Nonjudgmental attitudes in relationships foster safety by accepting partners without criticism, while empathetic approaches deeply understand and share their feelings, promoting emotional connection. Explore this article to learn how balancing nonjudgmental and empathetic behaviors strengthens relationship bonds.
Table of Comparison
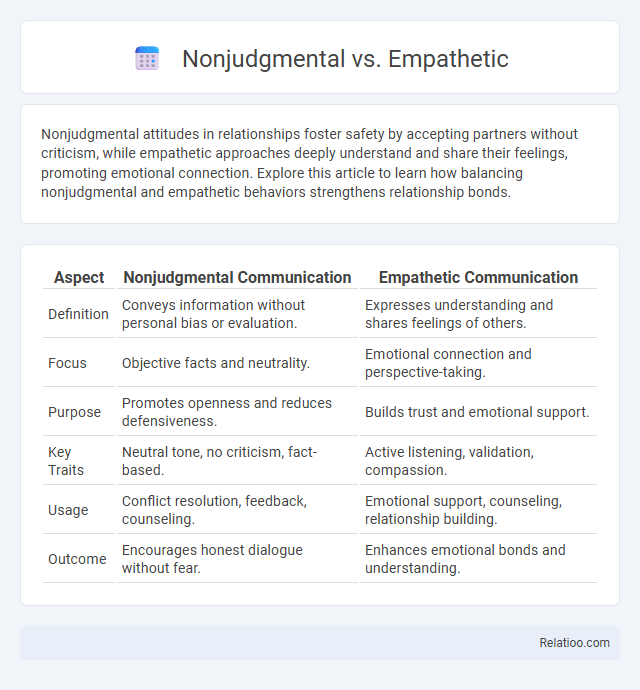
| Aspect | Nonjudgmental Communication | Empathetic Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conveys information without personal bias or evaluation. | Expresses understanding and shares feelings of others. |
| Focus | Objective facts and neutrality. | Emotional connection and perspective-taking. |
| Purpose | Promotes openness and reduces defensiveness. | Builds trust and emotional support. |
| Key Traits | Neutral tone, no criticism, fact-based. | Active listening, validation, compassion. |
| Usage | Conflict resolution, feedback, counseling. | Emotional support, counseling, relationship building. |
| Outcome | Encourages honest dialogue without fear. | Enhances emotional bonds and understanding. |
Introduction: Understanding Nonjudgmental vs. Empathetic Approaches
Understanding the differences between nonjudgmental and empathetic approaches is vital for effective communication and support. A nonjudgmental stance involves withholding criticism and acceptance of others' experiences without forming opinions, while empathy requires actively feeling and expressing understanding of another's emotions. Your ability to distinguish and apply these approaches enhances interpersonal connections and fosters trust in personal and professional relationships.
Defining Nonjudgmental Attitude
A nonjudgmental attitude involves accepting others without criticism or bias, fostering an environment of trust and openness. This approach emphasizes listening and understanding without forming negative opinions or making assumptions. By practicing nonjudgmental behavior, you create a safe space for honest communication and emotional support.
What Does It Mean to Be Empathetic?
Being empathetic means deeply understanding and sharing another person's feelings and experiences without imposing judgment. It requires active listening, emotional resonance, and recognizing emotions from the other person's perspective. Empathy fosters connection by validating emotions and offering support rather than criticism or unsolicited advice.
Key Differences Between Nonjudgmental and Empathetic Responses
Nonjudgmental responses focus on withholding personal opinions or criticisms, creating a safe space where your feelings and experiences are accepted without evaluation. Empathetic responses actively convey understanding and emotional resonance by acknowledging and reflecting your emotions, helping you feel heard and validated. The key difference lies in nonjudgmental communication prioritizing neutrality, while empathetic communication involves emotional connection and shared feelings.
Psychological Benefits of a Nonjudgmental Approach
A nonjudgmental approach fosters a safe space where your thoughts and feelings can be expressed without fear of criticism, promoting psychological well-being and reducing anxiety. Empathy allows for understanding and validation of emotions, but nonjudgmental attitudes specifically encourage acceptance that leads to emotional resilience and improved self-esteem. Embracing nonjudgmental interactions supports mental clarity and facilitates personal growth by preventing negative self-assessment.
The Role of Empathy in Emotional Intelligence
Empathy plays a crucial role in emotional intelligence by enabling individuals to accurately perceive and understand others' emotions, fostering deeper interpersonal connections. Unlike a nonjudgmental approach that emphasizes withholding judgment, empathy involves actively engaging with and feeling another person's emotional experience. This capacity enhances social awareness and emotional regulation, key components of emotional intelligence that contribute to effective communication and relationship management.
Practical Examples: Nonjudgmental vs. Empathetic Communication
Nonjudgmental communication involves listening and responding without assigning blame or making moral evaluations, such as calmly hearing a friend's mistake without criticism. Empathetic communication goes further by actively trying to understand and share the speaker's feelings, for example, expressing sorrow for a colleague facing a personal loss. While both approaches foster trust, nonjudgmental acts as a neutral space, and empathy builds emotional connection through shared understanding.
When to Use Nonjudgmental vs. Empathetic Listening
Nonjudgmental listening is essential when creating a safe space for individuals to share thoughts without fear of criticism, fostering openness and trust. Empathetic listening becomes crucial when responding to emotional experiences, as it involves understanding and validating feelings to support emotional healing. Choosing nonjudgmental listening emphasizes impartiality during sensitive disclosures, while empathetic listening deepens connection through emotional resonance.
Common Misconceptions About Nonjudgmental and Empathetic Behaviors
Nonjudgmental behavior is often misconstrued as passivity or acceptance of harmful actions, while empathetic behavior is sometimes mistaken for agreement with others' feelings. Both approaches require clear boundaries but differ fundamentally; nonjudgmental involves withholding personal bias, whereas empathy involves deeply understanding another's emotional state. Misunderstanding these nuances can hinder effective communication and emotional support in interpersonal relationships.
Developing Both Skills for Healthier Relationships
Developing both nonjudgmental and empathetic skills cultivates healthier relationships by fostering open communication and emotional safety. Nonjudgmental attitudes involve consciously withholding criticism or bias, creating a supportive environment where individuals feel accepted regardless of their actions or feelings. Empathy enhances this dynamic by allowing a deeper understanding of others' emotions and perspectives, which strengthens trust and connection.
Infographic: Nonjudgmental vs Empathetic
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com