Formal relationships often involve structured communication and clear boundaries, typical in professional or official settings. Informal relationships prioritize casual interactions and emotional connections found among friends and family; explore more distinctions between these relationship types in this article.
Table of Comparison
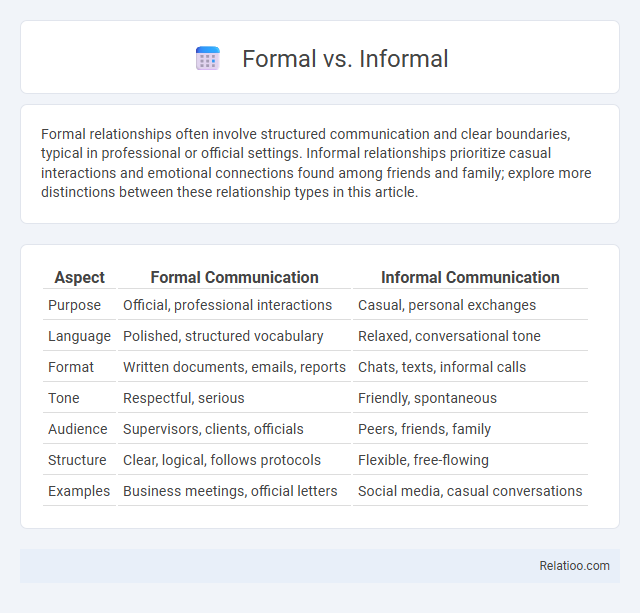
| Aspect | Formal Communication | Informal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Official, professional interactions | Casual, personal exchanges |
| Language | Polished, structured vocabulary | Relaxed, conversational tone |
| Format | Written documents, emails, reports | Chats, texts, informal calls |
| Tone | Respectful, serious | Friendly, spontaneous |
| Audience | Supervisors, clients, officials | Peers, friends, family |
| Structure | Clear, logical, follows protocols | Flexible, free-flowing |
| Examples | Business meetings, official letters | Social media, casual conversations |
Understanding Formal and Informal Communication
Formal communication follows structured protocols and official language, typically used in professional or organizational contexts to ensure clarity and respect. Informal communication utilizes casual language and spontaneous interactions, fostering personal connections and quick information exchange among peers or friends. Understanding the distinctions assists in selecting the appropriate tone, format, and channel to enhance message effectiveness and maintain relationship dynamics.
Key Differences Between Formal and Informal Language
Formal language uses precise vocabulary, full sentences, and structured grammar, suitable for academic, professional, or official communication, while informal language features colloquial expressions, contractions, and relaxed grammar, common in casual conversations or personal writing. Formal language maintains a respectful tone and avoids slang, whereas informal language embraces a friendly, approachable style with idiomatic phrases. Summoning is unrelated to language style, referring to the act of calling or requesting presence, typically in legal or mystical contexts.
When to Use Formal Communication
Formal communication is essential for professional settings, official documents, and situations requiring clarity and respect, such as business meetings, academic presentations, and legal correspondence. You should use formal language when addressing superiors, clients, or unfamiliar audiences to ensure professionalism and avoid misunderstandings. This style emphasizes structured sentences, precise vocabulary, and polite tone, distinguishing it from informal or casual communication.
Appropriate Contexts for Informal Language
Informal language is most appropriate in casual conversations, personal emails, and social media interactions where a relaxed tone fosters connection and relatability. It suits settings involving friends, family, or colleagues in a non-professional environment, allowing for expressions with slang, contractions, and colloquialisms. Using informal language in professional or official contexts, such as business meetings or legal documents, may undermine credibility and clarity, emphasizing the importance of selecting the communication style based on the audience and purpose.
Structure and Tone: Formal vs Informal
Formal communication utilizes structured sentences, professional vocabulary, and a respectful tone to convey clarity and seriousness. Informal communication adopts a relaxed sentence structure, colloquial language, and a friendly or casual tone to foster approachability and ease. Summoning varies in structure and tone depending on context but generally demands urgency and directness, often reflecting authority.
Common Examples of Formal and Informal Writing
Formal writing commonly appears in academic papers, business reports, and official documents, characterized by complex sentence structures and precise vocabulary. Informal writing is often used in personal emails, text messages, and social media posts, featuring colloquial language and contractions. Summoning, in a different context, refers to calling forth or requesting the presence of a person or entity, such as in legal summons or fictional narratives.
Advantages of Formal Communication
Formal communication ensures clarity and professionalism, reducing misunderstandings in corporate environments. It establishes a documented trail, facilitating accountability and future reference. This structured approach enhances credibility and strengthens organizational hierarchy.
Benefits of Informal Interaction
Informal interaction fosters a relaxed environment that encourages open communication and creativity, enhancing collaboration and problem-solving within teams. It reduces social barriers, enabling quicker trust-building and stronger relationships among colleagues. These benefits contribute to increased productivity and a more cohesive workplace culture compared to formal or summoning interactions.
Pitfalls to Avoid in Formal and Informal Communication
Formal communication requires careful attention to clarity and professionalism, avoiding slang, ambiguous phrases, and overly complex jargon that can confuse the audience. Informal communication risks misunderstandings by relying too heavily on colloquialisms, incomplete sentences, or inappropriate tone for the context, which may undermine credibility. Both styles should steer clear of assumptions about shared knowledge and cultural differences that can lead to misinterpretation or offense.
Tips for Switching Between Formal and Informal Styles
Mastering the art of switching between formal and informal writing styles requires awareness of context, audience, and purpose, ensuring appropriate tone and vocabulary choices. Use formal language, complex sentence structures, and professional vocabulary when addressing official communications or academic topics, while adopting colloquial expressions, contractions, and simpler sentences for casual conversations or personal messages. Practice code-switching by reading diverse materials, engaging in varied social scenarios, and revising drafts to balance clarity and tone effectively.
Infographic: Formal vs Informal
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com