Passive-aggressive behavior in relationships involves indirect resistance and hidden hostility, while submissive behavior is characterized by compliance and yielding to others' demands. Discover effective strategies to identify and address these contrasting dynamics in this article.
Table of Comparison
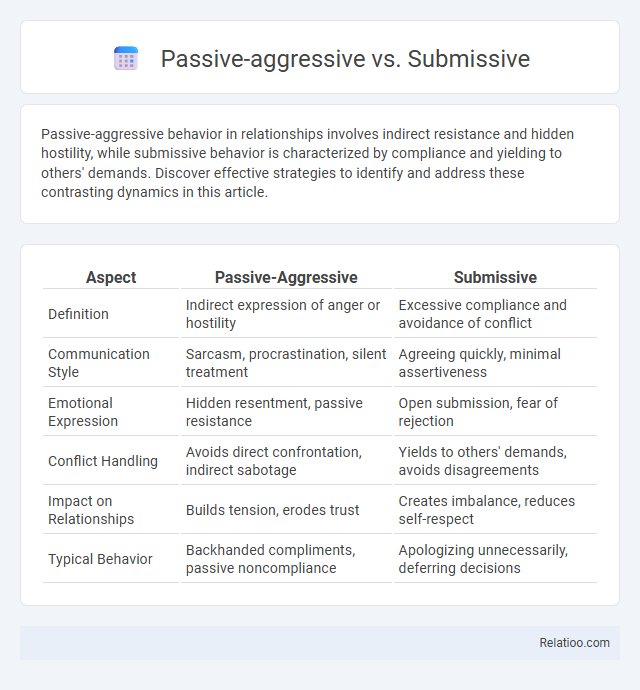
| Aspect | Passive-Aggressive | Submissive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Indirect expression of anger or hostility | Excessive compliance and avoidance of conflict |
| Communication Style | Sarcasm, procrastination, silent treatment | Agreeing quickly, minimal assertiveness |
| Emotional Expression | Hidden resentment, passive resistance | Open submission, fear of rejection |
| Conflict Handling | Avoids direct confrontation, indirect sabotage | Yields to others' demands, avoids disagreements |
| Impact on Relationships | Builds tension, erodes trust | Creates imbalance, reduces self-respect |
| Typical Behavior | Backhanded compliments, passive noncompliance | Apologizing unnecessarily, deferring decisions |
Understanding Passive-Aggressive Behavior
Passive-aggressive behavior manifests as indirect resistance, where individuals express negative feelings through procrastination, sarcasm, or stubbornness instead of openly addressing issues. Unlike submissive behavior, which involves yielding and avoiding conflict to please others, passive-aggression covertly undermines relationships while appearing compliant. Understanding passive-aggressive behavior requires recognizing these subtle expressions of anger that mask deeper frustrations and hinder effective communication.
Defining Submissive Personality Traits
Submissive personality traits include a tendency to prioritize others' needs over their own, often resulting in low assertiveness and avoidance of conflict. Individuals exhibiting submissiveness may display compliance, a desire to please, and difficulty expressing personal opinions. Understanding these attributes is crucial when distinguishing submissive behavior from passive-aggressive tendencies, which involve indirect resistance or covert hostility.
Key Differences Between Passive-Aggressive and Submissive Communication
Passive-aggressive communication involves indirect resistance and hidden hostility, characterized by subtle digs, sarcasm, or procrastination, while submissive communication reflects a tendency to avoid conflict by always agreeing or deferring to others' opinions. Key differences lie in the intent and expression: passive-aggressive individuals mask their anger through covert actions, whereas submissive communicators suppress their own needs to please others. Understanding these distinctions can help you navigate interpersonal dynamics more effectively by recognizing when aggression is concealed versus when compliance stems from self-effacement.
Psychological Roots of Passive-Aggressive Tendencies
Passive-aggressive behavior often stems from underlying feelings of powerlessness, unresolved anger, and difficulty expressing emotions directly, differentiating it from submissive or purely passive behaviors characterized by avoidance and compliance. Submissive individuals tend to surrender control due to fear of conflict or rejection, whereas passive-aggressive individuals covertly express hostility through indirect actions or procrastination. Psychological roots of passive-aggressiveness frequently include childhood experiences of neglect, inconsistent parenting, or environments where open communication was discouraged, leading to suppressed resentment and indirect defiance.
Causes and Triggers for Submissive Behavior
Submissive behavior often stems from deep-seated fears of conflict or rejection, frequently influenced by past experiences of trauma or an environment that discourages assertiveness. Triggers include high-stress situations, authoritative demands, or interpersonal dynamics where power imbalances are evident, prompting avoidance of confrontation to maintain peace. Understanding these causes is crucial for differentiating submissive behavior from passive-aggressive reactions, which are typically driven by hidden resentment and indirect resistance.
Common Signs of Passive-Aggressive Interactions
Passive-aggressive interactions often include indirect resistance, sarcasm, and subtle sabotage, which contrast with submissive behavior characterized by avoidance and compliance. Common signs of passive-aggressive behavior in your relationships may involve procrastination, silent treatment, and backhanded compliments. Recognizing these patterns helps you navigate and address conflicts more effectively.
Typical Behaviors of Submissive Individuals
Typical behaviors of submissive individuals include consistently deferring to others' opinions, avoiding conflict by acquiescing, and displaying low assertiveness in social or professional interactions. They often prioritize others' needs over their own, exhibit reluctance to express disagreement, and may experience anxiety when faced with decision-making or confrontations. This contrasts with passive-aggressive individuals who indirectly express hostility and resentment while appearing compliant.
Impacts on Relationships: Passive-Aggressive vs Submissive
Passive-aggressive behavior often leads to confusion and frustration in relationships due to hidden resentment and indirect communication, undermining trust and emotional intimacy. Submissive behavior, characterized by excessive compliance and avoidance of conflict, can result in unbalanced dynamics where Your needs are consistently neglected, fostering resentment and dissatisfaction over time. Understanding these impacts helps improve communication and create healthier, more respectful connections.
How to Respond to Passive-Aggressive People
When responding to passive-aggressive people, maintain clear and calm communication by addressing their behavior directly without confrontation. Use assertive language to set boundaries and encourage open dialogue, avoiding confusion caused by indirect or hostile expressions. Recognize the difference between passive-aggressive, submissive, and assertive behaviors to tailor your response effectively and prevent escalating tension.
Strategies for Empowering Submissive Individuals
Strategies for empowering submissive individuals focus on building assertiveness, enhancing self-confidence, and establishing clear personal boundaries to counterbalance passive-aggressive behaviors. You can encourage open communication and teach techniques to express needs and emotions directly, fostering healthier interactions. Developing a support system and engaging in assertiveness training programs also help transform submissive tendencies into proactive, empowered decision-making.
Infographic: Passive-aggressive vs Submissive
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com