Positive framing in relationships emphasizes strengths and opportunities, fostering trust and emotional connection, while negative framing highlights faults and challenges, which can breed resentment and distance. Discover how shifting your perspective to positive framing can transform your relationship in this article.
Table of Comparison
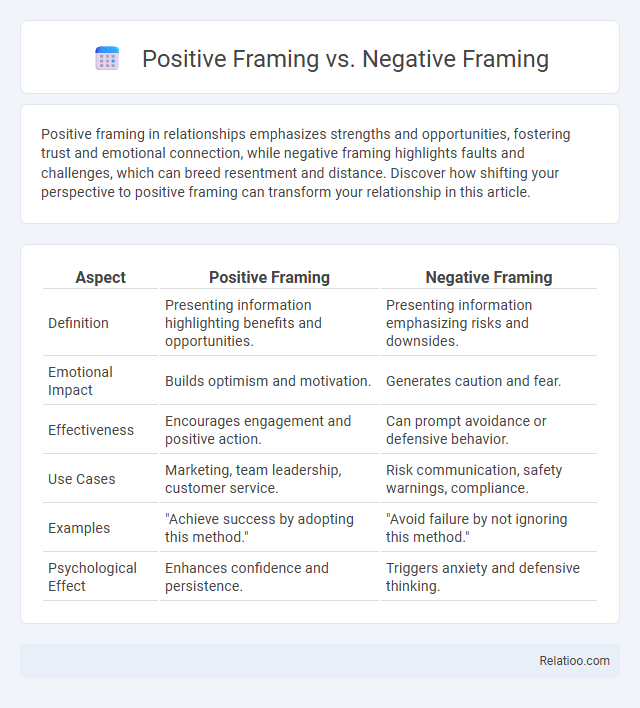
| Aspect | Positive Framing | Negative Framing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Presenting information highlighting benefits and opportunities. | Presenting information emphasizing risks and downsides. |
| Emotional Impact | Builds optimism and motivation. | Generates caution and fear. |
| Effectiveness | Encourages engagement and positive action. | Can prompt avoidance or defensive behavior. |
| Use Cases | Marketing, team leadership, customer service. | Risk communication, safety warnings, compliance. |
| Examples | "Achieve success by adopting this method." | "Avoid failure by not ignoring this method." |
| Psychological Effect | Enhances confidence and persistence. | Triggers anxiety and defensive thinking. |
Understanding Positive and Negative Framing
Positive framing emphasizes the potential benefits or gains of a decision, influencing individuals to perceive outcomes more favorably, while negative framing highlights potential losses or risks, often triggering cautious or risk-averse behavior. Understanding positive and negative framing is crucial in fields like marketing, psychology, and communication, as subtle shifts in message presentation can significantly impact decision-making processes. Research in cognitive psychology demonstrates how framing effects alter perception, guiding behavior through emotional and cognitive biases related to gain and loss evaluation.
The Psychology Behind Framing Effects
Framing effects in psychology reveal how the presentation of information influences decision-making and perception, with positive framing highlighting benefits and negative framing emphasizing potential losses or risks. Your choices and attitudes can shift significantly depending on whether information is framed in an optimistic or pessimistic manner, demonstrating the mind's sensitivity to context and subtle cues. Understanding the underlying cognitive biases and emotional reactions that drive framing effects helps explain why identical facts can lead to different conclusions based on their semantic framing.
How Positive Framing Influences Perception
Positive framing focuses on highlighting the benefits or favorable outcomes of a situation, significantly influencing perception by fostering optimism and acceptance. By emphasizing gains rather than losses, positive framing enhances motivation and encourages proactive decision-making, making messages more persuasive and memorable. Research in cognitive psychology confirms that individuals respond more favorably to positively framed information, which shapes attitudes and behaviors effectively.
Consequences of Negative Framing
Negative framing can lead your audience to focus on losses, risks, and potential failures, which often increases anxiety and reduces motivation to take action. This cognitive bias causes people to perceive situations as more threatening or discouraging, potentially hindering decision-making and problem-solving. Understanding the consequences of negative framing can help you reframe messages to promote confidence and positive outcomes.
Positive Framing in Marketing and Advertising
Positive framing in marketing emphasizes benefits, gains, and desirable outcomes to influence consumer behavior and decision-making, effectively increasing product appeal and brand loyalty. Unlike negative framing, which highlights losses or risks, positive framing leverages optimistic messaging and success stories to create emotional connections and enhance perceived value. Framing overall shapes consumer perceptions by presenting information in specific contexts, but positive framing specifically drives higher engagement and conversion rates through uplifting and motivating content.
Negative Framing in Media and Communication
Negative framing in media and communication emphasizes adverse aspects of a story, shaping audience perception by highlighting risks, losses, or threats. This approach often triggers stronger emotional reactions, such as fear or anxiety, which can influence public opinion and behavior more powerfully than positive framing. While framing overall refers to how information is presented to influence interpretation, negative framing specifically exploits human cognitive biases towards negative information for persuasive or manipulative purposes.
Comparing Outcomes: Positive vs Negative Framing
Positive framing emphasizes the benefits and favorable aspects of a message, leading to higher motivation and more optimistic decision-making outcomes. Negative framing highlights potential losses or adverse consequences, often increasing risk-averse or cautious behaviors in recipients. Comparing outcomes reveals that positive framing generally fosters engagement and confidence, while negative framing can enhance vigilance and risk mitigation depending on the context.
Strategies to Apply Positive Framing
Positive framing emphasizes presenting information with an optimistic perspective to enhance receptivity and motivation, such as highlighting benefits and opportunities in communication. Strategies to apply positive framing include focusing on solution-oriented language, using affirming statements, and framing challenges as manageable growth experiences. This approach contrasts with negative framing, which centers on potential losses or risks, affecting decision-making and emotional responses differently.
Common Pitfalls of Negative Framing
Negative framing often leads to cognitive biases such as loss aversion, where individuals disproportionately focus on potential losses rather than equivalent gains, impairing decision-making processes. Common pitfalls include heightened anxiety, reduced motivation, and increased resistance to change, which can undermine effective communication and behavior modification. Using balanced or positive framing enhances receptivity by emphasizing benefits and opportunities, thus fostering better engagement and constructive outcomes.
Choosing the Right Frame for Effective Communication
Choosing the right frame in communication significantly impacts how messages are perceived, with positive framing emphasizing benefits and motivation, while negative framing highlights risks and consequences. Positive framing tends to increase openness and cooperation, making it effective in encouraging behavior change and boosting morale, whereas negative framing can trigger caution and prompt immediate attention in high-stakes situations. Understanding the audience and context ensures the frame aligns with communication goals, optimizing message clarity and persuasive power.
Infographic: Positive Framing vs Negative Framing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com