Empathetic listening involves actively understanding and sharing the feelings of your partner, fostering deeper emotional connection and trust. Explore this article to learn how empathetic listening transforms relationships compared to sympathetic listening.
Table of Comparison
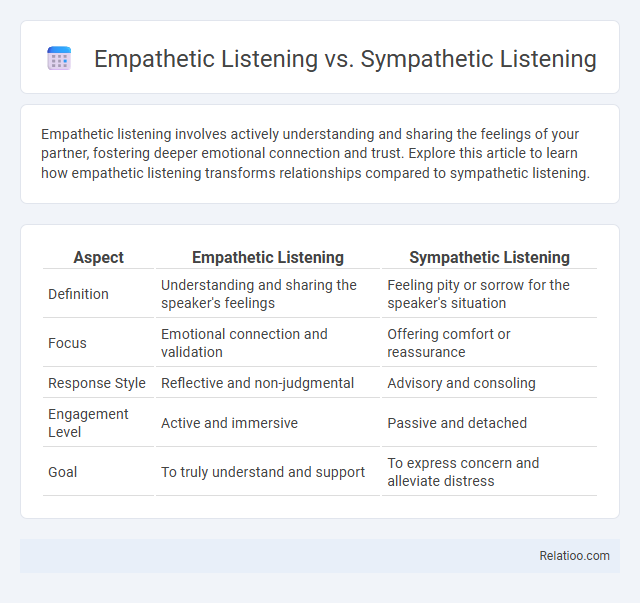
| Aspect | Empathetic Listening | Sympathetic Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding and sharing the speaker's feelings | Feeling pity or sorrow for the speaker's situation |
| Focus | Emotional connection and validation | Offering comfort or reassurance |
| Response Style | Reflective and non-judgmental | Advisory and consoling |
| Engagement Level | Active and immersive | Passive and detached |
| Goal | To truly understand and support | To express concern and alleviate distress |
Introduction to Empathetic and Sympathetic Listening
Empathetic listening involves actively understanding and sharing the feelings of the speaker, creating a deep emotional connection that fosters trust and support. Sympathetic listening focuses on acknowledging the speaker's distress and offering comfort without fully immersing in their emotional experience. Your ability to distinguish between these listening styles enhances communication effectiveness by responding appropriately to emotional contexts.
Defining Empathetic Listening
Empathetic listening involves fully understanding and sharing the feelings of the speaker, engaging both emotional and cognitive empathy to create authentic connection. Unlike sympathetic listening, which entails feeling concern or pity without deep emotional resonance, empathetic listening requires active involvement and reflection to accurately grasp the speaker's perspective. Listening broadly encompasses hearing and processing information but lacks the emotional attunement that characterizes empathetic listening.
Understanding Sympathetic Listening
Sympathetic listening involves recognizing and sharing another person's emotions, creating a supportive environment that validates their feelings without necessarily solving the problem. Unlike empathetic listening, which seeks to deeply understand and experience the speaker's perspective, sympathetic listening offers comfort from a more detached standpoint. Effective sympathetic listening enhances emotional connection and trust, especially in situations requiring compassion without intense emotional involvement.
Key Differences Between Empathy and Sympathy
Empathetic listening involves deeply understanding and sharing Your feelings by putting Yourself in another's position, while sympathetic listening simply acknowledges someone's emotions without fully experiencing them. The key difference lies in empathy's active engagement with another's emotional state versus sympathy's passive concern or pity. Effective listening requires empathy to build genuine connections, whereas sympathy may maintain emotional distance.
Core Skills in Empathetic Listening
Empathetic listening requires core skills such as active attention, emotional intelligence, and nonjudgmental feedback, enabling you to truly understand and connect with the speaker's feelings. Unlike sympathetic listening, which involves feeling pity or sorrow for someone's situation, empathetic listening fosters a deeper bond by fully engaging with their perspective without immediately offering advice or judgment. Effective listening overall depends on these skills to improve communication, build trust, and support emotional well-being in relationships.
Common Scenarios for Sympathetic Listening
Sympathetic listening is commonly employed in scenarios where you seek to express compassion, such as consoling a friend who has experienced a loss, comforting a colleague facing stress, or responding to a loved one's frustration. Unlike empathetic listening, which involves deeply understanding and sharing feelings, sympathetic listening focuses on acknowledging emotions and offering reassurance without delving into the speaker's inner experience. Your ability to recognize these contexts enables more appropriate and supportive communication tailored to the listener's emotional needs.
Benefits of Practicing Empathetic Listening
Practicing empathetic listening improves your ability to understand and connect with others on a deeper emotional level, fostering trust and stronger relationships. Unlike sympathetic listening, which often involves feeling pity, empathetic listening actively involves sharing and validating the speaker's emotions, leading to more effective communication. Enhanced emotional intelligence gained through empathetic listening supports conflict resolution and promotes a supportive environment in both personal and professional settings.
Drawbacks of Excessive Sympathy in Communication
Excessive sympathy in communication often leads to emotional overwhelm and hinders objective problem-solving, limiting the listener's ability to offer constructive feedback. Empathetic listening fosters a deeper understanding by genuinely connecting with the speaker's feelings without losing personal boundaries, whereas sympathetic listening may create dependency and reduce the speaker's sense of agency. Your communication effectiveness improves when you balance empathy with active listening, avoiding the pitfalls of excessive sympathy that can stall meaningful dialogue.
Developing Effective Listening Habits
Empathetic listening involves fully understanding and sharing the feelings of the speaker, which builds deeper connections and trust. Sympathetic listening acknowledges the speaker's emotions but maintains a degree of emotional distance, offering support without fully immersing yourself in their experience. Developing effective listening habits means prioritizing empathetic listening to enhance communication skills, foster meaningful relationships, and ensure your responses are thoughtful and relevant.
Empathetic vs Sympathetic Listening: Choosing the Right Approach
Empathetic listening involves genuinely understanding and sharing the feelings of the speaker, creating a deeper emotional connection that validates their experience. Sympathetic listening, on the other hand, offers compassion and concern but maintains an emotional distance, often providing comfort without fully engaging with the speaker's emotions. Choosing your approach depends on the situation and the needed level of emotional involvement to support effective communication and foster trust.
Infographic: Empathetic Listening vs Sympathetic Listening
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com