Agreement involves a mutual understanding and explicit consent between parties, while acceptance signifies one party's approval or willingness to receive an offer. Explore the key differences and practical implications of Agreement versus Acceptance in this article.
Table of Comparison
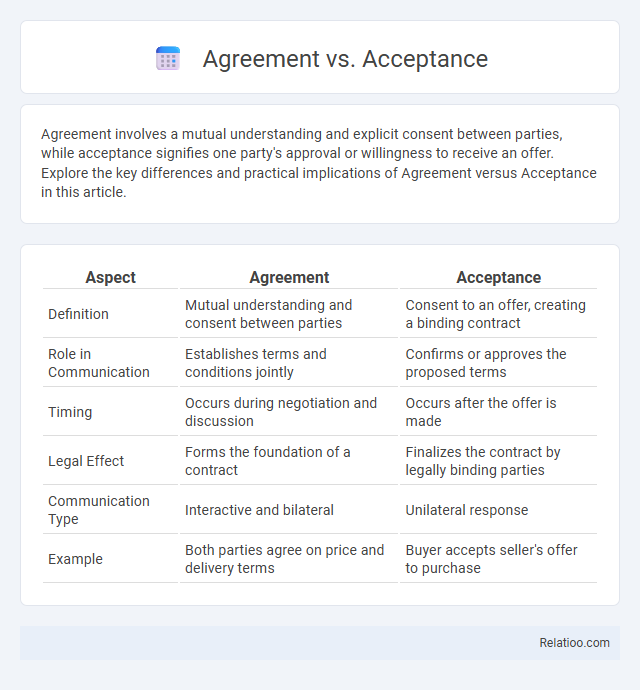
| Aspect | Agreement | Acceptance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mutual understanding and consent between parties | Consent to an offer, creating a binding contract |
| Role in Communication | Establishes terms and conditions jointly | Confirms or approves the proposed terms |
| Timing | Occurs during negotiation and discussion | Occurs after the offer is made |
| Legal Effect | Forms the foundation of a contract | Finalizes the contract by legally binding parties |
| Communication Type | Interactive and bilateral | Unilateral response |
| Example | Both parties agree on price and delivery terms | Buyer accepts seller's offer to purchase |
Understanding Agreement vs Acceptance
Understanding Agreement vs Acceptance hinges on the distinction between mutual consent and individual approval in contract formation. Agreement refers to the mutual understanding and consent between parties on the terms of a contract, while acceptance is the expression of assent by one party to the offer made by another, completing the contract formation. Your clarity on these differences ensures stronger negotiation, precise communication, and legally binding contracts.
Defining Agreement in Legal and Social Contexts
Agreement in legal contexts refers to a mutual understanding between parties that creates enforceable rights and obligations, often requiring an offer, acceptance, and consideration. In social contexts, agreement signifies a shared consensus or harmony in opinions and decisions without necessarily binding obligations. Your clarity on these distinctions ensures proper application whether drafting contracts or facilitating interpersonal consensus.
What Does Acceptance Really Mean?
Acceptance in contract law signifies a clear, unequivocal consent to the exact terms of an offer, creating a binding agreement between parties. Unlike a general agreement, acceptance must mirror the offer precisely without modifications, establishing mutual assent. Understanding acceptance is crucial as it marks the moment when parties become legally obligated, distinguishing it from mere negotiations or preliminary discussions.
Key Differences Between Agreement and Acceptance
Agreement and acceptance are crucial concepts in contract law where acceptance is the expression of assent by the offeree to the terms proposed by the offeror, forming a binding agreement upon mutual consent. An agreement represents the overall mutual understanding between parties encompassing offer, acceptance, and consideration, while acceptance specifically refers to the unconditional agreement to the exact terms of the offer. Key differences include that acceptance must be communicated effectively to create an agreement, whereas an agreement is the final contract resulting from valid offer and acceptance.
The Role of Communication in Agreement and Acceptance
Communication plays a crucial role in both agreement and acceptance by ensuring that the parties clearly convey their intentions and consent, which forms the foundation of any valid contract. Agreement requires mutual understanding through clear offers and corresponding acceptances, while acceptance must be communicated effectively to avoid misunderstandings or disputes. Your ability to articulate and receive messages accurately determines the legitimacy and enforceability of the agreement in legal contexts.
Psychological Perspectives: Agreement vs Acceptance
Understanding the psychological perspectives of Agreement vs Acceptance reveals that agreement involves conscious intellectual alignment or consent to an idea or proposal, often driven by social or cognitive factors. Acceptance, however, signifies a deeper emotional or psychological accommodation where an individual embraces realities or feelings without the necessity of agreement or approval, promoting internal peace and resilience. Your ability to differentiate these processes enhances emotional intelligence and improves interpersonal relationships by recognizing when to negotiate opinions and when to accommodate differences.
Agreement vs Acceptance in Contract Law
Agreement in contract law refers to the mutual understanding and intention between parties on the terms of a contract, while acceptance is the unconditional assent to the offer's terms, finalizing the contract formation. An agreement is established through an offer and acceptance, but acceptance specifically signifies the offeree's expression of consent, creating a binding contract. Distinguishing acceptance from mere agreement ensures clarity in contract enforceability and prevents disputes over whether a contract has been validly formed.
Real-World Examples of Agreement vs Acceptance
Agreement involves a mutual understanding between parties where terms align, such as in a contract negotiation where both buyer and seller consent to price and delivery details. Acceptance occurs when one party agrees to the offer as presented, exemplified when a homeowner signs a lease agreement after reviewing the terms proposed by a landlord. Your clarity in distinguishing agreement from acceptance helps ensure contractual obligations are enforceable in practical scenarios.
Common Misconceptions About Agreement and Acceptance
Common misconceptions about agreement and acceptance often confuse these legal concepts with each other, yet they serve distinct roles in contract formation; agreement refers to the mutual understanding between parties, whereas acceptance is the explicit expression by one party to agree to the terms offered. People mistakenly believe that reaching an agreement alone finalizes a contract, but your acceptance is crucial to create a binding contract, as it confirms your consent to the offer. Understanding the difference helps prevent disputes and ensures that all parties clearly comprehend when a contract has been validly formed.
Importance of Distinguishing Agreement from Acceptance
Distinguishing agreement from acceptance is crucial in contract law because agreement refers to the mutual understanding between parties on terms, while acceptance is the explicit approval of an offer that transforms it into a legally binding contract. Your ability to identify acceptance signals when a contract is formed and enforceable, preventing misunderstandings and disputes. Clear differentiation ensures proper legal protections and helps enforce obligations as intended by the contracting parties.
Infographic: Agreement vs Acceptance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com