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) and the Emotional Quotient Inventory (EQ-i), measures a person's ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions. These distinct metrics provide insights into cognitive potential versus emotional competence, highlighting the complementary nature of IQ and EI in personal and professional success.
The Role of EI in Personal and Professional Success
Emotional Intelligence (EI) significantly impacts both personal and professional success by enhancing your ability to manage emotions, build relationships, and navigate social complexities, unlike Intelligence Quotient (IQ), which primarily measures cognitive abilities. High EI fosters empathy, effective communication, and conflict resolution skills, crucial for leadership and teamwork in the workplace. Developing emotional intelligence leads to better decision-making and stress management, directly contributing to improved career advancement and overall well-being.
Limitations of Relying Solely on IQ
Relying solely on Intelligence Quotient (IQ) overlooks crucial aspects of emotional regulation, empathy, and social skills essential for real-world success. Emotional Intelligence (EI) encompasses abilities such as self-awareness, emotional management, and interpersonal communication that IQ tests do not measure. The limitations of IQ emphasize the growing recognition that high cognitive ability alone does not guarantee effective leadership, decision-making, or relationship-building.
The Interplay Between EI and IQ
The interplay between Emotional Intelligence (EI) and Intelligence Quotient (IQ) reveals that while IQ measures cognitive abilities such as logic and reasoning, EI assesses your capacity to recognize, understand, and manage emotions effectively. High EI enhances decision-making, leadership, and interpersonal skills even when IQ remains constant, showing that emotional skills are critical in navigating social complexities and stress. Integrating EI with IQ creates a balanced approach to problem-solving and personal development, maximizing success in both professional and personal spheres.
Can Emotional Intelligence Be Developed?
Emotional Intelligence (EI) differs from Intelligence Quotient (IQ) by emphasizing skills such as self-awareness, empathy, and emotional regulation rather than cognitive abilities and logical reasoning. Unlike IQ, which is often considered a fixed trait, Emotional Intelligence can be developed and enhanced through targeted practices like mindfulness, social skills training, and reflective exercises. Studies show that consistent effort in building emotional competencies leads to improved interpersonal relationships, decision-making, and stress management.
Balancing EI and IQ for Holistic Growth
Balancing Emotional Intelligence (EI) and Intelligence Quotient (IQ) is crucial for holistic growth, as EI enhances self-awareness, empathy, and interpersonal skills while IQ measures cognitive abilities like logic and problem-solving. Individuals who develop both EI and IQ tend to perform better in professional and personal settings, leveraging analytical skills alongside emotional regulation and social understanding. Integrating emotional awareness with intellectual capabilities fosters well-rounded decision-making and resilience in complex environments.
Infographic: Emotional Intelligence vs Intelligence Quotient
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com