Apathetic responses lack emotional engagement and often ignore the feelings of others, while sympathetic responses acknowledge and validate others' emotions with compassion. Discover the key differences and impacts of apathetic versus sympathetic reactions in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
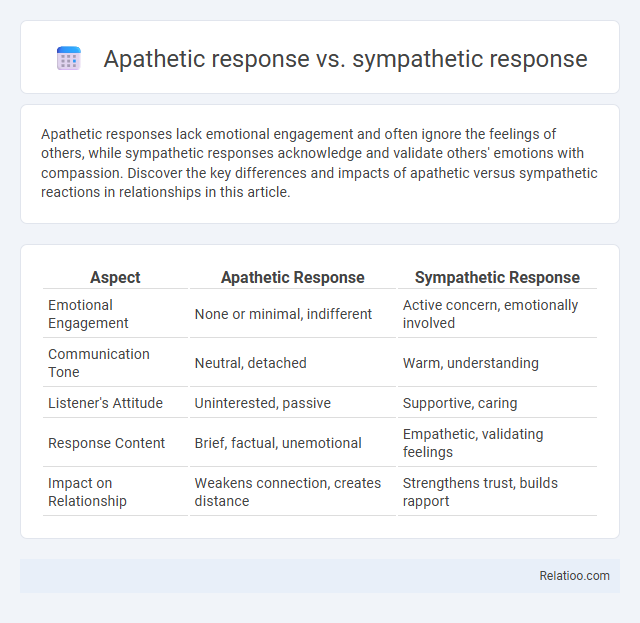
| Aspect | Apathetic Response | Sympathetic Response |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Engagement | None or minimal, indifferent | Active concern, emotionally involved |
| Communication Tone | Neutral, detached | Warm, understanding |
| Listener's Attitude | Uninterested, passive | Supportive, caring |
| Response Content | Brief, factual, unemotional | Empathetic, validating feelings |
| Impact on Relationship | Weakens connection, creates distance | Strengthens trust, builds rapport |
Understanding Apathetic and Sympathetic Responses
Sympathetic responses activate the body's fight-or-flight mechanism, increasing heart rate and releasing adrenaline to prepare you for immediate action, while apathetic responses involve a lack of emotional engagement or concern, often leading to indifference or inaction. Understanding these responses helps identify how your body and mind react to stress or emotional stimuli, with sympathetic responses signaling heightened alertness and apathetic ones indicating emotional withdrawal. Recognizing these differences is crucial for managing emotional health and improving interpersonal interactions.
The Psychology Behind Apathetic Reactions
Apathetic responses involve a lack of emotional engagement or concern toward situations that typically evoke feelings, stemming from psychological mechanisms such as emotional numbing or defense against overwhelming stress. Sympathetic responses activate your emotional capacity to understand and share another's feelings, facilitating connection and empathy through the brain's mirror neuron system. Understanding apathetic reactions involves exploring how certain psychological conditions, like depression or trauma, dampen emotional responsiveness to protect your mental state from distress.
Characteristics of Sympathetic Responses
Sympathetic responses are characterized by activation of the autonomic nervous system, leading to increased heart rate, dilated pupils, and energy mobilization for 'fight or flight' reactions. These responses rapidly prepare the body to confront or escape perceived threats through heightened alertness and enhanced physical performance. In contrast, apathetic responses involve emotional indifference and lack of concern, while sympathetic responses specifically engage physiological mechanisms to support immediate survival.
Key Differences: Apathetic vs Sympathetic
Apathetic response involves indifference or lack of emotional engagement, whereas sympathetic response shows understanding and concern for another's feelings. Your ability to distinguish between these reactions is crucial in social interactions, as sympathy fosters connection while apathy can create emotional distance. Key differences include emotional involvement, with sympathy actively acknowledging others' experiences, and apathy, which reflects disengagement or disregard.
Causes of Apathetic Behavior
Apathetic behavior often stems from underlying causes such as depression, neurological disorders, or chronic stress, which diminish emotional responsiveness and motivation. Unlike sympathetic responses that involve empathy and emotional engagement, apathetic responses reflect a lack of concern or interest, frequently linked to disruptions in brain regions like the prefrontal cortex or amygdala. Recognizing these causes is crucial for understanding your emotional state and seeking appropriate support or treatment to restore engagement.
Triggers for Sympathetic Reactions
Sympathetic responses are primarily triggered by perceived threats or stressors activating the autonomic nervous system, such as danger, fear, or intense emotional stimuli, leading to the "fight or flight" reaction. In contrast, apathetic responses occur in situations where there is indifference or lack of emotional engagement, often due to fatigue, depression, or learned helplessness, resulting in minimal physiological arousal. Distinguishing these responses is crucial in understanding behavioral and physiological reactions to environmental cues and emotional challenges.
Effects of Apathetic Responses on Relationships
Apathetic responses, characterized by indifference and lack of emotional engagement, can severely damage relationships by creating emotional distance and feelings of neglect. Unlike sympathetic responses, which show understanding and concern, apathetic reactions fail to validate others' feelings, leading to decreased trust and communication breakdown. Your relationships may weaken significantly if apathy persists, as partners or friends feel unsupported and unvalued.
Positive Outcomes of Sympathy in Social Interactions
Sympathetic responses foster empathy and understanding, enhancing emotional connections and trust in social interactions. Unlike apathetic reactions, sympathy encourages active support and validation, which improves communication and strengthens relationships. Your ability to express sympathy can lead to positive social outcomes, such as increased cooperation and emotional bonding.
Overcoming Apathetic Tendencies
Overcoming apathetic tendencies requires recognizing the emotional disengagement characteristic of apathetic responses, which contrast with the emotional investment seen in sympathetic responses. Developing empathy by actively listening and engaging with others' experiences helps shift from indifference to connection, promoting emotional responsiveness. Strategies such as mindfulness, perspective-taking, and intentional emotional reflection enhance motivation to care and counteract apathy.
Cultivating Sympathy for Better Communication
Sympathetic response involves recognizing and validating another person's feelings, fostering emotional connection and trust. Apathetic response, characterized by indifference or lack of concern, often leads to communication breakdown and alienation. Cultivating sympathy enhances interpersonal relationships by promoting empathy, active listening, and supportive dialogue, essential for effective communication in personal and professional contexts.
Infographic: Apathetic response vs Sympathetic response
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com